Summary
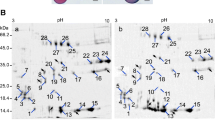
Protein extracts from four self-incompatible genotypes of Phalaris coerulescens were subjected to analysis by sodium dodecyl sulphate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and ultra-thin isoelectric focusing. A comparison between stigma, root and leaf extracts showed that there was no significant difference in electrophoretic or isoelectric focusing patterns between the genotypes for both root and leaf proteins. However, stigma protein patterns did vary between genotypes especially within the molecular weight region of 43 000–97 000 and within the pI range 5–7. The stigma-specific changes strongly suggest a link between the self-incompatible genotype and these stigma proteins. However, because there are two loci involved, it is not yet possible to precisely assign particular proteins to each S- or Z-allele.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bredermeijer GMM, Blaas J (1981) S-specific proteins in styles of self-incompatible Nicotiana alata. Theor Appl Genet 59:185–190
Hayman DL (1956) The genetic control of incompatibility in Phalaris coerulescens. Aust J Biol Sci 9:321–333
Kamboj RK, Jackson JF (1986) Self-incompatibility alleles control a low molecular weight, basic protein in pistils of Petunia hybrida. Theor Appl Genet 71:815–819
Laemmli WK, Favre M (1973) Maturation of the head of bacteriophage T4. J Mol Biol 80:575–599
Lewis D (1979) Genetic versatility of incompatibility of plants. NZ J Bot 17:637–644
Linskens HF (1975) Incompatibility in Petunia. Proc R Soc London Ser B 188:299–331
Lundquist A (1956) Self-incompatibility in rye. I. Genetic control in the diploid. Hereditas 42:293–348
Mau SL, Raff J, Clarke AE (1982) Isolation and partial characterization of components of Prunus avium L. styles, including an antigenic glycoprotein associated with a self-incompatible genotype. Planta 156:506–516
Morrissey JH (1981) Silver stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels: a modified procedure with enhanced uniform sensitivity. Anal Biochem 117:307–310
Nasrallah ME (1979) Self-incompatibility antigens and S-gene expression in Brassica. Heredity 43:259–263
Nasrallah ME, Nasrallah JB (1986) Molecular biology of self-incompatibility in plants. Trends Genet 2:239–244
Nasrallah JB, Kao T-H, Chen C-H, Goldberg ML, Nasrallah ME (1987) Amino acid sequence of glycoproteins encoded by three alleles of the S-locus of Brassica oleracea. Nature 326:617–619
Nishio T, Hinata K (1978) S-allele specificity of stigma proteins in Brassica oleracea and Brassica campestris. Heredity 41:93–100
Tan LW, Jackson JF (1987) Self-incompatibility in Phalaris coerulescens. Plant Molecular Biology Conference, University of Auckland, New Zealand, pp 2–3
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tan, L.W., Jackson, J.F. Stigma proteins of the two loci self-incompatible grass Phalaris coerulescens . Sexual Plant Reprod 1, 25–27 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00227018
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00227018