Summary
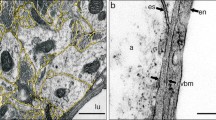
Blood vessels surrounded by unusually wide perivascular spaces rich in connective tissue were observed in the brain of Lepidosteus (Ganoidei). Connective-tissue sheaths measuring up to 13 μm in width enclose arterioles and venules (40–70 μm in diameter), and even capillaries may be encompassed by a cuff formed by collagen fibers. Blood vessels with wide perivascular spaces are mainly located in the subependymal layer of the lateral ventricles, near the mesencephalic aqueduct and in the folded basal lining of the fourth ventricle. At the light-microscopic level these vessels do not show any distinct contact with nervous elements (axons). Some other brain regions of Lepidosteus, e.g. mesencephalic tectum, are supplied by a conventional type of capillaries, free of connective-tissue linings. For comparative reasons, brains of several selachian and teleostean species were examined with comparable histological methods. Distinct perivascular spaces were found in the pike, in the trout and in the eel. They are considerably richer in connective tissue than the occasionally observed narrow perivascular spaces in the shark. The significance of the abundant perivascular connective tissue in the brain of Lepidosteus is open to discussion; structural and functional problems of the brain-blood-barrier have been reviewed in this context. The brain of Lepidosteus appears to be a very suitable model for studies of blood supply, vascular ultrastructure and blood-brain-barrier functions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahlborn, F.: Untersuchungen über das Gehirn der Petromyzonten. Z. wiss. Zool. 39, 191–294 (1883)
Bodenheimer, T. S., Brightman, M. W.: A blood-brain barrier to peroxidase in capillaries surrounded by perivascular spaces. Amer. J. Anat. 122, 249–267 (1968)
Brightman, M. W., Klatzo, L., Olsson, Y., Reese, T. S.: The blood-brain-barrier to proteins under normal and pathological conditions. J. neurol. Sci. 10, 215–239 (1970)
Brizzee, K. R.: A comparison of cell structure in the area postrema, supraoptic crest and intercolumnar tubercle with notes on the neurohypophysis and pineal body in the cat. J. comp. Neurol. 100, 699–716 (1954)
Craigie, E. H.: The architecture of the cerebral capillary bed. Biol. Rev. 20, 133–146 (1945)
Dempsey, E. W.: Neural and vascular ultrastructure of the area postrema in the rat. J. comp. Neurol. 150, 177–200 (1973)
Desaga, U.: Form und Verteilung subependymaler Basalmembranlabyrinthe am Ventrikel-system der Ratte. Z. Zellforsch. 132, 553–562 (1972)
Friede, R. L.: Die Bedeutung der Glia-Saugfüßchen für das Elektrolytgleichgewicht im Gehirn. Triangel 9, 165–173 (1971)
Friede, R. L., Hu, K. H., Cechner, R.: Glial footplates in the bowfin. II. Effects of ouabain and selective damage to footplates on electrolyte composition, glycogen content, fine structure and electrophysiology of bowfin brain incubated in vitro. J. Neuropath, exp. Neurol. 28, 540–570 (1969)
Friede, R. L., Hu, K. H., Johnstone, M.: Glial footplates in the bowfin. I. Fine structure and chemistry. J. Neuropath, exp., Neurol. 28, 513–539 (1969)
Gillian, L. A.: Blood supply to primitive mammalian brains. J. comp. Neurol. 145, 209–222 (1972)
Kappers, C. U., Ariëns, Huber, G. C., Crosby, E. C.: The comparative anatomy of the nervous system of vertebrates including man. Vol. I–III. New York: Hafner Publ. Comp. 1960
Kimble, J. E., Sørensen, S. C., Møllgaard, K.: Cell junctions in the subcommissural organ of the rabbit as revealed by use of ruthenium red. Z. Zellforsch. 138, 375–386 (1973)
Kingsbury, B. F.: The encephalic evaginations in ganoids. J. comp. Neurol. 7, 37 (1897)
Leonhardt, H.: Über die topographische Verteilung der subependymalen Basalmembran-labyrinthe im Ventrikelsystem des Kaninchengehirns. Z. Zellforsch. 127, 392–406 (1972)
Long, D. M., Bodenheimer, T. S., Hartmann, J. F., Klatzo, J.: Ultrastructural features of the shark brain. Am. J. Anat. 122, 209–236 (1968)
Pappas, G. D.: Some morphological considerations of the blood-brain-barrier. J. neurol. Sci. 10, 241–246 (1970)
Rossbach, R.: Das neurosekretorische System der Amsel, Turdus merula L. im Jahresablauf und nach Wasserentzug. Z. Zellforsch. 71, 118–145 (1966).
Scharrer, E.: The histology of the meningeal myeloid tissue in the ganoids Amia and Lepisosteus. Z. Zellforsch. 88, 291–310 (1944)
Schöbl, J.: Über eine eigentümliche Schleifenbildung der Blutgefäße im Gehirn und Rückenmark der Saurier. Arch. mikr. Anat. 15, 60–64 (1878)
Schöbl, J.: Über die Blutgefäße des cerebrospinalen Nervensystems der Urodelen. Arch. mikr. Anat. 20, 87–92 (1882)
Simonescu, N., Simonescu, M., Palade, G. E.: Permeability of intestinal capillaries. J. Cell Biol. 53, 365–392 (1972)
Wartenberg, H., Hadziselimović, F., Seguchi, H.: Experimentelle Untersuchungen über die Passage der Blut-Gewebs-Schranke in den zirkumventrikulären Organen des Meerschweinchengehirns. Anat. Anz. (Erg. Bd.) 130, 345–355 (1973)
Weindl, A., Joint, R. J.: The median eminence as a circumventricular organ. In: Median eminence: Structure and function (K. M. Knigge, D. E. Scott and A. Weindl, Eds.). Int. Symp. Munich 1971, p. 280–297. Basel: Karger 1972
Westergaard, E., Brightman, M. W.: Transport of proteins across normal cerebral arterioles. J. comp. Neurol. 152, 17–44 (1973)
Ziesmer, C.: Eine Verbesserung der Silber-Imprägnierung nach Bodian. Z. wiss. Mikr. 60, 57–59 (1951/52).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
The investigations reported herein were supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft. The authors are greatly indebted to Dr. K. R. Brizzee, Delta Regional Primate Research Center of the Tulane University, for his generous help in obtaining the animal material and for his critical reading of the manuscript. The valuable technical assistance of Miss Margarete Langbein and Mrs. Gertrud Möller, Giessen, is most gratefully acknowledged.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Merker, G., Oksche, A. & Hofer, H.O. Blood vessels surrounded by connective tissue (perivascular space) in the brain of Lepidosteus (Ganoidei) and some teleost fishes. Cell Tissue Res. 153, 435–448 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00231539
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00231539