Abstract
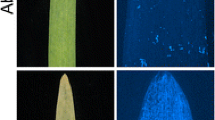
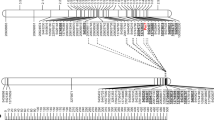
Isolate WELA of the plant pathogenic oomycete fungus Peronospora parasitica causes downy mildew in the Arabidopsis thaliana ecotypes Weiningen (Wei-0) and La-er, whereas ecotypes RLD and Col-0 are resistant. Genetic crosses between resistant RLD and susceptible Wei-0 showed that resistance was inherited in a simple Mendelian fashion as a monogenic dominant trait. The interactions between different isolates of P. parasitica and ecotypes of A. thaliana show race-specific variation and fit a gene-for-gene relationship. The RPP11 resistance gene was mapped by following the co-segregation of the resistance phenotype with RFLP markers in a mapping population of 254 F3 families derived from RLD x Wei-0 F2 individuals. Linkage analysis using version 1.9 of the MAPMAKER program placed the RPP11 resistance locus on chromosome III between marker m249 (two recombinants) and marker g2534 (six recombinants). Markers g2534 and g4117 are on YAC EG7H1. Marker g4117 and one end probe (N5) generated from YAC EG7H1 showed no recombinants. The YAC end probe N5, which was generated by plasmid rescue, was used to screen clones in the Eric Ward YAC library and a YAC was fished (EW19B12) which also hybridised with m249. Thus, a YAC contig has been established over the region where the resistance locus maps. Because the YACs were made with ecotype Columbia DNA it is necessary to isolate the equivalent region from RLD in order to clone the resistance locus. To this end a phage λ-DASH™ genomic library was prepared from RLD and a contig covering the relevant region of the YACs is currently under construction.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ausubel FM, Glazebrook J, Greenberg J, Mindrinos M, Yu GL (1993) Analysis of the Arabidopsis defence response to Pseudomonas pathogens. Adv Mol Genet Plant-Microbe Interact 2:393–403
Bent AF, Kunkel BN, Dahlbeck D, Brown KL, Schmidt R, Giraudat J, Leung J, Staskawicz BJ (1994) RPS2 of Arabidopsis thaliana: a leucine-rich repeat class of plant disease resistance genes. Science 265:1856–1860
Chang C, bowman JL, De John AW, Lander ES, Meyerowitz EM (1988) Restriction fragment length polymorphism linkage map for Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:6856–6860
Crute IR, Norwood JM (1986) Gene-dosage effects on the relationship between Bremia lactucae (downy mildew) and Lactuca sativa (lettuce); the relevance to a mechanistic understanding of host-parasite specificity. Physiol Plant Pathol 29:133–145
Crute IR, Holub, EB, Tör M, Brose E, Beynon JL (1993) The identification and mapping of loci in Arabidopsis thaliana for recognition of the fungal pathogens: Peronospora parasitica (downy mildew) and Albugo Candida (white blister). Adv Mol Genet Plant-Microbe Interact 2:437–444
Crute I, Beynon J, Dangl J, Holub E, Mauch-Mani B, Slusarenko AJ, Staskawicz B, Ausubel F (1994) Microbial pathogenesis of Arabidopsis. In: Meyerowitz EM, Somerville CR (eds) Arabidopsis. Cold Spring Harbour Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, NewYork, pp 705–747
Dangl JL (1993) Applications of Arabidopsis thaliana to outstanding issues in plant-pathogen interactions. Int Rev Cytol 144:53–83
Davis KR, Schott E, Ausubel FM (1991) Virulence of selected phytopathogenic pseudomonads in Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 4:477–488
Debener T, Lehnackers H, Arnold M, Dangl JL (1991) Identification and molecular mapping of a single Arabidopsis thaliana locus determining resistance to a phytopathogenic Pseudomonas syringae isolate. The Plant Jour 1:289–302
Dolferus R (1991) In: Negrutiu I, Gharti-Chhetri G, (eds) Biomethods: a laboratory guide for cellular and molecular plant biology Birkhäuser Verlag, Basel, pp 133–146
Gäumann E (1918) Über die Formen der Peronospora parasitica (Pers.). Fries Beitr Bot Zentralbl 35:395–533
Gibson SI, Somerville C (1992) Chromosome walking in Arabidopsis thaliana using yeast artifical chromosomes. In: Koncz C, Chua N-H, Schell J (eds) Methods in Arabidopsis research. World Scientific Publishing Co, Singapore, pp 119–143
Grill E, Sommerville C (1991). Construction and characterization of a yeast artificial chromosome library of Arabidopsis which is suitable for chromosome walking. Mol Gen Genet 226:484–490
Guzman P, Ecker J (1988) Development of large DNA methods in plants: molecular cloning of large segments of Arabidopsis and carrot DNA into yeast. Nucleic Acids Res 16:11091–11105
Hauge BM, Hanley SM, Cartinhour S, Cherry JM and Goodman HM, Koornneef M, Stam P, Chang C, Kempin S, Medrano L, Meyerowitz EM (1993) An Integrated genetic/RFLP map of the Arabidopsis thaliana genome. The Plant Jour 3:745–754
Holub EB, Crute I, Brose E, Beynon J (1993) Identification and mapping of loci in Arabidopsis for resistance to downy mildew and white blister. In: Davis KR, Hammerschmidt R (eds) Arabidopsis thaliana as a model for plant-pathogen interactions. APS Press, Minnesota, pp 21–35
Holub EB, Beynon JL, Crute IR (1994) Phenotypic and genotypic characterization of interactions between isolates of Peronospora parasitica and accessions of Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 7:223–239
Hwang I, Kohchi T, Hauge BM, Goodman HM, Schmidt R, Chops G, Dean C, Gibson S, Jba K, Lemieux B, Arondel V, Danhoff L, Somerville C (1991) Identification and map position of YAC clones comprising one-third of the Arabidopsis genome. Plant J 1:367–374
Jarvis P, Lister C, Szabo V, Dean C (1994) Integration of CAPS markers into the RFLP map generated using recombinant inbreds of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Mol Biol 24:685–687
Keogh RC, Deverall BJ, McLeod S (1980) Comparison of histological and physiological responses to Phakopsora pachyrhizi in resistant and susceptible soybean. Trans Br Mycol Soc 74:329–333
Koch E, Slusarenko A (1990) Arabidopdis is susceptible to infection by a downy mildew. Plant Cell 1:437–445
Lander ES, Green P (1987) Construction of multilocus genetic linkage maps in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:2363–2367
Lander ES, Green P, Abrahamson J, Barlow A, Daly M, Lincoln S, Newberg L (1987) Mapmaker: an interactive computer package for constructing primary genetic linkage maps of experimental and natural populations. Genomics 1:174–181
Lindau G (1901) Hilfsbuch für das Sammeln parasitischer Pilze. Börnträger Verlag, Berlin
Lister C, Dean C (1993) Recombinant inbred lines for mapping RFLP and phenotypic markers in Arabidopsis thaliana. The Plant Jour 4:745–750
Mauch-Mani B, Slusarenko AJ (1993) Arabidopsis as a model host for studying host-pathogen interactions. Trends Microbiol 1:265–270
Mauch-Mani B, Slusarenko AJ (1994) Systemic acquired resistance in Arabidopsis thaliana induced by a predisposing infection with a pathogenic isolate of Fusarium oxysporum. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 7:378–383
Mauch-Mani B, Croft KPC, Slusarenko AJ (1993) The genetic basis of resistance of Arabidopsis thaliana L. Heyhn. to Peronospora parasitica. In: Davis KR, Hammerschmidt R (eds) Arabidopsis thaliana as a model for plant-pathogen interactions. APS Press, Minnesota, pp 5–20
Mindrinos M, Katagiri F, Yu GL, Ausubel FM (1994) The Arabidopsis thaliana disease resistance gene RPS2 encodes a protein containing a nucleotide-binding site and leucine-rich repeats. Cell 78:1089–1099
Nam HG, Giraudat J, den Boer B, Moonan F, Loos DB, Hauge BM, Goodman HM (1989) Restriction fragment length polymorphism linkage map of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell 1:699–705
Parker JE, Szabo V, Staskawicz BJ, Lister C, Dean C, Daniels MJ, Jones JDG (1993) Phenotypic characterization and molecular mapping of the Arabidopsis thaliana locus RPP5, determining disease resistance to Peronospora parasitica. Plant Jour 4:821–831
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a Laboratory manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbour Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, New York
Schmidt R, Dean C (1993) Towards construction of an overlapping YAC library of the Arabibopsis thaliana genome. Genes and Genomes 15:63–69
Staskawicz BJ, Ausubel FM, Baker BJ, Ellis JG, Jones JDG (1995) Molecular Genetics of plant disease resistance. Science 268:661–667
Tör M, Holub EB, Brose E, Musker R, Gunn N, Can C, Crute IR, Beynon JL (1994) Map positions of four loci in Arabidopsis thaliana associated with isolate-specific recognition of Peronospora parasitica (downy mildew). Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 7:214–222
Ward ER, Jen GC (1990) Isolation of single-copy-sequence clones from a yeast artificial chromosome library of randomly sheared Arabidopsis thaliana DNA. Plant Mol Biol 14:561–568
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by M. Koornneef
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Joos, HJ., Mauch-Mani, B. & Slusarenko, A.J. Molecular mapping of the Arabidopsis locus RPP11 which conditions isolate-specific hypersensitive resistance against downy mildew in ecotype RLD. Theoret. Appl. Genetics 92, 281–284 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00223387
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00223387