Summary
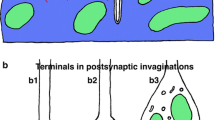
The frog motor endplate in its simplest form consists of an elongated, slender nerve ending embedded in a gutter-like depression of the sarcolemma. This nerve terminal contains the usual synaptic organelles. It is covered by a thin coating of Schwann cell cytoplasm which embraces the terminal with thin finger-like processes from both sides, thereby sub-dividing it into 300–1000 regularly spaced compartments. The individual synaptic compartments correspond to the strings of varicosities or grape-like configurations of motor nerve terminals in endplates of other species and in the cerebral neuropil of vertebrates.
Each compartment contains one or more bar-like densities of the presynaptic membrane, ‘active zones’, which are associated with the attachment sites between synaptic vesicles and plasmalemma. Active zones have a regular transverse arrangement and occur at specific loci opposite the junctional folds. The attachment sites for synaptic vesicles are at the edges of the bars which are bilaterally delineated by a double row of 10 nm particles attached to the A-face. The structural appearance of vesicle attachment sites in freeze-etch replicas corresponds to that of micropinocytosis. The active zones are often fragmented and the frequency of their association with vesicle attachment sites is highly variable.
The junctional folds are characterized by “specific sites” in which intramembranous particle aggregations occur at relatively high packing density (7500/μm2). These sites are located opposite the active zones at the juxtaneural lips, a location where one would expect ACh-sensitive receptors on the postsynaptic membrane.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akert, K., Moor, H., Pfenninger, K., Sandri, C.: Contribution of new impregnation methods and freeze-etching to the problems of synaptio fine structure. In: Mechanism of synaptic transmission (ed. K. Akert and P. Waser). Progr. Brain Res. 31, 223–240 (1969)
Akert, K., Peper, K.: Ultrastructure of chemical synapses: a comparison between synaptic membrane complexes of the motor endplate and the synaptic junction in the CNS. Golgi Centennial Symposium (ed. M. Santini). New York: Raven Press 1974 (in press)
Betz, W., Sakmann, B.: “Disjunction” of frog neuromuscular synapses by treatment with proteolytic enzymes. Nature (Lond.), New Biol. 232, 94–95 (1971)
Betz, W., Sakmann, B.: Effects of proteolytic enzymes on function and structure of frog neuromuscular junction. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 230, 673–688 (1973)
Birks, R., Huxley, H. E., Katz, B.: The fine structure of the neuromuscular junction of the frog. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 150, 134–144 (1960)
Ceccarelli, S., Hurlbut, W. P., Mauro, A.: Depletion of vesicles from frog neuromuscular junctions by prolonged tetanic stimulation. J. Cell Biol. 54, 30–38 (1972)
Cole, W. V.: Motor endings in striated muscle of vertebrates. J. comp. Neurol. 102, 671–716 (1955)
Couteaux, R.: Sur les gouttières synaptiques du muscle strié. C. R. Soc. Biol. (Paris) 140, 270–271 (1946)
Couteaux, R.: Contribution à l'étude de la synapse myoneurale. Rev. canad. Biol. 6, 563–711 (1947)
Couteaux, R.: Localization of cholinesterase at neuromuscular junctions. Int. Rev. Cytol. 4, 335–375 (1955)
Couteaux, R.: Morphological and cytochemical observations on the post-synaptic membrane at motor end-plates and ganglionic synapses. Exp. Cell Res., Suppl. 5, 294–322 (1958)
Couteaux, R.: Motor end-plate structure. In: The structure and function of muscle. Vol. 2: Structure (ed. G. H. Bourne), p. 337–380, New York and London: Academic Press 1960
Couteaux, R.: Principaux critéres morphologiques et cytochimiques utilisables aujourd'hui pour définir les divers types de synapses. Actualités Neurophysiol., 3° sér., 145–173 (1961)
Couteaux, R.: The differentiation of synaptic areas. Proc. roy. Soc. B 158, 457–480 (1963)
Couteaux, R., Pécot-Dechavassine, M.: L'ouverture des vésicules synaptiques au niveau des “zones actives”. In: Septième Congr. Internat, de Microscopie Electronique, Grenoble, vol. 3, 709–710 (1970a)
Couteaux, R., Pécot-Dechavassine, M.: Vésicules synaptiques et poches au niveau des “zones actives” de la jonction neuromusculaire. C. R. Acad. Sc. (Paris) 271, 2346–2349 (1970b)
Dreyer, F., Peper, K.: A monolayer preparation of innervated skeletal muscle fibres of the M. cutaneus pectoris of the frog. Pflügers Arch. 348, 257–262 (1974)
Dreyer, F., Peper, K., Akert, K., Sandri, C., Moor, H.: Ultrastructure of the “active zone” in the frog neuromuscular junction. Brain Res. 62, 373–380 (1973)
Hall, Z. W., Kelly, R. B.: Enzymatic detachment of endplate acetylcholinesterase from muscle. Nature (Lond.), New Biol. 232, 62–63 (1971)
Heuser, J. E., Reese, T. S.: Evidence for recycling of synaptic vesicle membrane during transmitter release at the frog neuromuscular junction. J. Cell Biol. 57, 315–344 (1973)
Katz, B.: The release of neural transmitter substances. Liverpool: University Press 1969
Koelliker, A.: Untersuchungen über die letzten Endigungen der Nerven. Mit 4 Kupfertafeln. Leipzig: W. Engelmann 1862
Koenig, J., Pécot-Dechavassine, M.: Relations entre l'apparition des potentiels miniatures et l'ultrastructure des plaques motrices en voie de réinnervation et de néoformation chez le rat. Brain Res. 27, 43–57 (1971)
Kuehne, W.: Über die peripherischen Endorgane der motorischen Nerven. Mit 5 Tafeln. Leipzig: W. Engelmann 1862
Kuehne, W.: Die Verbindung der Nervenscheiden mit dem Sarkolemm. Z. Biol. 19, 501–534 (1883)
Kuehne, W.: Neue Untersuchungen über motorische Nervenendigungen. Z. Biol. 23, 1–148 (1887)
McMahan, U. J., Spitzer, N. C., Peper, K.: Visual identification of nerve terminals in living isolated skeletal muscle. Proc. roy. Soc. B 181, 421–430 (1972)
McNutt, N. S., Weinstein, R. S.: Membrane ultrastructure at mammalian intercellular junctions. In: Progress in biophysics and molecular biology (ed. J.A.V. Butler and D. Noble), vol. 26, p. 47–101. Oxford: Pergamon 1973
Moor, H.: Recent progress in the freeze-etching technique. Phil. Trans. B. 261, 121–131 (1971)
Moor, R., Muehlethaler, K.: Fine structure in frozen-etched yeast cells. J. Cell Biol. 17, 609–628 (1963)
Nickel, E., Potter, L. T.: Ultrastructure of isolated membranes of Torpedo electric tissue. Brain Res. 57, 508–517 (1973)
Reger, J. P.: The fine structure of neuromuscular synapse of gastrocnemii from mouse and frog. Anat. Rec. 130, 7–24 (1958)
Retzius, G.: Zur Kenntnis der motorischen Nervenendigungen. Biol. Untersuchungen, N. F. 3, 41–52 (1892)
Robertson, J. D.: Some features of the ultrastructure of reptilian skeletal muscle. J.biophys. biochem. Cytol. 2, 369–380 (1956)
Robertson, J. D.: The ultrastructure of a reptilian myoneural junction. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol. 2, 381–394 (1956)
Sandri, C., Akert, K., Livingston, R. B., Moor, H.: Particle aggregations at specialized sites in freeze-etched postsynaptic membranes. Brain Res. 41, 1–16 (1972)
Satir, B., Schooley, C., Satir, P.: Membrane fusion in a model system. Mucocyst secretion in Tetrahymena. J. Cell Biol. 56, 153–176 (1973)
Streit, P., Akert, K., Sandri, C., Livingston, R. B., Moor, H.: Dynamic ultrastructure of presynaptic membranes at nerve terminals in the spinal cord of rats. Anesthetized and unanesthetized preparations compared. Brain Res. 48, 11–26 (1972)
Waser, P. G.: On receptors in the postsynaptic membrane of the motor endplate. In: Ciba Foundation Symposium on Molecular Properties of Drug Receptors, p. 59–75. London: Churchill 1970
Zacks, S. I.: The motor endplate, p. 321. Philadelphia and London: Saunders 1964
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work was supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (Sonderforschungsbereich 38, Projekt N), The Swiss National Foundation for Scientific Research (Grants Nr. 3 82372 and 3 77472) and the Dr. Eric Slack-Gyr Foundation Zürich.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peper, K., Dreyer, F., Sandri, C. et al. Structure and ultrastructure of the frog motor endplate. Cell Tissue Res. 149, 437–455 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00223024
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00223024