Summary
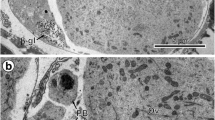
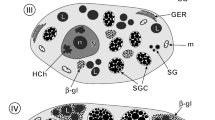
The ultrastructure and interrelationships of the Golgi body, endoplasmic reticulum and lipid droplets have been studied in the first cleavage Xenopus embryos. Lipid droplets, usually spherical or sometimes multilobed, did not have a discernible limiting membrane, although some had an incomplete electron dense partition. The Golgi bodies and endoplasmic reticulum were seen continuous with lipid droplets and the profiles indicated a probable formation of these membranes from lipid droplet material. Rough endoplasmic reticulum (ER) mainly consisted of paired tubular cisternae and vesicles containing filamentous material that gave a fringed appearance. The relationships of paired cisternae with the Golgi body suggested a transformation of ER membranes into the Golgi body membranes. In addition, paired ER cisternae showed a close apposition with the limiting membrane of the yolk platelet. Lone ER cisternae that contained moderately electron dense material instead of filaments were also present and showed numerous associated vesicles near the Golgi body. The Golgi body showed several morphological forms including a single fenestrated cisterna, two to four flat or cup-shaped cisternae, or up to seven cisternae, some of which were dilated and similar to fringed ER in appearance. These forms could be different developmental stages of the organelle. Coated vesicles were seen continuous with the cisternae of the Golgi body. A probable route for the assembly of the cell surface material has been proposed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armstrong, P. B.: Unusual yolk platelets in embryos of Xenopus laevis (amphibia). Z. Zellforsch. 129, 320–327 (1972)
Balinsky, B. I., Devis, R. J.: Origin and differentiation of cytoplasmic structures in the oocytes of Xenopus laevis. Acta Embryol. Morph. exp. 6, 55–108 (1963)
Beams, H. W.: In: Cellular membranes in development (M. Locke, ed.), p. 175-220. New York: Academic Press 1964
Beams, H. W., Kessel, R. G.: The Golgi apparatus. Structure and function. Int. Rev. Cytol. 23, 209–276 (1968)
Bennett, G., Leblond, C. P.: Passage of fucose-3H label from the Golgi apparatus into dense and multivesicular bodies in the duodenal columnar cells and hepatocytes of the rat. J. Cell Biol. 51, 875–881 (1971)
Bluemink, J. G.: Cytokinesis and cytochalasin-induced furrow regression in the first cleavage zygote of Xenopus laevis. Z. Zellforsch. 121, 102–126 (1971)
Bluemink, J. G., DeLaat, S. W.: New membrane formation during cytokinesis in normal and cytochalasin B-treated eggs of Xenopus laevis. J. Cell Biol. 59, 89–108 (1973)
Bouck, G. B.: Fine structure and organelle associations in brown algae. J. Cell Biol. 26, 523–537 (1965)
Brown, D. D.: Nucleic acid determination in embryos. In: Methods in developmental biology (F. H. Wilt and N. K. Wessels, eds.), p. 685–701. New York: T. Y.Crowell 1967
Dallner, G., Siekevitz, P., Palade, G. E.: Biogenesis of endoplasmic reticulum membranes. I. Structural and chemical differentiation in developing rat hepatocytes. J. Cell Biol. 30, 73–96 (1966)
Favard, P., Favard-Séréno, C.: Electron microscope study of polysaccharides in the amphibian oocytes. J. submicrosc. Cytol. 1, 91–111 (1969)
Flickinger, C. J.: The development of Golgi complexes and their dependence upon the nucleus in amoebae. J. Cell Biol. 43, 250–262 (1969)
Franke, W. W., Eckert, W. A., Krien, S.: Cytomembrane differentiation in a ciliate, Tetrahymena pyriformis. I. Endoplasmic reticulum and dictyosomal equivalents. Z. Zellforsch. 119, 577–604 (1971)
Friend, D. S.: The fine structure of Brunner's glands in the mouse. J. Cell Biol. 25, 563–576 (1965)
Holtfreter, J.: Experiments on the formed inclusions of the amphibian egg. I. The effect of pH and electrolytes on yolk and lipochondria. J. exp. Zool. 101, 355–405 (1946)
Kalt, M. R., Tandler, B.: A study of fixation of early amphibian embryos for electron microscopy. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 36, 633–645 (1971)
Karasaki, S.: Electron microscopic studies on cytoplasmic structures of ectoderm cells of the Triturus embryo during the early phase of differentiation. Embryologia 4, 247–272 (1959)
Karasaki, S.: Studies on amphibian yolk. 5. Electron microscopic observations on the utilization of yolk platelets during embryogenesis. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 9, 225–247 (1963a)
Karasaki, S.: Studies on amphibian yolk. I. The ultrastructure of the yolk platelet. J. Cell Biol. 18, 135–151 (1963b)
Kemp, N. E.: Electron microscopy of growing oocytes of Rana pipiens. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol. 2, 281–292 (1956)
Kessel, R. G.: Origin of the Golgi apparatus in embryonic cells of the grasshopper. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 34, 260–275 (1971)
Leonard, R., Deamer, D. W., Armstrong, P.: Amphibian yolk platelet ultrastructure visualized by freeze-etching. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 40, 1–24 (1972)
Longo, F. J.: An ultrastructural analysis of mitosis and cytokinesis in the zygote of the sea urchin, Arbacia punctulata. J. Morph. 138, 207–238 (1972)
Maddy, A. H.: The organization of proteins in the plasma membrane. In: Formation and fate of cell organelles (K. B. Warren, ed.), vol.6, p. 255–273. New York: Academic Press 1967
Manton, I.: Further observations on scale formation in Chrysochromulina chiton. J. Cell Sci. 2, 411–418 (1967)
Maul, G. G.: Golgi-melanosome relationship in human melanoma in vitro. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 26, 163–176 (1969)
Mercer, E. H.: The evolution of intracellular phospholipid membrane systems. In: The interpretation of ultrastructure (R.J.C. Harris, ed.), p. 369–384. New York: Academic Press 1962
Mollenhauer, H. H.: Transition forms of Golgi apparatus secretion vesicles. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 12, 439–446 (1965)
Mollenhauer, H. H., Morré, D. J.: Golgi apparatus and plant secretion. Ann. Rev. Plant Physiol. 17, 27–46 (1966)
Moore, R. T., McAlear, J. M.: Fine structure of mycota. 4. The occurrence of the Golgi dictyosome in the fungus Neobulgaria pura (Fr.) Petrak. J. Cell Biol. 16, 131–141 (1963)
Morré, D. J., Mollenhauer, H. H., Bracker, C. E.: Origin and continuity of Golgi apparatus. In: Origin and continuity of cell organelles. (J. Reinert and H. Ursprung, eds.), vol. 2, p. 82–126. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer 1971
Novikoff, A. B.: Enzyme localization and ultrastructure of neurons. In: The neuron (H. Hydén, ed.), p. 255–318. Amsterdam: Elsevier Publ. Co. 1967
Nørrevang, A.: Electron microscopic morphology of oogenesis. Int. Rev. Cytol. 23, 113–186 (1968)
Ohno, S., Karasaki, S., Takata, K.: Histo- and cytochemical studies on the superficial layer of yolk platelets in the Triturus embryo. Exp. Cell Res. 33, 310–318 (1964)
Ovtracht, L., Morré, D. J., Cheetham, R. D., Mollenhauer, H. H.: Subfractionation of Golgi apparatus from rat liver: Method and morphology. J. Microsc. (Paris) 18, 87–102 (1973)
Palade, G. E.: The endoplasmic reticulum. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol. 2, 85–97 (1967)
Redman, C. M., Sabatini, D. D.: Vectoral discharge of peptides released by puromycin from attached ribosomes. Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. (Wash.) 56, 608–615 (1966)
Ries, E.: Zur Histophysiologie des Mäusepankreas nach Lebendbeobachtung, Vitalfärbung und Stufenuntersuchung. Z. Zellforsch. 22, 523–585 (1935)
Ruby, J. R., Webster, R. M.: Origin of the Golgi complex in germ cells in the developing ovary of the rat. Z. Zellforsch. 133, 1–12 (1972)
Sanders, E. J.: Association of the Golgi complex with the plasma membrane of amphibian embryonic cells. Protoplasma 76, 115–122 (1973)
Sanders, E. J., Singal, P. K.: Visualization of the outer and interblastomeric surface of early embryos of Xenopus laevis by scanning electron microscopy. Micron 4, 156–162 (1973)
Sakai, A., Shigenaga, M.: Behaviour of cytoplasmic membraneous structures in spermatogenesis of the grasshopper, Atractomorphabedeli bolivar. Cytologia 32, 72–86 (1967)
Scharrer, B., Wurzelmann, S.: Ultrastructural study on nuclear-cytoplasmic relationships in oocytes of the African lungfish, Protopterus aethiopicus I. Nucleolocytoplasmic pathways Z. Zellforsch. 96, 325–343 (1969)
Singal, P. K., Sanders, E. J.: An ultrastructural study of the first cleavage of Xenopus embryos. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 47, 433–451 (1974a)
Singal, P. K., Sanders, E. J.: Xenopus embryos: membrane growth and distribution of cell surface material during the first cleavage. Proc. Can. Fed. Biol. Soc. 1715 (1974b)
Stang-Voss, C.: Zur Entstehung des Golgi-Apparates. Elektronenmikroskopische Untersuchungen an Spermatiden von Eisenia foetida (Annelidae). Z. Zellforsch. 109, 287–296 (1970)
Stoeckenius, W.: Some electron microscopical observations on liquid-crystalline phases in lipid-water systems. J. Cell Biol. 12, 221–229 (1962)
Tahdler, C. J., La Torre, J. L.: An acid polysaccharide in the yolk platelets of Bufo arenarum oocytes. Exp. Cell Res. 45, 491–494 (1967)
Thiery, J.-P.: Role de l'appareil de Golgi dans la synthèse des mucopolysaccharides, étude cytochimique. I. Mise en evidence de mucopolysaccharides dans les vésicules de transition entre l'ergastoplasme et l'appareil de Golgi. J. Microsc. (Paris) 8, 689–708 (1969)
Ward, R. T.: The origin of protein and fatty yolk in Rana pipiens. II. Electron microscopical and cytochemical observations of young and mature oocytes. J. Cell Biol. 14, 309–341 (1962)
Ward, R. T.: Formation of Golgi bodies during maturation of oocytes in Rana pipiens. Anat. Rec. 151, 430a (1965)
Whaley, W. G.: Proposals concerning replication of the Golgi apparatus. In: Probleme der Biologischen Reduplikation (P. Sitte, ed.), p. 340–371. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer 1966
Whaley, W. G., Dauwalder, M., Kephart, J. E.: Golgi apparatus: influence on cell surface. Science 175, 596–599 (1972)
Wischnitzer, S.: An electron microscope study of the nuclear envelope of amphibian oocytes. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 1, 201–222 (1958)
Wischnitzer, S.: The ultrastructure of the cytoplasm of the developing amphibian egg. Advanc. Morphogenes. 5, 131–179 (1966)
Wise, G. E., Flickinger, C. J.: Relation of the Golgi apparatus to the cell coat in amoebae. Exp. Cell Res. 61, 13–23 (1970)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work was supported by a grant from the Medical Research Council of Canada to one of us (E.J.S.).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singal, P.K., Sanders, E.J. Cytomembranes in first cleavage xenopus embryos. Cell Tissue Res. 154, 189–209 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00223164
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00223164