Abstract
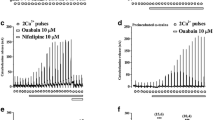
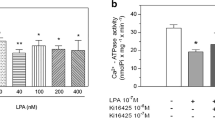
The regulation of the guinea-pig pancreatic acinar plasma membrane Ca2+ pump by protein kinase A, protein kinase C and calmodulin was investigated. The results were compared with the effects of these regulators on the high affinity Ca2+-ATPase found in this membrane preparation. The catalytic subunit of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase stimulated Ca2+ transport 2-fold, but had no effect on Ca2+-dependent ATPase activity. Purified protein kinase C, the phorbol ester 12-O-tetradecanoyl phorbol-13-acetate and diacylglycerol derivative, 1-stearoyl-2-arachidonoyl-sn-glycerol, failed to stimulate the Ca2+-uptake but augmented the Ca2+-dependent ATPase activity. Exogenously added calmodulin failed to stimulate either activity. In addition, two antagonists of calmodulin activity, trifluoperazine and compound 48/80 produced a concentration-dependent inhibition of Ca2+-transport. These data suggest the presence of endogenous calmodulin within guinea-pig pancreatic acinar plasma membranes. Both calmodulin antagonists failed to influence the Ca2+-dependent ATPase activity. The ability of boiled extracts from guinea-pig pancreatic acinar plasma membranes to stimulate the Ca2+-ATPase activity in calmodulin-depleted erythrocyte plasma membranes confirmed the presence of endogenous calmodulin. Our results imply a role for calmodulin and cAMP-dependent protein kinase, but not protein kinase C, in the regulation of Ca2+ efflux from pancreatic acinar cells. These results also provide further evidence suggesting that the high affinity Ca2+-ATPase does not catalyze the plasma membrane Ca2+-transport activity observed in pancreatic acini.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AMP:
-
adenosine 5′-monophosphate
- CaM:
-
calmodulin
- EDTA:
-
ethylenediaminetetraacetate
- EGTA:
-
ethylene glycol bis (β-aminoethyl ether)-N,N,N′,N′-tetraacetic acid
- PKA:
-
protein kinase A
- PKC:
-
protein kinase C
- PS:
-
phosphatidylserine
- SA-DG:
-
1 stearoyl-2-arachidonoyl-sn-glycerol
- TFP:
-
trifluoperazine
- TPA:
-
12-O-tetradecanoyl phorbol-13-acetate
References
Dormer RL, Brown GR, Doughney C, McPherson MA: Intracellular Ca2+ in pancreatic acinar cells: regulation and role in stimulation of enzyme secretion. Biosci Rep 7: 333–344, 1987
Mahey R, Bridges MA, Katz S: Relationship between Ca2+-transport and ATP hydrolytic activities in guinea-pig pancreatic acinar plasma membranes. Mol Cell Biochem 105: 137–147, 1991
Muallem S, Pandol SJ, Beeker TG: Calcium mobilizing hormones activate the plasma membrane Ca2+ pump of pancreatic acinar cells. J Membr Biol 106: 57–69, 1988
Bayerdörffer E, Eckhardt L, Haase W, Schutz I: Electrogenic calcium transport in plasma membrane of rat pancreatic acinar cells. J Membr Biol 84: 45–60, 1985
Kribben A, Tyrakowski T, Schulz I: Characterization of Mg-ATP-dependent Ca2+ transport in cat pancreatic microsomes. Am J Physiol 244: G480-G490, 1983
Ansah T-A, Molla A, Katz S: Ca2+-ATPase activity in pancreatic acinar plasma membranes. Regulation by calmodulin and acidic phospholipids. J Biol Chem 259: 13442–13450, 1984
Al-Mutairy AR, Dormer RL: Isolation of plasma membranes from pancreatic acinar cells: demonstration of a Ca2+-activated Mg2+-ATPase activity. Biochem Soc Trans 13: 900–901, 1985
Dormer RL, Al-Mutairy AR: Pancreatic acinar cell plasma-membrane enzymes involved in stimulus-secretion coupling. In: E Reid, GMW Cook and JP Luzio (eds.) Cells, Membranes, and Disease, Including Renal. Plenum Publishing Corporation, New York, 1987, pp 273–283
Allen BG, Katz S: Isolation and characterization of the calcium- and phospholipid-dependent protein kinase (protein kinase C) subtypes from bovine heart. Biochemistry 30: 4334–4343, 1991
Schatzmann HJ: Calcium extrusion across the plasma membrane by the calcium-pump and the Ca2+-Na+ exchange system. In: D Marmé (ed) Calcium and Cell Physiology. Springer-Verlag, New York, 1985, pp 18–52
Carafoli E, Niggli V, Penniston JT: Purification and reconstitution of the calcium, magnesium ATPase of the erythrocyte membrane. Ann NY Acid Sci 358: 159–168, 1980
Meyer T, Regenass U, Fabbro D, Alter E, Rösel J, Müller M, Caravatti G, Matter A: A derivative of staurosporine (CGP 41 251) shows selectivity for protein kinase C inhibition and in vitro anti -proliferative as well as in vivo anti-tumor activity. Int J Cancer 43: 851–856, 1989
Norman JA, Ansell J, Stone GA, Wennogle LP, Wasley JWF: CGS 9343B, a novel, potent, and selective inhibitor of calmodulin activity. Mol Pharmacol 31: 535–540, 1987
Neyes L, Reinlib L, Carafoli E: Phosphorylation of the Ca2+-pumping ATPase of heart sarcolemma and erythrocyte plasma membrane by the cAMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem 260: 10283–10287, 1985
Caroni P, Carafoli E: Regulation of Ca2+-pumping ATPase of heart sarcolemma by a phosphorylation-dephosphorylation process. J Biol Chem 256: 9371–9373, 1981
Smallwood JI, Gügi B, Rasmussen H: regulation of erythrocyte Ca2+ pump activity by protein kinase C. J Biol Chem 263: 2195–2202, 1988
Wang KKW, Wright LC, Machan CL, Allen BG, Conigrave AD, Roufogalis BD: Protein kinase C phosphorylates the carboxyl terminus of the plasma membrane Ca2+-ATPase from human erythrocytes. J Biol Chem 266: 9078–9085, 1991
Furukawa K-I, Tawada Y, Shigekawa M: Protein kinase C activation stimulates plasma membrane Ca2+ pump in cultured vascular smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem 264: 4844–4849, 1989
Ochs DL, Belanger DM, Kalnitsky-Aliff J: Calcium-stimulated ATPase activity in plasma membrane vesicles from pancreatic acinar cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 156: 746–751, 1988
Lin S-H, Fain JN: Purification of (Ca2+-Mg2+)-ATPase from rat liver plasma membranes. J Biol Chem 259: 3016–3020, 1984
Lotersztajn S, Hanoune J, Pecker F: A high affinity calcium-stimulated magnesium-dependent ATPase in rat liver plasma membranes. Dependence on an endogenous protein activator distinct from calmodulin. J Biol Chem 256: 11209–11215, 1981
Verma AK, Penniston JT: A high affinity Ca2+-stimulated and Mg2+-dependent ATPase in rat corpus luteum plasma membrane fractions. J Biol Chem 256: 1269–1275, 1981
Carafoli E, Zurini M, Benaim G: The calcium pump of plasma membrane. In: Calcium and the Cell. Wiley, Chichester, 1986, pp 58–72
Caroni P, Zurini M, Clark A, Carafoli E: Further characterization and reconstitution of the purified Ca2+-pumping ATPase of heart sarcolemma. J Biol Chem 258: 7305–7310, 1983
Lucchesi PA, Cooney RA, Mangsen-Baker C, Honeyman TW, Scheid CR: Assessment of transport capacity of plasmalemmal Ca2+ pump in smooth muscle. Am J Physiol 255: C226-C236, 1988
Gietzen K, Adamczyk-Engelmann P, Wüthrich A, Konstantinova A, Bader H: Compound 48/80 is a selective and powerful inhibitor of calmodulin-regulated functions. Biochim Biophys Acta 736: 109–118, 1983
Mousli M, Bronner C, Landry Y, Bockaert J, Rouot B: Direct activation of GTP-binding regulatory proteins (G-Proteins) by Substance P and compound 48/80. FEBS Lett 259: 260–262, 1990
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mahey, R., Allen, B.G., Bridges, M.A. et al. Regulation of calcium transport in pancreatic acinar plasma membranes from guinea pig. Mol Cell Biochem 112, 155–162 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00227572
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00227572