Summary
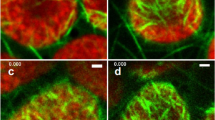
Isometric contracting protoplasmic veins of Physarum polycephalum show cycling patterns of cytoplasmic F-actin, dependent on their oscillating contraction behaviour (minute rhythms). The process of fibrillogenesis represents a parallel arrangement of F-actin chains (“plasma filaments, microfilaments”) during the isometric contraction phase. A part of the results of the present work corroborates previous results on stretch-activated veins which showed that the fibrillar form of F-actin reflects the isometric contracted state.
During isometric relaxation phase, a disaggregation of the fibrillar pattern takes place and is accompanied by a deparallelisation of F-actin chains. Therefore, the isometric relaxed state of cytoplasmic actomyosin is non-fibrillar in nature. Thus, the morphologically detectable fibrillar form of cytoplasmic actomyosin, according to physiological interpretation, is solely representative of the isometric contracted state.
The question whether assembly-disassembly processes, e.g. G⇌F-actin-transformation, play a role in the contraction-relaxation cycle is discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alléra, A., Beck, R., Wohlfarth-Bottermann, K.E.: Weitreichende fibrilläre Protoplasmadifferenzierungen und ihre Bedeutung für die Protoplasmaströmung. VIII. Identifizierung der Plasmafilamente von Physarum polycephalum als F-Actin durch Anlagerung von heavy meromysin in situ. Cytobiologie 4, 437–449 (1971)
Alléra, A., Wohlfarth-Bottermann, K.E.: Weitreichende fibrilläre Protoplasmadifferenzierungen und K.-E. Wohlfarth-Bottermann and M. Fleischer ihre Bedeutung für die Protoplasmaströmung. IX. Aggregationszustände des Myosins und Bedingungen zur Entstehung von Myosinfilamenten in den Plasmodien von Physarum polycephalum. Cytobiologie 6, 261–286 (1972)
Fleischer, M., Wohlfarth-Bottermann, K.E.: Correlation between tension force generation, fibrillogenesis and ultrastructure of cytoplasmic actomyosin during isometric and isotonic contractions of protoplasmic strands. Cytobiologie 10, 339–365 (1975)
Hatano, S.: Contractile proteins from the myxomycete plasmodium. Advan. in Biophys. 5, 143–176 (1973)
Hinssen, H.: Actin im isolierten Grundplasma von Physarum polycephalum. Cytobiologie 5, 146–164 (1972)
Hülsmann, N., Haberey, M., Wohlfarth-Bottermann, K.E.: Vitalmikroskopische Darstellung cytoplasmatischer Actomyosin-Fibrillen. Microscopica Acta 76, 38–47 (1974)
Isenberg, G., Giesbrecht, P., Wecke, J., Wohlfarth-Bottermann, K.E.: Demonstration of cytoplasmic actomyosin fibrils by the freeze-etching technique. Microscopica Acta 77, 30–36 (1975)
Kamiya, N.: Contractile properties of the plasmodial strand. Proc. Japan Acad. 46, 1026–1031 (1970)
Kamiya, N.: Contractile characteristics of the myxomycete plasmodium. Proc. IV. Internat. Biophysics Congress Moscow, 1972 (Symposium III, in press)
Komnick, H., Stockem, W., Wohlfarth-Bottermann, K.E.: Cell Motility: Mechanisms in protoplasmic streaming and ameboid movement. Int. Rev. Cytol. 34, 169–249 (1973)
Lazarides, E.: Tropomyosin antibody: The specific localisation of tropomyosin in non-muscle cells. J. Cell Biol. 65, 549–561 (1975)
Lazarides, E., Weber, K.: Actin antibody: The specific visualisation of actin filaments in non-muscle cells. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 71, 2268–2272 (1974)
Lüscher, E.F.: Microfilaments in blood platelets. Hoppe-Seyler's Zeitschr. Physiol. Chemie 356, 382 (1975)
Nagai, R., Yoshimoto, Y., Kamiya, N.: Changes in fibrillar structures in the plasmodial strand in relation to the phase of contraction-relaxation cycle. Proc. Japan Acad. 51, 38–43 (1975)
Parducz, B.: Eine neue Schnellfixierungsmethode im Dienste der Protistenforschung und des Unterrichts. Ann. Mus. Nat. Hung. 2, 5–12 (1952)
Pollack, R., Osborn, M., Weber, K.: Patterns of organization of actin and myosin in normal and transformed cultured cells. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 72, 994–998 (1975)
Pollard, T.D., Weihing, R.R.: Actin and myosin and cell movement. CRC Critical Rev. Biochem. 2, 1–65 (1974)
Schliwa, M., Bereiter-Hahn, J.: Pigment movement in fish melanophores: Morphological and physiological studies. Cell Tiss. Res. 158, 61–73 (1975)
Schroeder, T.E.: The contractile ring. II. Determining its brief existence, volumetric changes, and vital role in cleaving Arbacia eggs. J. Cell Biol. 53, 419–434 (1972)
Weber, K., Gröschel-Stewart, U.: Antibody to myosin: The specific visualization of myosin-containing filaments in non-muscle cells. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 71, 4561–4564 (1974)
Wohlfarth-Bottermann, K.E.: Cell structures and their significance for ameboid movement. Int. Rev. Cytol. 16, 61–131 (1964)
Wohlfarth-Bottermann, K.E.: Weitreichende fibrilläre Protoplasmadifferenzierungen und ihre Bedeutung für die Protoplasmaströmung. III. Entstehung und experimentell induzierbare Musterbildungen. Roux' Archiv f. Entwicklungsmechanik 156, 371–403 (1965)
Wohlfarth-Bottermann, K.E.: Plasmalemma invaginations as characteristic constituents of plasmodia of Physarum polycephalum. J. Cell Sci. 16, 23–27 (1974)
Wohlfarth-Bottermann, K.E.: Tensiometric demonstration of endogenous oscillating contractions in plasmodia of Physarum polycephalum. Zeitschr. Pflanzenphysiol. 76, 14–27 (1975a)
Wohlfarth-Bottermann, K.E.: Weitreichende fibrilläre Protoplasmadifferenzierungen und ihre Bedeutung für die Protoplasmaströmung. X. Die Anordnung der Actomyosin-Fibrillen in experimentell unbeeinflußten Protoplasmaadern von Physarum in situ. Protistologica 11, 19–30 (1975b)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Dedicated to Prof. Dr. Dr. h.c. W. Bargmann on the occasion of his 70 birthday. — Paper presented at the Cell Surface Project Group workshop “Interrelation of cell surface and cell locomotion”, European Organization for Research on Treatment of Cancer (EORTC), June 6–8, 1975, Zürich, Switzerland.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wohlfarth-Bottermann, K.E., Fleischer, M. Cycling aggregation patterns of cytoplasmic F-actin coordinated with oscillating tension force generation. Cell Tissue Res. 165, 327–344 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00222437
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00222437