Abstract
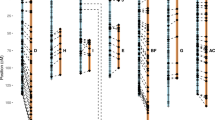
The three B genomes of Brassica contained in B. nigra, B. carinata and B. juncea were dissected by addition in B. napus. Using phenotypic, isozyme and molecular markers we characterized 8 alien B-genome chromosomes from B. nigra and B. carinata and 7 from B. juncea by constructing synteney groups. The alien chromosomes of the three different sources showed extensive intragenomic recombinations that were detected by the presence of the same loci in more than one synteny group but flanked by different markers. In addition, intergenomic recombinations were observed. These were evident in euploid AACC plants of the rapeseed phenotype derived from the addition lines carrying a few markers from the B genome due to translocations and recombinations between non-homoeologous chromosomes. The high plasticity of the Brassica genomes may have been an powerful factor in directing their evolution by hybridization and amphiploidy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armstrong K, Keller WA (1981) Chromosome pairing in haploids of Brassica compestris. Theor Appl Genet 59:49–52
Attia T, Röbbelen G (1986) Cytogenetic relationship within cultivated Brassica analyzed in amphihaploids from the three diploid ancestors. Can J Genet Cytol 28:323–329
Catcheside DG (1934) The chromosomal relationship in the Swede and turnip groups of Brassica. Ann Bot 601:33
Chen BY, Heneen WK, Jönnson R (1988) Independent inheritance of erucic acid content and flower color in the C-genome of Brassica napus L. Plant Breed 100:147–149
Chevre AM, This P, Eber F, Deschamps M, Renard M, Delseny M, Quiros CF (1991) Characterization of disomic addition lines Brassica napus-Brassica nigra by isozyme, fatty acid, and RFLP markers. Theor Appl Genet 81:43–49
Dorrel DC, Downey RK (1964) The inheritance of erucic acid content in rapeseed (Brassica compestris). Can J Plant Sci 44:499–504
Fernandez-Escobar J, Dominguez AM, Martin A, Fernandez-Martinez JM (1988) Genetics of the erucic acid content in interspecific hybrids of Ethiopian mustard (Brassica carinata Braun) and rapeseed (B. napus L.). Plant Breed 100:310–315
Hoenecke M, Chyi YS (1991) Comparison of Brassica napus and B. rapa genomes based on restriction fragment length polymorphism mapping. In: McGregor DI (ed) Proc 8th Int Rapeseed Congr, vol 4. GCIRC, Saskatoon, Canada, pp 1102–1107
Jönsson R (1977) Breeding for improved oil and meal quality in rape (Brassica napus L.) and turnip rape (Brassica compestris L.). Hereditas 87:205–218
Kianian SF, Quiros CF (1992) Generation of a Brassica oleracea composite map linkage arrangements among various populations and evolutionary implications. Theor Appl Genet 84:544–554
Kräling K, Röbbelen G, Thies W, Herrmann M, Ahmady MR (1990) Variation of seed glucosinolates in lines of Brassica napus. Plant Breed 100:33–39
Lukaszewski AJ, Gustafson JP (1983) Translocations and modifications of chromosomes in triticale wheat hybrids. Theor Appl Genet 64:239–248
McGrath JM, Quiros CF (1991) Inheritance of isozyme and RFLP markers in Brassica compestris and comparison with B. oleracea. Theor Appl Genet 82:668–673
Prakash S (1973) Haploidy in Brassica nigra Koch. Euphytica 22:613–614
Quiros CF, Hu J, This P, Chevre AM, Delseny M (1991) Development and chromosomal localization of genome specific markers by polymerase chain reaction in Brassica. Theor Appl Genet 82:627–632
Quiros CF, Hu J, Truco MJ (1994) DNA-Based marker maps of Brassica. In: Philipps RL, Vasil IK (eds) DNA based markers in plants. Kluwer Academic Publ, Dordrecht, 11:199–222
Ren ZL, Lelley T, Röbbelen G (1990) The use of monosomic rye addition lines for transferring rye chromatin into bread wheat. I. The occurrence of translocations. Plant Breed 105:257–264
Röbbelen G (1960) Beiträge zur Analyse des Brassica-Genoms. Chromosoma 1:205–228
Rogers SO, Bendich AJ (1988) Extraction of DNA from plant tissues. Plant Mol Biol Manual A6:1–10
Sacristan MD, Gerdemann M (1986) Different behavior of Brassica juncea and B. carinata as sources of Phoma lingam resistance in experiments of interspecific transfer to Brassica napus. Plant Breed 97:304–314
Sears ER (1972) Chromosome engineering in wheat. Stadler Genet Symp 4:23–28
Sharpe AG, Parkin IAP, Keith DJ, Lydiate DJ (1995) Frequent nonreciprocal translocations in the amphidiploid genome of oilseed rape (Brassica napus). Genome 38:1112–1121
Sikka SM (1940) Cytogenetics of Brassica hybrids and species. J Genet 40:441–509
Slocum MK (1989) Analyzing the genomic structure of Brassica species using RFLP analysis. In: Helentjaris T, Burr B (eds) Development and application of molecular markers to problems in plant genetics. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, N.Y.
Song KM, Osborn TC (1994) A method for examining expression of homologous genes in plant polyploids. Plant Mol Biol 26:1065–1071
Song KM, Osborn TC, Williams PH (1988) Brassica taxonomy based on molecular restriction fragment length polymorphisms (RFLPs). I. Genome evolution of diploid and amphidiploid species. Theor Appl Genet 75:784–749
Struss D, Quiros CF, Röbbelen G (1991a) Construction of different B-genome addition lines of Brassica napus L. In: McGregor DI (ed) Proc 8th Int Rapeseed Congr, vol 2. GCIRC, Saskatoon, Canada, pp 358–363
Struss D, Bellin U, Röbbelen G (1991b) Development of B-genome chromosome addition lines of B. napus using different interspecific Brassica hybrids. Plant Breed 106:209–214
Struss D, Quiros CF, Röbbelen G (1992) Mapping of phenotypic and molecular markers on Brassica B-genome chromosomes using addition lines of rapeseed. Plant Breed 108:320–32
Struss D, Plieske J, Quiros CF (1995) Evidence of intergenomic B-genome translocation in B. napus using molecular markers. In: Murphy D (ed) Proc 9th Int Rapeseed Congr, vol 4. GCIRC, Cambridge, England, pp 1125–1127
Thies W (1974) New methods for the analysis of rapeseed constituents. In: DGF, Proc 4th Int Rapeseed Congr. GCIRC, Giessen eds, pp 275–282
This P, Ochoa O, Quiros CF (1990) Dissection of the Brassica nigra genome by monosomic addition lines. Plant Breed 105:211–220
Truco MJ, Quiros CF (1994) Structure and organization of the B genome based on a linkage map in Brassica nigra. Theor Appl Genet 89:590–598
U N (1935) Genome analysis in Brassica with special reference to the experimental formation of B. napus and peculiar mode of fertilization. Jpn J Bot 7:389–452
Warwick SI, Black LD (1991) Molecular systematics of Brassica and allied genera (subtribe Brassicinae, Brassiceae) — chloroplast genome and cytodeme congruence. Theor Appl Genet 83:839–850
Williams JG, Kubelik AE, Levak KJ, Rafalski JA, Tingey SC (1990) DNA polymorphisms amplified by arbitrary primers are useful as genetic markers. Nucleic Acids Res 18:6531–6535
Zhu J, Struss D, Röbbelen G (1993) Studies on Resistance to Phoma lingam in Brassica napus-Brassica nigra addition lines. Plant Breeding 111:192–197
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by G. Wenzel
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Struss, D., Quiros, C.F., Plieske, J. et al. Construction of Brassica B genome synteny groups based on chromosomes extracted from three different sources by phenotypic, isozyme and molecular markers. Theoret. Appl. Genetics 93, 1026–1032 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00230120
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00230120