Summary
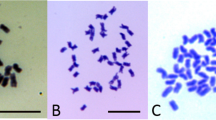
A colchicine-doubled F1 hybrid (2n=118) of a cross between PI 360841 (Glycine max) (2n=40) x PI 378708 (G. tomentella) (2n=78), propagated by shoot cuttings since January 1984, produced approximately 100 F2 seed during October 1988. One-fourth of the F2 plants or their F3 progeny have been analyzed for chromosome number, pollen viability, pubescence tip morphology, seed coat color, and isoenzyme variation. Without exception, all plants evaluated possessed the chromosome number of the G. max parent (2n=40). Most F2 plants demonstrated a high level of fertility, although 2 of 24 plants had low pollen viability and had large numbers of fleshy pods. One F2 plant possessed sharp pubescence tip morphology, whereas all others were blunt-tipped. All evaluated F2 and F3 plants expressed the malate dehydrogenase and diaphorase isoenzyme patterns of the G. max parent and the endopeptidase isoenzyme pattern of the G. tomentella parent. Mobility variants were observed among progeny for the isoenzymes phosphoglucomutase, aconitase, and phosphoglucoisomerase. This study suggests that the G. Tomentella chromosome complement has been eliminated after genetic exchange and/or modification has taken place between the genomes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barclay I (1975) High frequencies of haploid production in wheat (Triticum aestivum) by chromosome elimination. Nature 256:410–411
Broue P, Douglass J, Grace T, Marshall D (1982) Interspecific hybridization of soybeans and perennial Glycine species indigenous to Australia via embryo culture. Euphytica 31:715–724
Burdon J (1988) Major gene resistance to Phakopsora pachyrhizi in Glycine canescens, a wild relative of soybean. Theor Appl Genet 75:923–928
Cardy B, Beversdorf W (1984) Identification of soybean cultivars using isoenzyme electrophoresis. Seed Sci Technol 12:943–954
Fedak G (1977) Haploids from barley x rye crosses. Can J Genet Cytol 19:15–19
Gupta S, Gupta P (1973) Selective somatic elimination of Nicotiana glutinosa chromosomes in the F1 hybrids of N. suaveolens and N. glutinosa. Genetics 73:605–612
Hart S, Glenn D, Kenworthy W (1988) Herbicide tolerance of wild Glycine species. In: Proc Northeast Weed Sci Soc, vol 42. Weed Science Society of America, Champaign/IL, p 54
Hood M, Allen F (1987) Crossing soybeans with a wild perennial relative. Tenn Farm Home Sci Prog Resp 144:26–30
Hymowitz T, Singh R (1984) A soybean x G. tomentella hybrid: progress and problems. Soybean Genet Newslett 11:90
Hymowitz T, Wooley J, Peters D (1987) Preliminary investigations on the salt tolerance of wild perennial Glycine species. Soybean Genet Newsl 14:271–272
Keim P, Shoemaker R (1988) Construction of a random recombinant DNA library that is primarily single copy sequence. Soybean Genet Newslett 15:147–148
Keim P, Shoemaker R, Palmer R (1989a) Restriction fragment length polymorphism diversity in soybean. Theor Appl Genet 77:786–792
Keim P, Diers B, Palmer R, Shoemaker R, Macalma T, Lark K (1989b) Mapping the soybean genome with RFLP markers. In: Pascale JA (ed) Proc 4th World Soybean Res Conf. Orientation Grafica Editora, Buenos Aires, Argentina, pp 1246–1251
Kenworthy W (1989) Potential genetic contributions of wild relatives to soybean improvement. In: Pacale JA (ed) Proc 4th World Soybean Res Conf. Orientation Grafica Editora, Buenos Aires, Argentina, pp 883–888
Kenworthy W, Brown A, Thibou G (1989) Variation in flowering response to photoperiod in perennial Glycine species. Crop Sci 29:678–682
Lim S, Hymowitz T (1987) Reactions of perennial wild species of genus Glycine to Septoria glycines. Plant Dis 71:891–893
Macfarlane-Smith W, Jones J (1985) Intergeneric crossses with Fragaria and Potentilla: crosses between Fragaria moschata and Potentilla fruticosa. Euphytica 34:725–735
Newell C, Hymowitz T (1982) Successful wide hybridization between the soybean and a wild perennial relative, G. tomentella Hayata. Crop Sci 22:1062–1065
Newell C, Delannay X, Edge M (1987) Interspecific hybrids between the soybean and wild perennial relatives. J Hered 78:301–306
Newell C, Hymowitz T (1983) Hybridization in the genus Glycine subgenus Glycine willd. (Leguminosae, Papilionoideae). Am J Bot 70:334–348
Orton T, Tai W (1977) Chromosome elimination in a complex hybrid of the genus Hordeum. Can J Bot 55:3023–3033
Palmer R, Heer H (1973) A root-tip squash technique for soybean chromosomes. Crop Sci 13:389–391
Palmer R, Newhouse K, Graybosch R, Delannay X (1987) Chromosome structure of the wild soybean. J Hered 78:243–247
Singh R, Hymowitz T (1985) An interspecific hybrid between Glycine tomentella Hayata and the soybean, G. max (L.) Merr. Euphytica 34:187–192
Subrahmanyam N (1982) Species dominance in chromosome elimination in barley hybrids. Curr Sci 51:28–31
Thomas H (1988) Chromosome elimination and chromosome pairing in tetraploid hybrids of Hordeum vulgare x H. bulbosum. Theor Appl Genet 76:118–124
Thomas H, Pickering R (1983) Chromosome elimination in Hordeum vulgare x H. bulbosum hybrids. Theor Appl Genet 66:135–140
Tindale M, Craven L (1988) Three new species of Glycine (Fabaceae: Phaseolae) from northwestern Australia, with notes on amphicarpy in the genus. Aust Syst Bot 1:399–410
Vaughan D, Hymowitz T (1983) Progress in wild perennial soybean characterization. Plant Genet Resour Newslett (IBPGR) 546:7–12
Wendel J, Parks C (1982) Genetic control of isozyme variation in Camellia japonica L. J Hered 73:197–204
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by A. L. Kahler
Journal Paper No. J-13776 of the Iowa Agriculture and Home Economics Experiment Station, Ames, IA, USA, Project 2763
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shoemaker, R.C., Heath, M.S., Skorupksa, H. et al. Fertile progeny of a hybridization between soybean [Glycine max (L.) Merr.] and G. tomentella Hayata. Theoret. Appl. Genetics 80, 17–23 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00224010
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00224010