Abstract
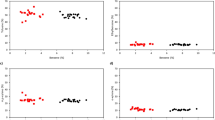
Air pollution meteorology related to the dispersion of toxic chemicals in the southeast Ohio River valley was analyzed for a 32-mo period. Attendant air quality measurements of benzene, benzo(a)pyrene, As, Cd, and Cr concentrations were also studied for a 24-mo period. Analysis of the meteorological data showed that wind flow in the valley is significantly affected by the synoptic wind pattern above the hilltop. Sampling at multiple stations showed that daily average concentrations were on the order of 7 μg m−3 for benzene, 2 ng m−3 for benzo(a)pyrene and As, 7 ng m−3 for Cd, and 20 ng m−3 for Cr. Correlations between different species concentrations ranged from 0.25 to 0.6. Based on multi-variable regression analysis, the average benzene concentrations were shown to correlate with the average wind speed and the morning and evening potential temperature gradients at the airport, with a correlation coefficient on the order of 0.5.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benaric, M.: 1976, Urban Air Pollution Modeling Without Computers, EPA-600/4–76–055, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Research Triangle Park, North Carolina.
Benarie, M.: 1978, Atmos. Environ. 12, 1229.
Briggs, G.: 1975, ‘Plume Rise Predictions’, in D. Haugen (ed.), Lectures on Air Pollution and Environmental Impact Analysis, American Meteorological Society, Boston, Massachusetts, pp. 59–105.
Draper, N. and Smith, H.: 1981, Applied Regression Analysis, Wiley and Sons, New York.
Gifford, F. and Hanna, S.: 1973, Atmos. Environ. 7, 131.
Hasanen, E., Karlsson, V., Leppamaki, E., and Juhala, M.: 1981, Atmos. Environ. 15, 1755.
Martin, B. E., Clark, T., Bumgarner, J., and Evans, G. F.: 1980, Ambient Air Monitoring for Benzene, EPA-600/4–80–027, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Research Triangle Park, North Carolina.
Panofsky, H. and Prasad, B.: 1967, J. Applied Meteor. 6, 493.
Pasquill, F.: 1974, Atmospheric Diffusion, Halsted Press, New York.
Singer, I.: 1967, J. Applied Meteor. 6, 1033.
Venkatram, A.: 1980, Atmos. Environ. 14, 1.
Wathne, B. M.: 1983, Atmos. Environ. 17, 1713.
Willson, R., Shain, F., Reynolds, B., and Greene, W.: 1983, Atmos. Environ. 17, 1633.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Langstaff, J.E., Seigneur, C., Liu, MK. et al. The effect of meteorology on the atmospheric dispersion of toxic chemicals in a river valley. Water Air Soil Pollut 32, 31–41 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00227681
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00227681