Summary
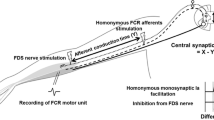
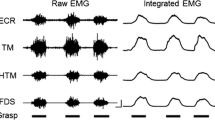
The pattern of projections of low threshold afferents from triceps and biceps brachii muscles onto motoneurones innervating muscles acting at the wrist was assessed by a reflex and a poststimulus time histogram (psth) technique. Activation of low-threshold afferents originating from elbow flexors or extensors resulted in an early, short-lasting inhibition of wrist flexor motoneurones (flexor carpi radialis, flexor carpi ulnaris). An inhibition was also found in the extensor carpi radialis (ECR) motoneurones after stimulation of low-threshold afferents from triceps. Evidence is presented that Ia fibres contribute to these effects. The inhibitory effects were found in all subjects, but they were constant in only 57% of the reflex experimental sessions and in 25% of the explored motor units. Stimulation of biceps low-threshold afferents was always ineffective on ECR motoneurones. No early facilitation was ever seen in motor nuclei innervating wrist muscles following stimulation of low threshold afferents from biceps and triceps. The pattern of transjoint projections of group I afferents from proximal to distal muscles and from distal to proximal ones (Cavallari and Katz 1989) is discussed in relation to that described in the cat forelimb.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baldissera F, Campadelli P, Cavallari P (1983) Inhibition from radial group I afferent of H reflex in wrist flexors. Electromyogr Clin Neurophysiol 23: 187–193
Cavallari P, Katz R (1989) Pattern of projections of group I afferents from forearm muscles to motoneurones supplying biceps and triceps muscles in man. Exp Brain Res 78: 465–478
Clamann HP, Gillies JD, Henneman R (1974) Effects of inhibitory inputs on critical firing level and rank order of motoneurones. J Neurophysiol 37: 1350–1360
Coppin CMC, Jack JJB, MacLennan CR (1970) A method for the selective electrical stimulation of tendon organ afferent fibres from the cat soleus muscle. J Physiol (Lond) 210: 18–20
Crone C, Hultborn H, Jespersen B, Nielsen J (1987) Reciprocal Ia inhibition between ankle flexors and extensors in man. J Physiol (Lond) 389: 163–185
Day BL, Marsden CD, Obeso JA, Rothwell JC (1984) Reciprocal inhibition between the muscles of the human forearm. J Physiol (Lond) 349: 519–534
Fetz E, Gustafsson B (1983) Relation between shapes of post-synaptic potentials and changes in firing probability of cat motoneurones. J Physiol (Lond) 341: 387–410
Fetz E, Jankowska E, Johanisson T, Lipski J (1979) Autogenic inhibition of motoneurones by impulses in group Ia muscle spindle afferents. J Physiol (Lond) 293: 173–195
Fournier E, Meunier S, Pierrot-Deseilligny E, Shindo M (1986) Evidence for interneuronally mediated Ia excitatory effects to human quadriceps motoneurones. J Physiol (Lond) 377: 143–169
Fritz N, Illert M, de la Motte S, Reeh P, Saggau P (1989) Pattern of monosynaptic Ia connections in the cat forelimb. J Physiol (Lond) 419: 321–351
Gustafsson B, McCrea D (1984) Influence of stretch-evoked synaptic potentials on firing probability of cat spinal motoneurones. J Physiol (Lond) 347: 431–451
Heckman CJ, Condon MS, Hutton RS, Enoka RM (1984) Can Ib axons be selectively activated by electrical stimuli in human subjects? Exp Neurol 86: 576–582
Hultborn H, Meunier S, Morin C, Pierrot-Deseilligny E (1987) Assessing changes in presynaptic inhibition of Ia fibres: a study in man and the cat. J Physiol (Lond) 389: 729–756
Katz R, Pénicaud A, Rossi A (1991) Reciprocal Ia inhibition between elbow flexors and extensors in the human. J Physiol (Lond) 437: 269–286
Lundberg A, Winsbury G (1960) Selective adequate activation of large afferents from muscle spindles and Golgi tendon organs. Acta Physiol Scand 49: 155–164
Roll JP, Vedel JP (1982) Kinaesthetic role of muscle afferents in man, studied by tendon vibration and microneuronography. Exp Brain Res 47: 177–190
Stephens JA, Usherwood TP, Garnett R (1976) Technique for studying synaptic connections of single motoneurones in man. Nature 263: 343–344
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cavallari, P., Katz, R. & Penicaud, A. Pattern of projections of group I afferents from elbow muscles to motoneurones supplying wrist muscles in man. Exp Brain Res 91, 311–319 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00231664
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00231664