Summary
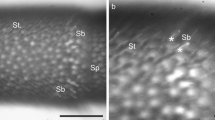
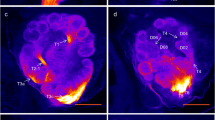
The topography of the antennal afferent path-ways was studied comparatively in the worker bee and the drone of Apis mellifera L. by cellular marking, following localized application of cobalt chloride to the cut end of one antenna. This study dealt principally with the first relay of the afferent pathway in the glomeruli of the antennal lobe. The counting and measurement of all the glomeruli were performed on 5 worker bees and 5 drones. An important sexual dimorphism, represented by 4 large and easily identifiable glomerular complexes, was demonstrated in the drone. In both worker bee and drone, four main regions of the glomerular neuropil were distinguished according to corresponding afferent bundles. The worker possessed 166 glomeruli and the drone 103. The number, position and dimensions of the glomeruli indicated that the glomerular organization was unvarying in worker bees and in drones. Concerning the internal structure of the glomeruli, two types were distinguished: the great majority (95%) exhibited a cortical layer, whereas in the 7 posterior glomeruli the synaptic fields of association seemed to be scattered throughout the whole volume. The main results of this work (glomerular invariance, sexual dimorphism) support the hypothesis of the functional unit of the glomeruli.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altner H, Sass H, Altner I (1977) Relationship between structure and function of antennal chemo-, hygro- and thermoreceptive sensilla in Periplaneta americana. Cell Tissue Res 176:389–409
Arnold G, Masson C (1983) Mise en place des connexions synaptiques de la voie afférente antennaire au cours du développement nymphal de l'ouvrière d'abeille Apis mellifica ligustica. C R Acad Sc Paris III:131–136
Arnold G, Masson C, Budharugsa S (1983) Organisation spatiale du système nerveux antennaire de l'abeille étudiée au moyen d'une technique de marquage aux ions cobalt. Apidologie 14 (2): 127–135
Arnold G, Masson C, Budharugsa S (1984) Demonstration of a sexual dimorphism in the olfactory pathways of the drones (Apis mellifica L, Hymenoptera, Apidae). Experientia 40:723–725
Boeckh J, Sandri C, Akert K (1970) Sensorische Eingänge und synaptische Verbindungen im zentralen Nervensystem von Insekten. Z Zellforsch 103:429–446
Boeckh J, Ernst KD, Sass H, Waldow U (1976) Zur nervösen Organisation antennaler Sinneseingänge bei Insekten. Berücksichtigung der Riechbahn. Verh dt Zool Ges: 123–139
Boeckh J, Boeckh V, Kühn A (1977) Further data on the topography and physiology of central olfactory neurons in insects. In: Le Magnen J, MacLeod P, (eds) Olfaction and taste VI IRL London Washington DC pp 315–321
Chambille I, Rospars JP (1981) Deutocerebron de la blatte Blaberus craniifer Burm (Dictyoptera: Blaberidae): Etude qualitative et identification morphologique des glomérules. Int J Insect Morphol Embryol 10 (2): 141–165
Chambille I, Rospars JP, Masson C (1978) The organization of the sensory deutocerebral glomeruli of the cockroach Blaberus craniifer. Congr ECRO III, Pavia: 67
Chambille I, Rospars JP, Masson C (1980) The deutocerebrum of the cockroach Blaberus craniifer. Spatial organization of the sensory glomeruli. J Neurobiol 11 (2): 135–157
Delabie J (1984) Etude morpho-fonctionnelle de la perception olfactive chez la fourmi champignonniste Acromyrmex octospinosus. Aspects du polymorphisme et du développement. Thèse de 3ème cycle. Univ P et M Curie, Paris 6
Ernst KD, Boeckh J (1983) A neuroanatomical study on the organization of the central antennal pathways in insects. III. Neuroanatomical characterization of physiologically defined response types of deutocerebral neurons in Periplaneta americana. Cell Tissue Res 229:1–22
Ernst KD, Boeckh J, Boeckh V (1977) A neuroanatomical study on the organization of the central antennal pathways in insects. II. Deutocerebral connections in Locusta migratoria and Periplaneta americana. Cell Tissue Res 176:295–308
Esslen J, Kaissling KE (1976) Zahl und Verteilung antennaler Sensillen bei der Honigbiene (Apis melifera L) Zoomorphologie 83:227–251
Etievant P, Azar M, Pham-Delegue MH, Masson C (1984) Isolation and Identification of volatile constituents of sunflower (He- lianthus annuus L.). J Agric Food Chem 32:503–509
Fonta C (1984) La communication chimique chez les bourdons Bombus sp: une approche neurobiologique pluridisciplinaire. Thèse 3ème cycle Entomologie, Univ P et M Curie, Paris 6
Frisch K von (1967) The dance language and orientation of bees. Harvard University Press, Cambridge, Mass
Hildebrand JG, Matsumoto SG, Camazine SM, Tolbert LP, Blank S, Ferguson H, Ecker V (1980) Organization and physiology of antennal centers in the brain of the moth Manduca sexta. In: Insect neurobiology and pesticide action, Society for Chemical Industry (ed), London, pp 375–382
Homberg U (1984) Processing of antennal information in extrinsic mushroom body neurons of the bee brain. J Comp Physiol A 154:825–836
Jawlowski H (1948) Studies on the insects brain. Annls Universitatis Mariae Curie-Sklodowska (C) 3:1–37
Jawlowski H (1957) Nerve tracts in bee (Apis mellifica) running from the sight and antennal organs to the brain. Annls Universitatis Mariae Curie-Sklodowska Vol 12 (22): 307–322
Masson C (1972) Le système antennaire chez les fourmis. Histologie et ultrastructure du deutocérébron. Etude comparée chez Camponotus vagus (Formicinae) et Mesoponera cqffraria (Ponerinac). Z Zellforsch 134:31–64
Masson C (1973) Contribution à l'étude du système antennaire chez les fourmis. Approche morphologique, ultrastructurale et électrophysiologique du système sensoriel. Thèse doctorat d'Etat. Université de Provence
Masson C (1977) Central olfactory pathways and plasticity of responses to odorous stimuli. In: Le Magnen J, Mac Leod P (eds) Olfaction and taste VI IRL London Washington DC pp 305–314
Masson C (1980) Mécanismes de détection et d'identification des phéromones par le système nerveux de l'insecte. In: Les phéromones sexuelles et les médiateurs chimiques chez les insectes. INRA(ed) Paris pp 11–17
Masson C (1982) Basic mechanisms of sensory antennal information processing in insects, with special reference to social insects. In: Breed MD, Michener CD, Evans HE (eds) The biology of social insects, Westview Press, pp 380–384
Masson C (1984) Neural basis of olfaction in insects. In: Bolis L, Keynes RD, Maddrell SHP (eds) Comparative physiology of sensory system, Cambridge University Press, London, pp 245–255
Masson C, Arnold G (1984) Ontogeny, maturation and plasticity of the olfactory system in the worker bee. J Insect Physiol 30 (1): 7–14
Masson C, Brossut R (1981) La communication chimique chez les insectes. La Recherche 12 (121): 406–416
Masson C, Strambi C (1977) Sensory antennal organization in an ant and a wasp. J Neurobiol 8 (6): 537–548
Matsumoto SG, Hildebrand JG (1981) Olfactory mechanisms in the moth Manduca sexta: response characteristics and morphology of the central neurons in the antennal lobes. Proc R Soc Lond B 213:249–277
Mobbs PG (1982) The brain of the honey bee Apis mellifera. I. The connections and spatial organization of the mushroom bodies. Philos Trans R Soc Lond Biol 298:309–354
Pareto A (1972) Die zentrale Verteilung der Fühlerefferenz bei Arbeiterinnen der Honigbiene, Apis mellifera. Z Zellforsch 131:109–140
Pham-Delegue MH (1983) Etude par conditionnement associatif des paramètres olfactifs qui déterminent le comportement alimentaire sélectif chez l'abeille (Apis mellifica L). Thèse 3ème cycle Neurosciences. Univ P et M Curie, Paris 6
Pham-Delegue MH, Masson C (1984) Analyse par conditionnement associatif du mécanisme de la reconnaissance de sources alimentaires par l'abeille. C R Soc Entomol France (in press)
Pham-Delegue MH, Masson C, Etievant P (1984) Selective olfactory choices among food scents by honeybee: a study by coupled associative conditioning and chemical analyses (Submitted for publication)
Prigent JP (1966) La structure du deutocérébron de l'adulte de Periplaneta americana L. Bull Soc Zool Fr 91:365–374
Prillinger L (1981) Postembryonic development of antennal lobes in Periplaneta americana. Cell Tissue Res 215:563–575
Rospars JP (1983) Invariance and sex specific variations of the glomerular organization in the antennal lobes of a moth Mamestra brassicae, and a butterfly, Pieris brassicae. J Comp Neurol 220:80–96
Sanes JR, Hildebrand JG (1976) Acetylcholine and its metabolic enzymes in developing antennae of the moth, Manduca sexta. Dev Biol 52:105–120
Schürmann FW, Wechsler W (1970) Synapsen im Antennenhügel von Locusta migratoria (Orthoptera, Insecta). Z Zellforsch 108:563–581
Schweitzer ES, Sanes JR, Hildebrand JG (1976) Ontogeny of electroantennogram responses in the moth, Manduca sexta. J Insect Physiol 22:995–960
Stocker RF, Singh RN, Schorderet M, Siddiqi O (1983) Projection patterns of different types of antennal sensilla in the antennal glomeruli of Drosophila melanogaster. Cell Tissue Res 237–248
Suzuki H (1975) Antennal movements induced by odour and central projection of the antennal neurones in the honey-bee. J Insect Physiol 21:831–847
Tolbert LP, Hildebrand JG (1981) Organization and synaptic ultrastructure of glomeruli in the antennal lobes of the moth Manduca sexta: a study using thin section and freeze-fracture. Proc R Soc Lond Biol 213:279–301
Tyrer NM, Altman JS (1974) Motor and sensory flight neurons in a locust demonstrated using cobalt chloride. J Comp Neurol 157:117–138
Tyrer NM, Bell EM (1974) The intensification of cobalt filled neurone profiles using a modification of Timm's sulphide-silver method. Brain Res 73:151–155
Waldow U (1975) Multimodale Neurone im Deutocerebrum von Periplaneta americana. J Comp Physiol 101:329–341
Waldow U (1977) CNS units in cockroach (Periplaneta americana): specificity of response to pheromones and other odor stimuli. J Comp Physiol 116:1–17
Waller GD, Loper GM, Berdel RL (1973) A bioassay for determining honeybee responses to flower volatiles. Environ Entomol 2 (2): 225–259
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Unité de Recherche Associée au CNRS, UA 483
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arnold, G., Masson, C. & Budharugsa, S. Comparative study of the antennal lobes and their afferent pathway in the worker bee and the drone (Apis mellifera). Cell Tissue Res. 242, 593–605 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00225425
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00225425