Summary
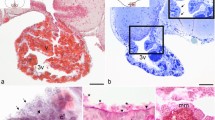
Fetal parietal cerebral cortex was homologously transplanted to the anterior chambers of the eyes of adult rats. The transplants got vascularized, proliferated, as measured by in vivo stereoscopic inspections, and differentiated into brain tissue similar to cortex cerebri in situ and survived for long times,> 41/2 months. Fibers from the intact sympathetic adrenergic ground plexus of the iris were able to innervate the transplants in an organotypic way regarding fluorescence morphology, pattern of distribution of the nerve terminals and, to a certain extent, density of innervation, the only variable parameter being density of innervation. Thus, in unpretreated or MAO inhibited transplants only rather few to scattered terminals could be found, while after preincubation in 10-5M α-methyl-noradrenaline the number of visible terminals was normal or slightly less than normal, as compared to cortex cerebri in situ.
When superior cervical ganglia (SCG) were transplanted together with fetal cortex tissue to sympathetically denervated eyes the ingrowth in the cortex tissue was similar to that after single cortex transplantation combined with 5 day old SCG, while a marked hyperinnervation was encountered when combined with adult SCG.
It is concluded that the developing cortex cerebri, deprived of its normal CNS source of adrenergic nerves, is able to receive sympathetic adrenergic nerves from the iris in an organotypic way upon transplantation to the anterior chamber of the eye.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bär, Th., Wolff, J. B.: The formation of capillary basement membranes during internal vascularization of the rat's cerebral cortex. Z. Zellforsch. 133, 231–248 (1972)
Bass, N. H., Netsky, M. G., Young, E.: Effect of neonatal malnutrition on developing cerebrum. Arch. Neurol. (Chic.) 23, 289–302 (1970)
Berry, M., Hollingworth, T.: Development of isolated neocortex. Experientia (Basel) 29, 204–207 (1973)
Corrodi, H., Jonsson, G.: The formaldehyde fluorescence method for the histochemical demonstration of biogenic monoamines. A review on the methodology. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 15, 65–78 (1967)
Crain, S. M., Peterson, E. R.: Development of neural connections in culture. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci 228, 6–34 (1974)
DeLong, G. R.: Histogenesis of fetal mouse isocortex and hippocampus in reaggregating cell cultures Develop. Biol. 22, 563–583 (1970)
DeLong, G. R.: Long-term organotypic patterning of nerve cell aggregates. In: NRP Bulletin 10, 535–539 (1972)
Edvinsson, L., Lindvall, M., Nielsen, K. C., Owman, Ch.: Are brain vessels innervated also by central (non-sympathetic) adrenergic neurones ? Brain Bes. 63, 496–499 (1973)
Falck, B., Hillarp, N.-Å., Thieme, G., Torp, A.: Fluorescence of catechol amines and related compounds condensed with formaldehyde. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 10, 348–354 (1962)
Freedman, B., Hoffer, B., Olson, L., Seiger, Å.: Electrophysiology and cytology of hippocampal formation transplants in the anterior chamber of the eye. III. Adrenergic and cholinergic influence on normal and epileptogenic activity. (1975) (to be publ.)
Freedman, B., Seiger, Å., Hoffer, B.: Electrophysiology and cytology of hippocampal formation transplants in the anterior chamber of the eye. I. Intrinsic organization. (1975) (to be publ.)
Fuxe, K., Hamberger, B., Hökfelt, T.: Distribution of noradrenaline nerve terminals in cortical areas of the rat. Brain Res. 8, 125–131 (1968)
Hamberger, B.: Reserpine-resistant uptake of catecholamines in isolated tissues of the rat. A histochemical study. Acta physiol. scand., Suppl. 295, 1–56 (1967)
Hartman, B. K., Zide, D., Udenfriend, S.: The use of dopamine β-hydroxylase as a marker for the central noradrenergic nervous system in the brain. Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. (Wash.) 69, 2722–2726 (1972)
Hoffer, B., Olson, L., Seiger, Å,, Bloom, F.: Formation of a functional adrenergic input to intraocular cerebellar grafts: ingrowth of sympathetic fibers and inhibition of Purkinje cell activity by adrenergic input. J. Neurobiol. (1975) (in press)
Hoffer, B., Seiger, Å., Ljungberg, T., Olson, L.: Electrophysiological and cytological studies of brain homografts in the anterior chamber of the eye: maturation of cerebellar cortex in oculo. Brain Bes. 79, 165–184 (1974)
Krieg, W. J. S.: Connections of the cerebral cortex. I. The albino rat. B. Structure of the cortical areas. J. comp. Neurol. 84, 277–323 (1946)
Krnjevic, K., Reiffenstein, R. J., Silver, A.: Chemical sensitivity of neurons in long isolated slabs of rat cerebral cortex. Electroenceph. clin. Neurophysiol. 29, 269–282 (1970)
Loizou, L.: The postnatal ontogeny of monoamine-containing neurones in the central nervous system of the albino rat. Brain Bes. 40, 395–418 (1972)
Nelson, G. N., Hoffer, B. J., Chu, N.-S., Bloom, F. E.: Cytochemical and pharmacological studies on polysensory neurons in the primate frontal cortex. Brain Bes. 62, 1–20 (1973)
Olson, L., Malmfors, T.: Growth characteristics of adrenergic nerves in the adult rat. Fluorescence histochemical and 3H-noradrenaline uptake studies using tissue transplantations to the anterior chamber of the eye. Acta physiol. scand., Suppl. 348, 1–112 (1970)
Olson, L., Seiger, Å.: Brain tissue transplanted to the anterior chamber of the eye. 1. Fluorescence histochemistry of immature catecholamine and 5-hydroxytryptamine neurons reinnervating the rat iris. Z. Zellforseh. 135, 175–194 (1972)
Olson, L., Seiger, Å.: Brain tissue transplanted to the anterior chamber of the eye: 2. Fluorescence histochemistry of immature catecholamine- and 5-hydroxytryptamine neurons innervating the rat vas deferens. Cell. Tiss. Bes. (1975) (in press)
Olson, L., Ungerstedt, U.: A simple high capacity freeze-drier for histochemical use. Histochemie 22, 8–19 (1970)
Seiger, Å., Olson, L.: Late prenatal ontogeny of central monoamine neurons in the rat: fluorescence histochemical observations. Z. Anat. Entwickl.-Gesch. 140, 281–318 (1973)
Stone, T. W.: Pharmacology of pyramidal tract cells in the cerebral cortex. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 278, 333–346 (1973)
Ungerstedt, U.: Stereotaxic mapping of the monoamine pathways in the rat brain. Acta physiol. scand., Suppl. 367, 1–48 (1971)
Vazquez, A. J., Krip, G.: Evidence for an inhibitory role for acetylcholine, catecholamines, and serotonin on the cerebral cortex, p. 137–159. New York: Raven Press 1973
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by the Swedish Medical Research Council (04X-3185), and by grants from “Magnus Bergvalls Stiftelse”, “Tidningen Expressens Prenatalforskningsfond” and “Karolinska Institutets fonder”. We thank miss Ingrid Strömberg for skilful technical assistance. The generous gifts of Nialamide® (Pfizer) and Pargyline® (Abbott) are gratefully acknowledged.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seiger, Å., Olson, L. Brain tissue transplanted to the anterior chamber of the eye: 3. Substitution of lacking central noradrenaline input by host iris sympathetic fibers in the isolated cerebral cortex developed in oculo . Cell Tissue Res. 159, 325–338 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00221780
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00221780