Summary
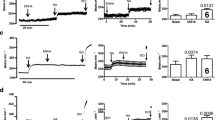
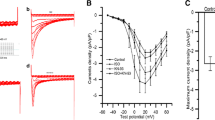
The Ca2+ channel blockers felodipine and bepridil are known to affect selectively functions of calmodulin. We studied their effects on calmodulin binding and ATPase activities of calmodulin-containing and calmodulin-depleted rabbit heart sarcolemma. Both drugs as well as the specific anti-calmodulin drug calmidazolium at a concentration of 50 µM, inhibited the Ca2+-stimulated calmodulin binding to calmodulin-depleted sarcolemma. Within the concentration range of 3 to 100 µM all three drugs also progressively inhibited Ca2+ pumping ATPase in calmodulin containing sarcolemma, although the enzyme was assayed at saturating Ca2+ (100 µM). The inhibitory potency of calmidazolium and bepridil, but not that of felodipine, increased when the membrane protein concentration in the ATPase assay was lowered. At low membrane protein concentration 30 µM calmidazolium completely blocked calmodulin-dependent Ca2+ pumping ATPase, whereas the inhibition caused by 30 µM felodipine or bepridil remained partially. A similar inhibition pattern of the drugs was found in the calmodulin binding experiments. Within a concentration range of 3 to 30 µM, all three drugs had negligible effects on the basal Ca2+ pumping ATPase which was measured in calmodulin-depleted sarcolemma. In conclusion, the characteristics of the anti-calmodulin action of felodipine on the rabbit heart sarcolemmal Ca2+ pumping ATPase are not different from those of bepridil. Both drugs may inhibit the enzyme by interference with the Ca2+-stimulated binding of calmodulin.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Ca2+ pumping ATPase:
-
Ca2+ stimulated Mg2+-dependent ATP hydrolyzing activity
- Na+ pumping ATPase:
-
Na+-stimulated K+- and Mg2+-dependent ATP hydrolyzing activity
- Tris-maleate:
-
tris (hydroxymethyl) aminomethane hydrogen maleate
- Hepes:
-
N-2-hydroxyethylpiperazine-N′-2-ethanesulfonic acid
- Mes:
-
2-(N-morpholino) ethane sulfonic acid and Egta, ethylene glycol bis (p-amino ethylether)-N,N,N′,N′ tetraacetic acid
References
Boström SL, Ljung B, Mardh S, Forsen S, Thulin E: Interaction of the antihypertensive drug felodipine with calmodulin. Nature, London 292: 777–778, 1981
Johnson JD, Wittenauer LA, Nathan RD: Calmodulin, Ca2+ antagonists and Ca2+ transporters in nerve and muscle. J. Neural Transmission 18 (supplement): 97–111, 1983
Inagaki M, Hidaka H: Two types of calmodulin antagonists: a structurally related interaction. Pharmacology 29: 75–84, 1984
Movsesian MA, Swain AL, Adelstein RS: Inhibition of turkey gizzard myosin light chain kinase activity by dihydropyridine calcium antagonists. Biochem Pharmacol 33: 3759–3764, 1984
Minocherhomjee AM, Roufogalis BD: Antagonism of calmodulin and phosphodiesterase by nifedipine and related calcium entry blockers. Cell Calcium 5: 57–63, 1984.
Epstein PM, Fiss K, Hachisu R, Adrenyak DM: Interaction of calcium antagonists with cyclic AMP phosphodiesterase and calmodulin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 105: 1142–1149, 1982
Thayer SA, Fairhurst AS: The interaction of dihydropyridine calcium channel blockers with calmodulin and calmodulin inhibitors. Mol Pharmacol 24: 6–9, 1983
Schlondorff D, Satriano JA: Interactions with calmodulin: potential mechanism for some inhibitory actions of tetracyclines and calcium channel blockers. Biochem Pharmacol 34: 3391–3394, 1985.
Silver PJ, Ambrose JM, Michalak RJ, Dachiw J: Effects of felodipine, nitrendipine and W-7 on arterial myosin phosphorylation, actin-myosin interaction and contraction. Eur J Pharmacol 102:417–424, 1984
Lamers JMJ, Cysouw KJ, Verdouw PD: Slow calcium channel blockers and calmodulin. Effect of felodipine, nifedipine, prenylamine and bepridil on cardiac sarcolemmal calcium pumping ATPase. Biochem Pharmacol 34:3837–3843, 1985
Mills JS, Bailey BL, Johnson JD: Cooperativity among calmodulin's drug binding sites. Biochemistry 24:4897–4902, 1985
Andersson A, Drakenberg T, Thulin E, Forsen S: A 113Cd and 1H-NMR study of the interaction of calmodulin with D600, trifluoperazine and other hydrophobic drugs. Eur J Biochem 134:459–465, 1983
Vincenzi FF: Calmodulin pharmacology. Cell Calcium 2:387–409, 1981
Janis RA, Scriabine A: Sites of action of Ca2+ channel inhibitors. Biochem Pharmacol 32:3499–3507, 1983
Weiss B, Prozialeck WC, Wallace TL: Interactions of drugs with calmodulin. Biochemical, pharmacological and clinical implications. Biochem Pharmacol 31:2217–2226, 1982
Johnson JD, Wittenauer LA: A fluorescent calmodulin that reports the binding of hydrophobic inhibitory ligands. Biochem J 211:473–479, 1983
Itoh H, Tanaka T, Mitani Y, Hidaka H: The binding of the calcium channel blocker bepridil to calmodulin. Biochem Pharmacol 35:217–220, 1986
Lamers JMJ, Stinis JT, De Jonge HR: On the role of cyclic AMP and Ca2+-calmodulin-dependent phosphorylaton in the control of (Ca2+ + Mg3)-ATPase of cardiac sarcolemma. FEBS Lett 127:139–143, 1981.
Lamers JMJ, Stinis JT: Inhibition of Ca2+-dependent protein kinase and Ca2+/Mg2+-ATPase in cardiac sarcolemma by the anti-calmodulin drug calmidazolium. Cell Calcium 4:281–294, 1983
Caroni P, Carafoli E: The Ca2+ pumping ATPase of heart sarcolemma. Characterization, calmodulin dependence and partial purification. J Biol Chem. 256:3263–3270, 1981
Mas-Oliva J, De Meis L, Inesi G: Calmodulin stimulates both adenosine 5′-triphosphate hydrolysis and synthesis catalyzed by a cardiac calcium ion dependent adenosine triphosphatase. Biochemistry 22:5822–5825, 1983
Tuana BS, Dzurba A, Panagia V, Dhalla NS: Stimulation of heart sarcolemmal calcium pump by calmodulin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 100:1245–1250, 1981
Adunyah ES, Niggli V, Carafoli E: The anticalmodulin drugs trifluoperazine and R24571 remove the activation of the purified erythrocyte Ca2+-ATPase by acidic phospholipids and by controlled proteolysis. FEBS Lett 143:65–69, 1982
Vincenzi FF, Adunyah ES, Niggli V, Carafoli E: Purified red blood cell Ca2+ pump ATPase: evidence for direct inturbation by presumed anti-calmodulin drugs in the absence of calmodulin. Cell Calcium 3:545–559, 1982
Mas-Oliva J: The effect of verapamil on the Ca2+ transporting and Ca2+-ATPase activity of isolated sarcolemmal preparations. Br J. Pharmacol 70:617–624, 1980
Ortega A, Mas-Oliva J: Cholesterol effect on enzyme activity of the sarcolemmal (Ca2+ + Mg2+)-ATPase from cardiac muscle. Biochim Biophys Acta 773:231–236, 1984
St. Louis PJ, Sulakhe PV: Isolation of sarcolemmal membranes from cardiac muscle. Int J Biochem 7:574–558, 1976
Bradford MM: A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254, 1976
Lamers JMJ, Stinis JT, Montfoort A, Hülsmann WC: The effect of lipid intermediates on Ca2+ and Na+ permeability and (Na+ + K+)-ATPase of cardiac sarcolemma. A possible role in myocardial ischemia. Biochim Biophys Acta 774:127–137, 1984
Fiske CH, Subbarow Y: The colorimetric determination of phosphorous. J Biol Chem 66:375–406, 1925
Fabiato A, Fabiato F: Calculator programs for computing the composition of the solution containing multiple metals and ligands used for experiments in skinned muscle cells. J Physiol (Paris) 75:463–505, 1979
Segel IH: Enzyme kinetics. Behavior and analysis of rapid equilibrium and steady state enzyme system. John Wiley and Sons, Toronto, 1975
Lamers JMJ, Cysouw J, Verdouw PD, Hugenholtz PG: A comparative study of the interactions of some slow calcium channel blockers and calmidazolium with calcium-calmodulin-regulated enzymes. In: PR Lichtlen (ed) 6th International Adalat Symposium. New Therapy of Ischaemic Heart Disease and Hypertension. Excerpta Medica, Amsterdam, 1986, pp 212–217
Van Belle H: R24571: A potent inhibitor of calmodulin-activated enzymes. Cell Calcium 2:483–494, 1981
Itoh H, Ishikawa T, Hidaka H: Effect on calmodulin of bepridil, an antianginal agent. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 230: 737–441, 1984
Agre P, Virshup D, Bennett V: Bepridil and cetiedil: vasodilators which inhibit Ca2+-dependent calmodulin interaction with erythrocyte membranes. J Clin Invest 74:812–820, 1984
Mas-Oliva J: Synthesis of ATP catalyzed by the (Ca2+ + Mg2+)-ATPase from erythrocyte ghost. Energy conservation in plasma membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta 812:163–167, 1985
Lamers JMJ: Calcium transport systems in cardiac sarcolemma and their regulation by the second messengers cyclic AMP and Ca2+-calmodulin. Gen Physiol Biophys 4:143–154, 1985
Wang T, Tsai LI, Schwartz A: Effects of verapamil, diltiazem, nisoldipine and felodipine on sarcoplasmic reticulum. Eur J Pharmacol 100:253–261, 1984
Colvin RA, Pearson N, Messineo FC, Katz AM: Effects of Ca channel blockers on Ca transport and Ca ATPase in skeletal and cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum vesicles. J. Cardiovasc Pharmacol 4:935–941, 1982
Movsesian MA, Ambudkar IS, Adelstein RS, Shamoo AE: Stimulation of canine cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ uptake by dihydropyridine Ca2+ antagonists. Biochem Pharmacol 34:195–201, 1985
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lamers, J.M.J., Verdouw, P.D. & Mas-Oliva, J. The effects of felodipine and bepridil on calcium-stimulated calmodulin binding and calcium pumping ATPase of cardiac sarcolemma before and after removal of endogenous calmodulin. Mol Cell Biochem 78, 169–176 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00229691
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00229691