Abstract
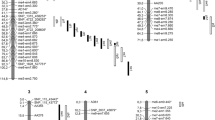
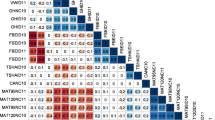
Quantitative trait loci (QTLs) affecting seed weight in pea (Pisum sativum L.) were mapped using two populations, a field-grown F2 progeny of a cross between two cultivated types (‘Primo’ and ‘OSU442-15’) and glasshouse-grown single-seed-descent recombinant inbred lines (RILs) from a wide cross between a P. sativum ssp. sativum line (‘Slow’) and a P. sativum ssp. humile accession (‘JI1794’). Linkage maps for these crosses consisted of 199 and 235 markers, respectively. QTLs for seed weight in the ‘Primo’ x ‘OSU442-15’ cross were identified by interval mapping, bulked segregant analysis, and selective genotyping. Four QTLs were identified in this cross, demonstrating linkage to four intervals on three linkage groups. QTLs for seed weight in the ‘JI1794’ x ‘Slow’ cross were identified by single-marker analyses. Linkage were demonstrated to four intervals on three linkage groups plus three unlinked loci. In the two crosses, only one common genomic region was identified as containing seed-weight QTLs. Seed-weight QTLs mapped to the same region of linkage group III in both crosses. Conserved linkage relationships were demonstrated for pea, mungbean (Vigna radiata L.), and cowpea (V. unguiculata L.) genomic regions containing seed-weight QTLs by mapping RFLP loci from the Vigna maps in the ‘Primo’ x ‘OSU442-15’ and ‘JI1794’ x ‘Slow’ crosses.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbo S, Ladzinsky G, Weeden NF (1992) Genetic analysis and linkage study of seed weight in lentil. Euphytica 58:259–266
Baggett JR, Hampton RO (1977) Oregon B442–15 and B445–66 pea seedborne mosaic virus-resistant breeding lines. Hort Science 12:506
Churchill GA, Doerge RW (1994) Empirical threshold values for quantitative trait mapping. Genetics 138:963–971
Davies DR (1975) Studies of seed development in Pisum sativum. Planta 124:297–302
deVicente MC, Tanksley SD (1993) QTL analysis of transgressive segregation in an interspecific tomato cross. Genetics 134:585–596
Ellis THN, Turner L, Hellens RP, Lee D, Harker CL, Enard C, Domoney C, Davies DR (1992) Linkage maps in pea. Genetics 130:649–663
Fatokun CA, Menancio-Hautea DI, Danesh D, Young ND (1992) Evidence for orthologous seed-weight genes in cowpea and mungbean based on RFLP mapping. Genetics 132:841–846
Gupta KR, Waldia RS, Dahiya BS, Singh KP, Sood DR (1984) Inheritance of seed yield and quality traits in peas (Pisum sativum L.) Theor Appl Genet 69:133–137
Imrie BC, Ahmed ZU, Eerens JPJ (1985) Heritability of seed weight in mungbean. Sabrao J 17:173–175
Johannsen W (1903) Heredity in populations and pure lines. Translated (1959) In: Peters JA (ed) Classic papers in genetics. Prentice-Hall, Englewood, New Jersey, pp 20–26
Lander ES, Green P, Abrahamson J, Barlow A, Daly MJ (1987) MAPMAKER: an interactive computer package for constructing primary genetic linkage maps of experimental and natural populations. Genomics 1:174–181
Leleji OI (1975) Inheritance of three agronomic characters in cowpea (Vigna unguiculata L.) Euphytica 24:371–378
Lincoln S, Daly M, Lander E (1992) Constructing genetic maps with MAPMAKER/EXP 3.0. Whitehead Institute Technical Report 3rd edn. Whitehead Institute, Cambridge, Massachusetts
Lincoln SE, Daly MJ, Lander ES (1993) Mapping genes controlling quantitative traits using MAPMAKER/QTL version 1.1: a tutorial and reference manual. Whitehead Institute for Biomedical Research Technical Report 2nd edn. Whitehead Institute, Cambridge, Massachusetts
Mansur LM, Lark KG, Kross H, Oliviera A (1993) Interval mapping of quantitative trait loci for reproductive, morphological and seed traits of soybean (Glycine max L.). Theor Appl Genet 86:907–913
McCouch SR, Kochert G, Yu ZH, Wang ZY, Khush GS, Coffman WR, Tanksley SD (1988) Molecular mapping of rice chromosomes. Theor Appl Genet 76:815–829
Menancio-Hautea DI, Fatokun CA, Kumar L, Danesh D, Young ND (1993) Comparative genome analysis of mungbean (Vigna radiata L. Wilczek) and cowpea (V. unguiculata L. Walpers) using RFLP mapping data. Theor Appl Genet 86:797–810
Michelmore RW, Paran I, Kesseli RV (1991) Identification of markers linked to disease resistance genes by bulked segregant analysis: a rapid method to detect markers in specific genomic regions by using bulked segregant populations. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:9828–9832
Niknejad M, Khosh-Khui M, Ghorashy SR (1971) Inheritance of seed size in chickpea (Cicer arietinum). Crop Sci 11:768–769
Paterson AH, Damon S, Hewitt JD, Zamir D, Rabinowitch HD, Lincoln SE, Lander ES, Tanksley SD (1991) Mendelian factors underlying quantitative traits in tomato: comparison across species, generations, and environments. Genetics 127:181–197
Pickering RA, Hill AM, Michel M, Timmerman-Vaughan GM (1995) The transfer of a powdery mildew resistance gene from Hordeum bulbosum L. to barley (H. vulgare L.) chromosome 2(2L). Theor Appl Genet 91:1288–1292
Sax K (1923) The association of size differences with seed coat pattern and pigmentation in Phaseolus vulgaris. Genetics 8:552–560
Simon CJ, Tahir M, Muehlbauer FJ (1993) Linkage map of lentil (Lens culinaris) 2N=14. In:O'Brien SJ (ed) Genetic maps, 6th edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, New York
Tahir M, Muehlbauer FJ, Spaeth SC (1994) Association of isozyme markers with quantitative trait loci in random single seed descent derived lines of lentil (Lens culinaris Medik.) Euphytica 75:111–119
Tanksley SG (1993) Mapping polygenes. Annu Rev Genet 27:205–233
Timmerman GM, Frew TJ, Miller AL, Weeden NF, Jermyn WA (1993) Linkage mapping of sbm-1, a gene conferring resistance to pea seed-borne mosaic virus, using molecular markers in Pisum sativum. Theor Appl Genet 85:609–615
Timmerman GM, Frew TJ, Weeden NF, Miller AL, Goulden DS (1994) Linkage analysis of er-1, a recessive Pisum sativum gene for resistance to powdery mildew fungus (Erysiphe pisi D.C.) Theor Appl Genet 88:1050–1055
Weeden NF, Muehlbauer FJ, Ladizinsky G (1992) Extensive conservation of linkage relationships between pea and lentil genetic maps. J. Hered 83:123–129
Weeden NF, Swiecicki WK, Ambrose M, Timmerman GM (1993a) Linkage groups of pea. Pisum Genetics 25: cover and p4
Weeden NF, Swiecicki WK, Timmerman G, Ambrose M (1993b) Guidelines for future mapping studies in Pisum. Pisum Genet 25:2–3
Wellensiek SJ (1925) Genetic monograph on Pisum. Biblio Genet 2:343–476
Zabeau M (1992) Selective restriction fragment amplifications general method for DNA fingerprinting. European Patent Application no. 92402629.7
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by J. Beckmann
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Timmerman-Vaughan, G.M., McCallum, J.A., Frew, T.J. et al. Linkage mapping of quantitative trait loci controlling seed weight in pea (Pisum sativum L.). Theoret. Appl. Genetics 93, 431–439 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00223187
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00223187