Summary
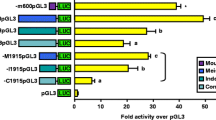
Placental chorionic somatomammotropin (hCS-A or B) and growth hormone variant (hGH-V) are members of the human growth hormone family, and are related by structure and function to pituitary growth hormone (hGH-N). However, while the hGH-N gene is expressed specifically in the anterior pituitary, hGH-V and hCS are produced in the placenta. Hybrid hGH-N, hGH-V and hCS-A genes containing 5′-flanking sequences, including the endogenous promoter, are preferentially expressed in rat pituitary tumor (GC) cells, after gene transfer. Since interaction with a pituitary-specific protein (Pit 1) is required for efficient hGH-N as well as rat growth hormone (rGH) gene expression in GC cells, binding of pituitary proteins to the hGH-V and hCS-A promoter sequences was investigated. Rat Pit 1 binds at two locations on the hGH-N gene, a distal (−140/−107) and proximal site (−97/−66), in a similar manner to that observed with the rGH gene. By contrast, efficient Pit 1 binding was seen only to the distal site of the hGH-V gene and the proximal site of the hCS-A gene. Although binding of a protein to the distal hCS-A sequences was observed, the site of interaction was truncated (−140/−116), not pituitary-specific, and was more consistent with the binding of Sp1. These data indicate that rat Pit 1 binds to the placental hGH-V and hCS-A genes and correlates with their promoter activity in GC cells after gene transfer. However, the data also indicate that rat Pit 1 binds to human and rat pituitary growth hormone in a similar manner (two sites of interaction) and that the pattern of binding is distinct from the placental members of the hGH gene family. These data indicate that human Pit 1, unlike the rat equivalent, might distinguish these genes functionally (tissue-specifically) as well as structurally.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen EY, Liao Y-C, Smith DH, Barrera-Saldana HA, Gelinas RE, Seeburg PH: The growth hormone locus: nucleotide sequence, biology and evolution. GENOMICS 4: 479–497,1989
Cooke NE, Ray J, Emery JG, Liebhaber SA: Two distinct species of human growth hormone variant mRNA in the human placenta predict the expression of novel growth hormone proteins. J Biol Chem 263: 9001–9006, 1988
Frankenne F, Closset J, Scippo ML, Smal J, Hennen G: The physiology of growth hormones (GHs) in pregnant women and partial characterization of the placental GH variant. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 66: 1171–1180, 1988
Liebhaber SA, Urbanek M, Ray J, Tuan RS, Cooke NE:Characterization and histologic localization of human growth hormone-variant gene expression in the placenta. J Clin Invest 83: 1985–1991, 1989
Miller WL, Eberhardt NL: Structure and evolution of the growth hormone gene family. Endocrine Rev 4: 97–130, 1983
Phillips III JA, Vnencak-Jones CL: Genetics of growth hormone and its disorders, in Harris H, Hirschhorn K (eds.) Advances in Human Genetics Vol 18. Plenum Press, New York, London, 1989
Eberhardt NL, Hirt H, Cattini PA, Anderson TR, Peritz L, Baxter JD, Mellon P, Isaacs R, Slater EP, Barta A: Human growth hormone genes: structure, evolution, expression and hormonal regulation, in Lau Y-F (ed.) Endocrine Genes. Oxford University Press, New York, 1988
Cattini PA, Peritz LN, Anderson TR, Baxter JD, Eberhardt NL: The 5′-flanking sequences of the human growth hormone gene contain a cell-specific control element. DNA 5:503–509,1986
Lefevre C, Imagawa M, Dana S, Grindlay J, Bodner M, Karin M: Tissue-specific expression of the human growth hormone gene is conferred in part by the binding of a specific trans-acting factor. EMBO J 6: 971–981, 1987
Ingraham HA, Chen R, Mangalam HJ, Elsholtz HP, Flynn SE, Lin CR, Simmons DM, Swanson L, Rosenfeld MG: A tissue-specific transcription factor containing a homeodomain specifies a pituitary phenotype. Cell 55: 519–529,1988
Catanzaro DF, West BL, Baxter JD, Reudelhuber TL: A pituitary-specific factor interacts with an upstream promoter element in the rat growth hormone gene. Mol Endocrinol 1: 90–96, 1987
West BL, Catanzaro DF, Mellon SH, Cattini PA, Baxter JD, Reudelhuber TL: Interaction of a tissue-specific factor with an essential rat growth hormone gene promoter element. Mol Cell Biol 7: 1193–1197, 1987
Ye Z-S, Forman BM, Aranda A, Pascual A, Park H-Y, Casanova J, Samuels HH: Rat growth hormone gene expression: Both cell-specific and thyroid hormone response elements are required for thyroid hormone regulation. J Biol Chem 263: 7821–7829, 1988
Nachtigal MW, Nickel BE, Klassen ME, Zhang W, Eberhardt NL, Cattini PA: Human chorionic somatomammotropin and growth hormone gene expression in rat pituitary tumour cells is dependent on proximal promoter sequences. Nucl Acids Res 17: 4327–4337, 1989
Nickel BE, Kardami E, Cattini PA: Differential expression of human placental growth hormone variant and chorionic somatomammotropin in culture. Biochem J 267: 653–658, 1990
Nickel BE, Nachtigal MW, Klassen ME, Cattini PA: Human growth hormone gene expression in human but not rat non-pituitary cells after stable gene transfer. Mol Cell Endocrinol 69: 93–99, 1990
Cattini PA, Eberhardt NL: Regulated expression of chimaeric genes containing the 5′-flanking regions of human growth hormone related genes in transiently transfected rat pituitary tumor cells. Nucl Acids Res 15: 1297–1309, 1987
Cattini PA, Klassen ME, Nachtigal MW: Regulation of human chorionic somatomammotropin gene expression in rat pituitary tumour cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol 60: 217–224, 1988
Neumann JR, Morency CA, Russian KO: A novel and rapid assay for chloramphenicol acetyltransferase gene expression. Biotechniques 5: 444–447, 1987
Dignam JD, Lebovitz RM, Roeder RG: Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucl Acids Res 11: 1475–1489,1983
Lemaigre FP, Courtois SJ, Lafontaine DA, Rousseau GG: Evidence that the upstream stimulatory factor and the Sp1 transcription factor bind in vitro to the promoter of the human-growth hormone gene. Eur J Biochem 181: 555–561,1989
Lemaigre FP, Lafontaine DA, Courtois SJ, Durviaux SM, Rousseau GG: Sp1 can displace GHF-1 from its distal binding site and stimulate transcription from the growth hormone promoter. Mol Cell Biol 10: 1811–1814,1990
Rogers BL, Sobnosky MG, Saunders GF: Transcriptional enhancer within the human placental lactogen and growth hormone multigene cluster. Nucl Acids Res 14: 7647–7659, 1986
Walker WH, Fitzpatrick SL, Saunders GF: Human placental lactogen transcriptional enhancer: Tissue specificity and binding with specific proteins. J Biol Chem 265: 12940–12948,1990
Fitzpatrick SL, Walker WH, Saunders GF: DNA sequences involved in the transcriptional activation of a human placental lactogen gene. Mol Endocrinol 4:1815–1826,1990
Nickel BE, Cattini PA: Tissue-specific expression and thyroid hormone regulation of the endogenous placental growth hormone variant and chorionic somatomammotropin genes in a human choriocarcinoma cell line. Endocrinol 128:2353–2359,1991
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nickel, B.E., Nachtigal, M.W., Bock, M.E. et al. Differential binding of rat pituitary-specific nuclear factors to the 5′-flanking region of pituitary and placental members of the human growth hormone gene family. Mol Cell Biochem 106, 181–187 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00230184
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00230184