Abstract
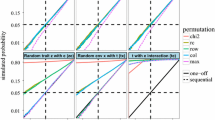
Stability analysis of multilocation trials is often based on a mixed two-way model. Two stability measures in frequent use are the environmental variance (S 2 i )and the ecovalence (W i). Under the two-way model the rank orders of the expected values of these two statistics are identical for a given set of genotypes. By contrast, empirical rank correlations among these measures are consistently low. This suggests that the two-way mixed model may not be appropriate for describing real data. To check this hypothesis, a Monte Carlo simulation was conducted. It revealed that the low empirical rank correlation amongS 2 i and W i is most likely due to sampling errors. It is concluded that the observed low rank correlation does not invalidate the two-way model. The paper also discusses tests for homogeneity of S 2 i as well as implications of the two-way model for the classification of stability statistics.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Becker HC (1981) Biometrical empirical relations between different concepts of phenotypic stability. In: Gallais A (ed) Quantitative genetics and breeding methods. I.N.R.A., Versailles, pp 307–314
Becker HC, Léon J (1988) Stability analysis in plant breeding. Plant Breed 101:1–23
Helms TC (1993) Selection for yield and stability among oats lines. Crop Sci 33:423–426
Hühn MM (1990) Nonparametric measures of phenotypic stability. Part 2. Applications. Euphytica 47:195–201
Hühn M, Lotito S, Piepho HP (1993) Relationships between genotype-environment interactions and rank orders for a set of genotypes tested in different environments. Theor Appl Genet 86:943–950
Jalaluddin Md, Harrison SA (1993) Repeatability of stability estimators for grain yield in wheat. Crop Sci 33:720–725
Léon J (1985) Beiträge zur Erfassung der phänotypischen Stabilität unter besonderer Berücksichtigung unterschiedlicher Heterogen-itäts-und Heterozygotiegrade sowie einer zusammenfassenden Beurteilung von Ertragshöhe und Ertragssicherheit. Dissertation, Kiel University
Léon J, Becker HC (1988) Repeatability of some statistical measures of phenotypic stability. Plant Breed 100:137–142
Lin CS, Binns MR, Levkovitch LP (1986) Stability analysis: where do we stand? Crop Sci 26:894–900
Lin CS, Binns MR (1988) A method of analysing cultivar x location x year experiments: a new stability parameter. Theor Appl Genet 76:425–430
Lin CS, Binns MR (1991) Genetic properties of four types of stability parameter. Theor Appl Genet 82:505–509
Pham HN, Kang MS (1988) Interrelationships and repeatability of several stability statistics estimated from international maize trials. Crop Sci 28:381–385
Piepho HP (1993a) Note on bias in estimates of the regression coefficient in the analysis of genotype-environmental interaction. Heredity 70:98–100
Piepho HP (1993b) Testing for homoscedasticity. Letter. Biometrics 49:1279–1280
Piepho HP (1994) Tests for pairwise commparison of variances in a two-way layout for the analysis of phenotypic stability. Informatik, Biometrie und Epidemiologie in Medizin and Biologie, 25:172–180
Piepho HP, Lotito S (1992) Rank correlation among parametric and nonparametric measures of phenotypic stability. Euphytica 64:221–225
SAS Institute (1989) SAS/IML software: usage and reference. Version 6. Cary, North Carolina
Shukla GK (1972) Some statistical aspects of partitioning genotype-environmental components of variability. Heredity 29:237–245
Weber WE, Wricke G (1987) Wie zuverlässig sind Schätzungen von Parametern der phänotypischen Stabilität? Vorträge Pflanzenzücht 12:120–133
Wricke G (1962) Über eine Methode zur Erfassung der ökologischen Streubreite. Z Pflanzenzücht 47:92–96
Wricke G, Weber WE (1980) Erweiterte Analyse von Wechselwirkungen in Versuchsserien. In: Köpeke W, Überla K (eds) Biometrie — heute und morgen. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, pp 87–95
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by P. M. A. Tigerstedt
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Piepho, HP. Implication of correlations among some common stability statistics — a Monte Carlo simulations. Theoret. Appl. Genetics 90, 457–461 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00221990
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00221990