Summary
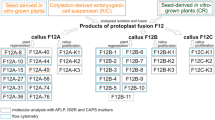
Several hybrid callus lines were produced through somatic hybridization between the diploid transformed Solanum tuberosum plant clone 413 (2n = 2x = 24) and a diploid wild-type plant clone of Nicotiana plumbaginifolia (2n = 2x = 20). The hybrid callus lines with subdiploid numbers of potato chromosomes were studied for karyotypic evolution as well as for segregation of the transformation marker characters (i.e. hormone autotrophy, opine synthesis, kanamycin resistance and β-glucuronidase activity). Initially, these hybrids (cultured in kanamycin-containing medium) expressed all of the transformation characters. Six callus lines were selected for the establishment of cell suspension cultures; two of these were also used to initiate sublines, one from single cells of a suspension culture, and the other from callus-derived protoplasts. The cell suspension cultures and the sublines were cultured in kanamycin-free medium. After prolonged culture, karyotypic analysis of the various cell suspension lines revealed independent evolution of both parental genomes. Out of the six suspension lines, four showed a considerably reduced number of potato chromosomes as compared to the original hybrid callus lines, whereas the karyotypes of the individual sublines generally reflected the karyotypic diversity of the original cultures. The fate of the marker characters in various suspension cultures and sublines revealed independent segregation of the markers of TL-DNA (hormone autotrophy) and vector T-DNA (kanamycin resistance and β-glucuronidase activity). Loss of the TR-DNA marker (opine synthesis) was observed only in combination with the simultaneous loss of the TL-DNA marker and the vector T-DNA markers. The results on segregation patterns of marker characters are discussed in the light of specific chromosome loss in the hybrid lines and gene linkage relationships.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bennett MD, Smith JB (1976) Nuclear DNA amounts in angiosperms. Philos Trans R Soc London Ser B 274:227–274
Bokelmann GS, Roest S (1983) Plant regeneration from protoplasts of potato (Solanum tuberosum cv ‘Bintje’). Z Pflanzenphysiol 109:259–265
Bradford M (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
De Vries-Uijtewaal E, Gilissen LJW, Flipse E, Sree Ramulu K, Stiekema WJ, De Groot B (1989) Fate of introduced genetic markers in transformed root clones and regenerated plants of monohaploid and diploid potato genotypes. Theor Appl Genet 78:185–193
Endo T, Komiya T, Mino M, Nakanischi K, Fujita S, Yamada Y (1988) Genetic diversity among sublines originating from single somatic hybrid cell of Duboisia hopwoodii+Nicotiana tabacum. Theor Appl Genet 76:641–646
Gilissen LJW, Hänisch ten Cate CH, Keen B (1983) A rapid method of determining growth characteristics of plant cell populations in batch suspension culture. Plant Cell Rep 2:232–235
Gilissen LJW, Sree Ramulu K, Flipse E, Meinen E, Stiekema WJ (1991) Transformation of diploid potato genotypes through Agrobacterium vectors and expression of T-DNA markers in root clones, regenerated plants and suspension cells. Acta Bot Neerl 40:53–61
Gilissen LJW, Van Staveren MJ, Verhoeven HA, Sree Ramulu K (1992) Somatic hybridization between potato and Nicotiana plumbaginifolia. 1. Spontaneous biparental chromosome elimination and production of asymmetric hybrids. Theor Appl Genet 84:73–80
Jefferson RA, Burgess SM, Hirsch D (1986) β-Glucuronidase from Escherichia coli as a gene fusion marker. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:8447–8451
Jefferson RA, Kavanagh TA, Bevan MW (1987) GUS fusions: β-glucuronidase as a sensitive and versatile gene fusion marker in higher plants. EMBO J 6:3901–3907
Kao FT (1983) Somatic cell genetics and gene mapping. Int Rev Cytol 85:109–146
Mouras A, Wildenstein C, Salesses G (1986) Analysis of karyotype and C-banding pattern of Nicotiana plumbaginifolia using two techniques. Genetica 68:197–202
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15:473–497
Negrutiu I, Hinnisdaels S, Mouras A, Gill BS, Gharti-Chhetri GB, Davey MR, Gleba YY, Sidorov V, Jacobs M (1989) Somatic versus sexual hybridization: features, facts and future. Acta Bot Neerl 38:253–272
Ottaviani MP, Hänisch ten Cate CH (1991) Cotransformation and differential expression of introduced genes into potato cv ‘Bintje’. Theor Appl Genet 81:761–768
Petit A, David C, Dahl GA, Ellis JG, Guyon P, Casse-Delbart F, Tempé J (1983) Further extension of the opine concept: plasmids in Agrobacterium rhizogenes cooperate for opine degradation. Mol Gen Genet 190:204–214
Pijnacker LP, Ferwerda MA (1984) Giemsa C-banding of potato chromosomes. Can J Genet Cytol 26:415–419
Pijnacker LP, Sree Ramulu K (1990). Somaclonal variation in potato: a karyotypic evaluation. Acta Bot Neerl 39:163–169
Sree Ramulu K, Dijkhuis P (1986) Flow cytometric analysis of polysomaty and in vitro genetic instability in potato. Plant Cell Rep 3:234–237
Sree Ramulu K, Dijkhuis P, Hänisch ten Cate CH, De Groot B (1985) Patterns of DNA and chromosome variation during in vitro growth in various genotypes of potato. Plant Sci 41:69–78
Super BS (1979) The ortho-cytofluorograph. In: Melamed MR, Mullaney PF, Mendelsohn ML (eds) Flow cytometry and sorting. John Wiley & Sons, New York, pp 639–652
Visser RGF, Hesseling-Meinders A, Jacobsen E, Nijdam H, Witholt B, Feenstra WJ (1989) Expression and inheritance of inserted markers in binary vector carrying Agrobacterium rhizogenes-transformed potato (Solanum tuberosum L.). Theor Appl Genet 78:705–714
Wijbrandi J, Zabel P, Koornneef M (1990) Restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis of somatic hybrids between Lycopersicon esculentum and irradiated L. peruvianum: evidence for limited donor genome elimination and extensive chromosome rearrangements. Mol Gen Genet 222:270–277
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by H. F. Linskens
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gilissen, L.J.W., van Staveren, M.J., Ennik, E. et al. Somatic hybridization between potato and Nicotiana plumbaginifolia . Theoret. Appl. Genetics 84, 81–86 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00223984
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00223984