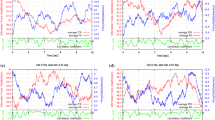
Summary
Length tuning was first described for the “hypercomplex cell category” in the visual cortex. However it has subsequently become apparent that cells in the dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus (dLGN) also exhibit a high degree of length tuning and that for the majority of the population this matches or exceeds that associated with cortical hypercomplex cells (Cleland et al. 1983; Jones and Sillito 1987). In this paper we describe a distinct subpopulation of dLGN Y cells that lack length tuning. These cells were also characterised by poor centre-surround antagonism, and tended to be located close to laminar borders. They appeared to constitute 25% of the Y cell population. Following recent evidence showing relay cells to be powerfully excited by acetylcholine, and inhibitory interneurones to be inhibited, we have examined the responses of these non-length tuned cells to iontophoretic application of acetylcholine. Their brisk excitatory responses suggest that these cells are in fact relay cells. Their presence raises the possibility of a discrete non-length tuned component to the geniculate input to the cortex, and has potentially important implications for the way in which synaptic processes contributing to the length tuning profiles of visual cortical cells are modelled.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahlsen G, Lindstrom S, Lo F-S (1984) Inhibition from the brainstem of inhibitory interneurons of the cat's dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus. J Physiol (Lond) 347:593–609
Bolz J, Gilbert CD (1986) Generation of end-inhibition in the visual cortex via interlaminar connections. Nature 320:362–365
Cleland BG, Dubin MW, Levick WR (1971) Sustained and transient neurones in the cat's retina and lateral geniculate nucleus. J Physiol (Lond) 217:473–496
Cleland BG, Lee BB, Vidyasagar TR (1983) Response of neurons in the cat's lateral geniculate nucleus to moving bars of different length. J Neurosci 3:108–116
De Lima AD, Montero VM, Singer W (1985) The cholinergic innervation of the visual thalamus: an EM immunocytochemical study. Exp Brain Res 59:206–212
Derrington AM, Fuchs AE (1979) Spatial and temporal properties of X and Y cells in the cat lateral geniculate nucleus. J Physiol (Lond) 293:347–364
Dubin MW, Cleland BG (1977) Organization of visual inputs to interneurons of lateral geniculate nucleus of the cat. J Neurophysiol 40:410–427
Enroth-Cugell C, Robson JG (1966) The contrast sensitivity of retinal ganglion cells of the cat. J Physiol (Lond) 187:517–552
Ferster D, Lindstrom S (1985) Synaptic excitation of neurones in area 17 of the cat by intracortical axon collaterals of corticogeniculate cells. J Physiol (Lond) 367:233–252
Fitzpatrick D, Penny GR, Schmechel DE (1984) Glutamic acid decarboxylase-immunocytoreactive neurons and terminals in the lateral geniculate nucleus of the cat. J. Neurosci 4:1809–1829
Francesconi W, Muller CM, Singer W (1988) Cholinergic mechanisms in the reticular control of transmission in the cat lateral geniculate nucleus. J Neurophysiol 59:1690–1718
Friedlander MJ, Lin C-S, Stanford LR, Sherman SM (1981) Morphology of functionally identified neurons in lateral geniculate nucleus of the cat. J Neurophysiol 46:80–129
Hamos JE, Van Horn SC, Raczkowski D, Sherman SM (1987) Synaptic circuits involving an individual retinogeniculate axon in the cat. J Comp Neurol 259:165–192
Hubel DH, Wiesel TN (1965) Receptive fields and functional architecture in two non-striate visual areas (18 and 19) of the cat. J Neurophysiol 28:229–287
Humphrey AL, Weller RE (1988) Functionally distinct groups of X-cells in the lateral geniculate nucleus of the cat. J Comp Neurol 268:429–447
Jones HE, Sillito AM (1987) The length tuning of cells in the feline dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus (dLGN). J Physiol (Lond) 390:32P
Jones HE, Sillito AM (1989a) A distinct subpopulation of non-length tuned cells in the dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus (dLGN) of the anaesthetized cat. J Physiol (Lond) 410:60P
Jones HE, Sillito AM (1989b) The discrete group of non-length tuned cells in the dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus (dLGN) of the anaesthetized cat may be relay cells. J Physiol (Lond) 415:67P
Kemp JA, Sillito AM (1982) The nature of the excitatory transmitter mediating X and Y cell inputs to the cat dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus. J Physiol (Lond) 323:377–391
McCormick DA, Pape H-C (1988) Acetylcholine inhibits identified interneurons in the cat lateral geniculate nucleus. Nature 334:246–248
McGuire BA, Hornung J-P, Gilbert CD, Wiesel TN (1984) Patterns of synaptic input to layer 4 of cat striate cortex. J Neurosci 4:3021–3033
Martin KAC (1988) The lateral geniculate nucleus strikes back. TINS 11:192–193
Mastronarde DN (1987) Two classes of single-input X-cells in cat lateral geniculate nucleus. I. Receptive field properties and classification of cells. J Neurophysiol 57:357–380
Montero VM (1989) The GABA-immunoreactive neurons in the interlaminar regions of the cat lateral geniculate nucleus: light and electron microscopic observations. Exp Brain Res. 75:497–512
Murphy PC, Sillito AM (1987) Corticofugal feedback influences the generation of length tuning in the visual pathway. Nature 329:727–729
Orban GA, Kato H, Bishop PO (1979) Dimensions and properties of end-zone inhibitory areas in receptive fields of hypercomplex cells in cat striate cortex. J Neurophysiol 42:833–849
Rinvik E, Ottersen OP, Storm-Mathisen J (1987) Gamma aminobutyrate-like immunoreactivity in the thalamus of the cat. Neuroscience 21:781–805
Robson JA, Martin-Elkins CL (1985) The effects of monocular deprivation on the size of GAD + neurons in the cat's dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus. J Comp Neurol 239:62–74
Rose D (1977) Responses of single units in cat visual cortex to moving bars of light as a function of bar length. J Physiol (Lond) 271:1–23
Sanderson KJ (1971) The projection of the visual field to the lateral geniculate and medial interlaminar nucleus in the cat. J Comp Neurol 143:101–118
Sherman SM, Friedlander MJ (1988) Identification of X versus Y properties for interneurons in the A-laminae of the cat's lateral geniculate nucleus. Exp Brain Res 73:384–392
Sillito AM, Kemp JA (1983) The influence of GABAergic inhibitory processes on the receptive field structure of X and Y cells in cat dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus (dLGN). Brain Res 277:63–77
Singer W (1973) The effect of mesencephalic reticular stimulation on intracellular potentials of cat lateral geniculate neurons. Brain Res 61:35–54
Wilson JR, Friedlander MJ, Sherman SM (1984) Fine structural morphology of identified X- and Y-cells in the cat's lateral geniculate nucleus. Proc R Soc Lond B 221:411–436
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jones, H.E., Sillito, A.M. A specific subgroup of non-length tuned relay cells in the feline dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus. Exp Brain Res 82, 33–39 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00230835
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00230835