Summary
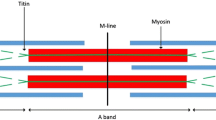
The ultrastructural study of cross sections of normal skeletal muscle cells showed the existence of irregular patterns of actin filaments in connection with the hexagonal pattern of the myosin filaments. The actin filaments surrounding each myosin filament vary in number from 6 to 11. The most frequent relationship is 9 to 1, followed by 10 to 1 and 8 to 1. The hexagonal pattern of actin filaments was observed only in the 6 to 1 arrays; as the actin filaments increase in number, they tend to form different polygons or circles around the myosin filaments. All described patterns may occur in each sarcomere. The actin to myosin filament ratio varies from 3 to 4 within each individual myofibril. The described variability of the actin filaments arrays leads to several difficulties in an explanation of the mechanism of muscular contraction.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dubowitz, V., Brooke, M.H.: Normal muscle. In: Major problems in neurology. Volume 2: Muscle biopsy. A modern approach (J.N. Walton, consulting editor), pp. 34–73. London: W.B. Saunders Company Ltd. 1973
Fischman, D.A.: An electron microscope study of myofibril formation in embryonic chick skeletal muscle. J. Cell Biol. 32, 555–575 (1967)
Fischman, D.A., Meltzer, H.Y., Popei, R.W.: The ultrastructure of human skeletal muscle. Variations from archetypal morphology. In: The striated muscle (C.M. Pearson and F.K. Mostofi, eds.), pp. 58–76. Baltimore: The Williams and Wilkins Company 1973
Huxley, H.E.: The double array of filaments in cross-striated muscle. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol. 3, 631–647 (1957)
Huxley, H.E.: The mechanism of muscular contraction. Science 164, 1356–1366 (1969)
Huxley, H.E.: The structural basis of muscular contraction. Proc. roy. Soc. B 178, 131–141 (1971)
Morel, J.E., Pinset-Härström, I.: Ultrastructure of the contractile system of striated skeletal muscle and the processes of muscular contraction. Biomedicine 22, 88–96 and 186–194 (1975)
Price, H.M.: Ultrastructure of the skeletal muscle fibre. In: Disorders of voluntary muscle (J.N. Walton, ed.), pp. 31–67. London: Churchill Livingstone 1974
Richter, G.W., Kellner, A.: Hypertrophy of the human heart at the level of fine structure. J. Cell Biol. 18, 195–206 (1963)
Schotland, D.L., Spiro, D., Rowland, L.P., Carmel, P.: Ultrastructural studies of muscle in McArdle's disease. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 24, 629–644 (1965)
Spiro, D., Hagopian, M.: On the assemblage of myofibrils. In: Symposia of the international society for cell biology, Vol. 6: Formation and fate of cell organelles (K.B. Warren, ed.), pp. 71–98. New York-London: Academic Press 1967
Stenger, R.J., Spiro, D.: The ultrastructure of mammalian cardiac muscle. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol. 9, 325–352 (1961)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Director, Chief of Section, Histology. Profesor Agregado de Embriología e Histología
Profesor Adjunto de Embriología e Histología
Residente de Anatomía Patol'ogica de la Ciudad Sanitaria La Paz
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nistal, M., Paniagua, R. & Morales, C. Irregular patterns of actin and myosin filaments in human skeletal muscle cells. Cell Tissue Res. 181, 403–407 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00223114
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00223114