Abstract
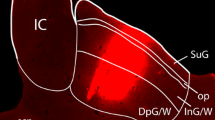
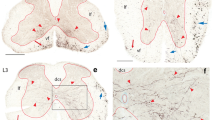
To investigate the topographic organization of nociceptive neurons in the caudal medullary reticular formation, the distribution of cells that exhibit c-fos expression was examined following a unilateral noxious facial stimulus: subcutaneous injection of formalin into the vibrissal pad of awake rats. Labelling for Fos-like immunoreactivity was present in a somatotopic distribution in a region of the lateral reticular formation adjacent to trigeminal nucleus caudalis, which corresponds approximately to lamina V of the medullary dorsal horn. Labelling in adjacent regions of the reticular formation showed no somatotopy but was predominantly ipsilateral. Contralateral labelling was concentrated ventrolaterally around the lateral reticular nucleus and dorsally near the nucleus of the solitary tract.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almeida A, Tavares I, Lima D, Coimbra A (1993) Descending projections from the medullary dorsal reticular nucleus make synaptic contacts with spinal cord lamina I cells projecting to that nucleus: an electron microscopic tracer study in the rat. Neuroscience 55:1093–1106
Amano N, Hu JW, Sessle BJ (1986) Responses of neurons in feline trigeminal subnucleus caudalis (medullary dorsal horn) to cutaneous, intraocal, and muscle afferent stimuli. J Neurophysiol 55:227–243
Benjamin RM (1970) Single neurons in the rat medulla responsive to nociceptive stimulation. Brain Res 24:525–529
Bereiter DA, Hathaway CB, Benetti AP (1994) Caudal portions of the spinal trigeminal complex are necessary for autonomie responses and display Fos-like immunoreactivity after corneal stimulation in the cat. Brain Res 657:73–82
Bullitt E (1990) Expression of c-fos-like protein as a marker for neuronal activity following noxious stimulation in the rat. J Comp Neurol 296:517–530
Burton H (1968) Somatic sensory properties of caudal bulbar reticular neurons in the cat (Felis domestica). Brain Res 11:357–372
Chan RK, Sawchenko PE (1994) Spatially and temporally differentiated patterns of c-fos expression in brainstem catecholaminergic cell groups induced by cardiovascular challenges in the rat. J Comp Neurol 348:433–460
Clavelou P, Pajot J, Dallel R, Raboisson P (1989) Application of the formalin test to the study of orofacial pain in the rat. Neurosci Lett 103:349–353
Darian-Smith I, Yokota T (1966) Corticofugal effects on different neuron types within the cat's brain stem activated by tactile stimulation of the face. J Neurophysiol 29:185–206
Darian-Smith I, Proctor R, Ryan RD (1963) A single-neurone investigation of somatotopic organization within the cat's trigeminal brain-stem nuclei. J Physiol (Lond) 168:147–157
Eisenberg E, Vos BP, Strassman AM (1993) The NMDA antagonist Memantine blocks pain behavior in a rat model of formalin-induced facial pain. Pain 54:301–307
Erickson JT, Millhorn DE (1991) Fos-like protein is induced in neurons of the medulla oblongata after stimulation of the carotid sinus nerve in awake and anesthetized rats. Brain Res 567:11–24
Gieroba ZJ, Yu Y-H, Blessing WW (1994) Vasoconstriction induced by inhalation of irritant vapour is associated with apearance of Eos protein in C1 catecholamine neurons in rabbit medulla oblongata. Brain Res 636:157–161
Gobel S, Falls WM, Hockfield S (1977) The division of the dorsal and ventral horns of the mammalian caudal medulla into eight layers using anatomical criteria. In: Anderson DJ, Matthews B (eds) Pain in the trigeminal region. Elsevier/North-Holland, Amsterdam, pp 443–453
Gordon G, Landgren S, Seed WA (1961) The functional characteristics of single cells in the caudal part of the spinal nucleus of the trigeminal nerve of the cat. J Physiol (Lond) 158:544–559
Hu JW, Dostrovsky JO, Sessle BJ (1981) Functional properties of neurons in cat trigeminal subnucleus caudalis (medullary dorsal horn). I. Responses to oral-facial noxious and nonnoxious stimuli and projections to thalamus and subnucleus oralis. JNeurophysiol 45:173–192
Jin GR, Rao ZR, Shi JW (1994) Visceral noxious stimulation induced expression of Fos protein in medullary catecholaminergic neurons projecting to nucleus accumbens in the rat: a study with triple labeling method of HRP tracing combined with Fos and TH immunohistochemistry. Brain Res 648:196–202
Jones SL, Blair RW (1995) Noxious heat-evoked fos-like immunoreactivity in the rat medulla, with emphasis on the catecholamine cell groups. J Comp Neurol 354:410–422
Kruger L, Michel F (1962) Reinterpretation of the representation of pain based on physiological excitation of single neurons in the trigeminal sensory complex. Exp Neurol 5:157–178
Lamarche G, Langlois JM, Heon M (1960) Unit study of the trigeminal projections in the reticular formation of the medulla oblongata in the cat. Can J Biochem Physiol 38:1163–1166
Lanteri-Minet M, Isnardon P, de Pommery J, Menetrey D (1993) Spinal and hindbrain structures involved in visceroception and visceronociception as revealed by the expression of Fos, Jun and krox-24 proteins. Neuroscience 55:737–753
Lanteri-Minet M, Weil-Fugazza J, de Pommery J, Menetrey D (1994) Hindbrain structures involved in pain processing as revealed by the expression of c-fos and other immediate early gene proteins. Neuroscience 58:287–298
Lima D (1990) A spinomedullary projection terminating in the dorsal reticular nucleus of the rat. Neuroscience 34:577–589
Lima D, Mendes-Ribeiro JA, Coimbra A (1991) The spino-lateroreticular system of the rat: projections from the superficial dorsal horn and structural characterization of marginal neurons involved. Neuroscience 45:137–152
Mayer ML, Hill RG (1978) The effect of intravenous fentanyl, morphine and naloxone on nociceptive responses of neurons in the rat caudal medulla. Neuropharmacology 17:533–539
McKitrick DJ, Krukoff TL, Calaresu FR (1992) Expression of c-fos protein in rat brain after electrical stimulation of the aortic depressor nerve. Brain Res 599:215–222
Nagano S, Myers JA, Hall RD (1975) Representation of the cornea in the brain stem of the rat. Exp Neurol 49:653–670
Narvaez JA, Covenas R, de Leon M, Aguirre JA, Cintra A, Goldstein M, Fuxe K (1993) Induction of c-fos immunoreactivity in tyrosine hydroxylase and phenylethanolamine-N-methyltransferase immunoreactive neurons of the medulla oblongata of the rat after phosphate-buffered saline load in the urethane-anaesthetized rat. Brain Res 602:342–349
Nishida Y, Yokota T (1991) Corneal representation within the trigeminal subnucleus caudalis and adjacent bulbar lateral reticular formation of the cat. Jpn J Physiol 41:551–565
Nord SG, Kyler HJ (1968) A single unit analysis of trigeminal projections to bulbar reticular nuclei of the rat. J Comp Neurol 134:485–494
Nord SG, Ross GS (1973) Responses of trigeminal units in the monkey bulbar lateral reticular formation to noxious and nonnoxious stimulation of the face: experimental and theoretical considerations. Brain Res 58:385–399
Paxinos G, Watson C (1986) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates. Academic Press, San Diego
Price DD, Dubner R, Hu JW (1976) Trigeminothalamic neurons in nucleus caudalis responsive to tactile, thermal, and nociceptive stimulation of monkey's face. J Neurophysiol 39:936–953
Renehan WE, Jacquin MF, Mooney RD, Rhoades RW (1986) Structure-function relationships in rat medullary and cervical dorsal horns. II. Medullary dorsal horn cells. J Neurophysiol 55:1187–1201
Rinaman L, Verbalis JG, Stricker EM, Hoffman GE (1993) Distribution and neurochemical phenotypes of caudal medullary neurons activated to express cFos following peripheral administration of cholecystokinin. J Comp Neurol 338:475–490
Segundo JP, Takenaka T, Encabo H (1967) Somatic sensory properties of bulbar reticular neurons. J Neurophysiol 30:1221–1238
Smith DW, Day TA (1994) C-fos expression in hypothalamic neurosecretory and brainstem catecholamine cells following noxious somatic stimuli. Neuroscience 58:765–775
Strassman A, Vos BP (1993) Somatotopic and laminar organization of fos-like immunoreactivity in the medullary and upper cervical dorsal horn induced by noxious facial stimulation in the rat. J Comp Neurol 331:495–516
Tavares I, Lima D (1994) Descending projections from the caudal medulla oblongata to the superficial or deep dorsal horn of the rat spinal cord. Exp Brain Res 99:455–463
Tavares I, Lima D, Coimbra A (1993) Neurons in the superficial dorsal horn of the rat spinal cord projecting to the medullary ventrolateral reticular formation express c-fos after noxious stimulation. Brain Res 623:278–286
Villanueva L, Bouhassira D, Bing Z, Le Bars D (1988) Convergence of heterotopic nociceptive information onto subnucleus reticularis dorsalis neurons in the rat medulla. J Neurophysiol 60:980–1009
Villanueva L, Bing Z, Bouhassira D, Le Bars D (1989) Encoding of electrical, thermal, and mechanical noxious stimuli by subnucleus reticularis dorsalis neurons in the rat medulla. J Neurophysiol 61:391–402
Villanueva L, Cliffer KD, Sorkin LS, Le Bars D, Willis WD Jr (1990) Convergence of heterotopic nociceptive information onto neurons of caudal medullary reticular formation in monkey (Macaca fascicularis). J Neurophysiol 63:1118–1127
Villanueva L, de Pommery J, Menetrey D, Le Bars D (1991) Spinal afferent projections to subnucleus reticularis dorsalis in the rat. Neurosci Lett 134:98–102
Wall PD, Taub A (1962) Four aspects of trigeminal nucleus and a paradox. J Neurophysiol 25:110–126
Yokota T, Nishikawa N (1980) Reappraisal of somatotopic tactile representation within trigeminal subnucleus caudalis. J Neurophysiol 43:700–712
Yokota T, Koyama N, Nishikawa Y, Nishikawa N, Nishida Y, Hasegawa A, Fujino Y (1991) Trigeminal nociceptive neurons in the subnucleus reticularis ventralis. I. Response properties and afferent connections. Neurosci Res 11:1–17
Yousfi-Malki M, Puizillout JJ (1994) Induction of Fos-like protein in neurons of the medulla oblongata after electrical stimulation of the vagus nerve in anesthetized rabbit. Brain Res 635:317–322
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mineta, Y., Eisenberg, E. & Strassman, A.M. Distribution of Fos-like immunoreactivity in the caudal medullary reticular formation following noxious facial stimulation in the rat. Exp Brain Res 107, 34–38 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00228014
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00228014