Summary
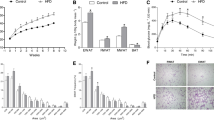
Previous studies examining the regulation of the synthesis of G6PDH and 6PGDH in rat liver and adipose tissue have focused on the induction of these enzymes by different diets and some hormones. In rat liver these enzymatic activities seem to be regulated by a mechanism involving changes in the NADPH requirements. In this paper we have studied the effect of changes in the flux through different NADPH-consuming pathways on G6PDH and 6PGDH levels in adipose tissue and on the NADPH/NADP ratio. The results show that: I) an increase in the consumption of NADPH, caused by the activation of either fatty acid synthesis or detoxification systems which consume NADPH, is paralleled by an increase in the levels of these enzymes; II) when the increase in consumption of NADPH is prevented, the G6PDH and 6PGDH levels do not change.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- G6PDH:
-
Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase
- 6PGDH:
-
6-Phosphogluconate Dehydrogenase
- GR:
-
Glutathione Reductase
- ME:
-
Malic Enzyme
- tBHP:
-
t-Butyl Hydroperoxide
- NF:
-
Nitrofurantoin
- CumOOH:
-
Cumene Hydroperoxide
References
Tepperman HM, Tepperman J: Pattern of dietary and hormonal induction of certain NADP-linked liver enzymes. Am J Physiol 206: 357–361, 1964
Garcia DR, Holten D: Inhibition of rat liver glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase synthesis by glucagon. J Biol Chem 250: 3960–3965, 1957
Tepperman HM, Tepperman J: On the response of hepatic glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase activity to changes in diet composition and food intake pattern. Adv Enzyme Regal 1: 121–136, 1963
Winberry L, Holten D: Rat liver glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase. Dietary regulation of the rate of synthesis. J Biol Chem 252: 779–781, 1977
Ayala A, Fabregat I, Machado A: Possible involvement of NADPH requirement in regulation of glucose-6-phosphate and 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase levels in rat liver. Mol Cell Biochem 95: 107–115, 1990
Sapag-Hagar M, Lagunas R, Sols A: Apparent unbalance between the activities of 6-phosphogluconate and glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase in rat liver. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 50: 179–185, 1972
Worthington DJ, Rosemeyer MH: Human glutathione reductase: purification of the crystalline enzyme from erythrocytes. Eur J Biochem 48: 167–177, 1974
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RI: Protein measurement with Folin Phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193: 265–275, 1951
Stansbie D, Brownsey RW, Crettaz M, Denton RM: Acute effects in vivo of anti-insulin serum on rates of fatty acid synthesis and activities of acetyl-coenzyme A carboxylase and pyruvate dehydrogenase in liver and epididymal adipose tissue of fed rats. Biochem J 160: 413–416, 1976
Fabregat I, Vitórica J, Satrustegui J, Machado A: The pentose phosphate cycle is regulated by NADPH/NADP ratio in rat liver. Arch Biochem Biophys 236: 110–118, 1985
Clauser J: In: T Work, E Work (eds.) Laboratory Techniques in Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. Elsevier, Amsterdam, 1972, pp 423–465
Young JW, Shrago E, Lardy HA: Metabolic control of enzymes involved in lipogenesis and gluconeogenesis. Biochemistry 3: 1687–1692, 1964
Timmers KI, Knittle JL: Regulation of glucose-6-dehydrogenase activity during caloric restriction in human adipose tissue. Enzyme 28: 66–70, 1982
Alexander MC, Palmer JL, Pointer RH, Howaloff EM, Koumjiam LL, Auruch J: Insulin-stimulated phosphorilation of ATP-citrate lyase in isolated hepatocytes. Stoichiometry and relation to the phosphoenzyme intermediate. J Biol Chem 257: 2049–2055, 1982
Ayala A, Machado A: Measurement ex-vivo of the inhibition of fatty acid biosynthesis by bezafibrate administration in different rat tissues. J Pharm Pharmacol 39: 551–552, 1987
Lotscher HR, Winterhalter KH, Carafoli E, Ritcher C: Hydroperoxides can modulate the redox state of pyridine nucleotides and calcium balance in rat liver mitochondria. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 76: 4340–4344, 1979
Kappus H, Sies H: Toxic drug effects associated with oxygen metabolism: redox cycling and lipid peroxidation. Experientia 37: 1233–1241, 1981
Griffin BW, Marth C, Yasukochi Y, Masters BSS: Radical mechanism of aminopyrine oxidation by cumene hydroperoxide catalyzed by purified liver microsomal cytochrome P-450. Arch Biochem Biophys 205: 543–553, 1980
Capdevila J, Estabrook RW, Pronyh RA: Differences in the mechanism of NADPH- and cumene hydroperoxidesupported reactions of cytochrome P-450. Arch Biochem Biophys 200: 186–195, 1980
Sies H, Brigelius R, Akerboom PM: Intrahepatic glutathione status. In: A Larson, S Orrenius, A Holmgrem, B Manner (eds.) Functions of Glutathione: Biochemical, Physiological, Toxicological and Clinical Aspects. B. Raven Press, New York, 1983, p. 51–64
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ayala, A., Fabregat, I. & Machado, A. The role of NADPH in the regulation of glucose-6-phosphate and 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenases in rat adipose tissue. Mol Cell Biochem 105, 1–5 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00230368
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00230368