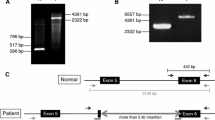
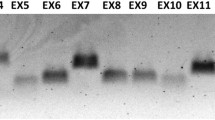
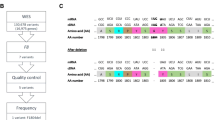
Abstract
Haemophilia A is a common X-linked recessive disorder of bleeding caused by deleterious mutations in the gene for clotting factor VIII. The large size of the factor VIII gene, the high frequency of de novo mutations and its tissue-specific expression complicate the detection of mutations. We have used a combination of reverse transcription/polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) of ectopic factor VIII transcripts and PCR of genomic DNA to amplify the entire essential sequence of the factor VIII gene. Chemical mismatch cleavage analysis and direct sequencing have then be empolyed in order to facilitate a comprehensive search for mutations. In this report, we describe the characterisation of nine potentially pathogenic mutations, six of which are novel. The mutations include six single base substitutions (five missense, viz. D56E, V162M, G701D, A1834T and R18691, and one nonsense, viz. R5X), a single base deletion (5697delC), a gross deletion of exon 16 and one mRNA abnormality characteristic of the common intron-22-embedded F8A-mediated DNA inversion. In each case, a correlation of the genotype with the observed phenotype is presented. In order to evaluate the pathogenicity of the five missense mutations, we have analysed them for evolutionary sequence conservation and for their involvement with sequence motifs catalogued in the PROSITE database of protein sites and patterns. Analysis of the sequences in the immediate vicinity of the mutations has revealed sequence features that may have had a possible role in mutagenesis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arai M, Scandella D, Hoyer LW (1989) Molecular basis of factor VIII inhibition by human antibodies: antibodies that bind to the factor VIII light chain prevent the interaction of factor VIII with phospholipid. J Clin Invest 83:1978–1983
Bairoch A (1993) The PROSITE dictionary of sites and patterns in proteins, its current status. Nucleic Acids Res 21:3097–3103
Bidichandani SI, Lanyon WG, Connor JM (1994) Characterisation of a 5 base pair deletion in exon 4 of the factor VIII gene: concordance with slipped-mispairing at DNA replication. Hum Genet 94:447–449
Chelly J, Concordet JP, Kaplan JC, Kahn A (1989) Illegitimate transcription: transcription of any gene in any cell type. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:2617–2621
Cooper DN, Krawczak M (1993) Human gene mutation. Bios Scientific, Oxford
Cotton RGH, Rodrigues NR, Campbell RD (1988) Reactivity of cytosine and thymine in single-base-pair mismatches with hydroxylamine and osmium tetroxide and its application to the study of mutations. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:4397–4401
Devereux J, Haeberli P, Smithies O (1984) A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res 12:387–395
Diamond C, Kogan S, Levinson B, Gitschier J (1992) Amino acid substitutions in conserved domains of factor VIII and related proteins: study of patients with mild and moderately severe hemophilia A. Hum Mutat 1:248–257
Elder B, Lakich D, Gitschier J (1993) Sequence of the murine factor VIII cDNA. Genomics 16:374–379
Foster PA, Fulcher CA, Houghten RA, Zimmerman TS (1990) Synthetic factor VIII peptides with amino acid sequences contained within the C2 domain of factor VIII inhibit factor VIII binding to phosphotidylserine. Blood 75:1999–2004
Gyllensten UB, Erlich HA (1988) Generation of single-stranded DNA by the polymerase chain reaction and its application to direct sequencing of the HLA-DQA locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:7652–7656
Higuchi M, Antonarakis SE, Kasch L, Oldenburg J, Economou EP, Olek K, Arai M, Inaba H, Kazazian HH (1991a) Molecular characterization of mild-to-moderate hemophilia A: detection of the mutation in 25 of 29 patients by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:8307–8311
Higuchi M, Kazazian HH, Kasch L, Warren TC, McGinniss MJ, Phillips JA, Kasper C, Janco R, Antonarakis SE (1991b) Molecular characterization of severe hemophilia A suggests that about half the mutations are not within the coding regions and splice junctions of the factor VIII gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:7405–7409
Kane WH, Davie EW (1988) Blood coagulation factor V and VIII: structural and functional similarities and their relationship to haemorrhagic and thrombotic disorders. Blood 71:539–555
Kochinsky ML, Funk WD, Oost VA van, MacGillivray RTA (1986) Complex cDNA sequence of human preceruloplasmin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:5086–5090
Krawczak M, Cooper DN (1991) Gene deletions causing human disease: mechanisms of mutagenesis and the role of the local DNA sequence environment. Hum Genet 86:425--441
Lakich D, Kazazian HH, Antonarakis SE, Gitschier J (1993) Inversions disrupting the factor VIII gene are a common cause of severe haemophilia A. Nature Genet 5:236–241
Lin SW, Lin SR, Shen MC (1993) Characterization of genetic defects of hemophilia A in patients of Chinese origin. Genomics 18:496–504
Messerschmidt A, Huber R (1990) The blue oxidases, ascorbate oxidase, laccase and ceruloplasmin. Modelling and structural relationships. Eur J Biochem 187:341–352
Mgone CS, Lanyon WG, Moore MR, Connor JM (1992) Detection of seven point mutations in the porphobilinogen deaminase gene in patients with acute intermittent porphyria by direct sequencing of in vitro amplified cDNA. Hum Genet 90:12–16
Naylor JA, Green PM, Rizza CR, Giannelli F (1993a) Analysis of factor VIII mRNA reveals defects in everyone of 28 haemophilia A patients. Hum Mol Genet 2:11–17
Naylor J, Brinke A, Hasscock S, Green PM, Giannelli F (1993b) Characteristic mRNA abnormality found in half the patients with severe haemophilia A is due to large DNA inversions. Hum Mol Genet 2:1773–1778
Ouzounis C, Sander C (1991) A structure-derived sequence pattern for the detection of type I copper binding domains in distantly related proteins. FEBS Lett 279:73–78
Pinna LA (1990) Casein kinase 2: an “eminence grise” in cellular regulation? Biochim et Biophys Acta 1054:267–284
Pittman DD, Kaufman RJ (1989) Structure-function relationships of factor VIII elucidated through recombinant DNA technology. Thromb Haemost 61:161–165
Rossiter JP, Young M, Kimberland ML, Hutter P, Ketterling RP, Gitschier J, Horst J, Morris MA, Schaid DJ, Moerloose P de, Sommer SS, Kazazian HH, Antonarakis SE (1994) Factor VIII gene inversions causing severe haemophilia A originate almost exclusively in male germ cells. Hum Mol Genet 3:1035–1039
Sanger F, Nicklen S, Coulson AR (1977) DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 74:5463–5467
Smith HO, Annau TM, Chandrasegaran S (1990) Finding sequence motifs in groups of related proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:826–830
Tuddenham EGD, Schwabb R, Seehafer J, Millar DS, Gitschier J, Higuchi M, Bidichandani S, Connor JM, Hoyer LW, Yoshioka A, Peake IR, Olek K, Kazazian HH, Lavergne JM, Giannelli F, Antonarakis SE, Cooper DN (1994) Haemophilia A: database of nucleotide substitutions, deletions, insertions, and rearrangements of the factor VIII gene, second edition. Nucleic Acids Res 22:3511–3533
Vehar GA, Keyt B, Eaton D, Rodriguez H, O'Brien D, Roblat F, Oppermann H, Keck R, Wood WI, Harkins RN, Tuddenham EGD, Lawn RM, Capon DJ (1984) Structure of human factor VIII. Nature 312:337–342
Wood WI, Capon DJ, Simonsen CC, Eaton DL, Gitschier J, Keyt B, Seeburg PH, Smith DH, Hollingshead P, Wion KL, Delwart E, Tuddenham EGD, Vehar GA, Lawn RM (1984) Expression of active factor VIII from recombinant DNA clones. Nature 312:330–337
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bidichandani, S.I., Lanyon, W.G., Shiach, C. et al. Detection of mutations in ectopic factor VIII transcripts from nine haemophilia A patients and the correlation with phenotype. Hum Genet 95, 531–538 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00223865
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00223865