Summary
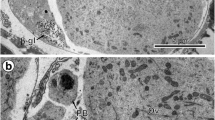
Lamellar bodies in first cleavage Xenopus laevis embryos have been examined with the electron microscope. Based on the arrangement and relative thickness of the lamellae, three types of lamellar bodies have been identified. In the first type, a band of two to ten lamellae (spacing about 3.5 nm) was intertwined at random. This type of lamellar body was seen closely associated with the concave or the forming face of the Golgi body and may have been derived from this organelle. The frequent association of these lamellar bodies with the growing cleavage furrow may suggest a transfer of materials from the Golgi body to the furrow through the lamellar bodies or their precursors. In the second type, typical myelin-like figures with a repeating distance of about 10 nm were located close to the furrow tip. In the third type, membrane whorls containing tetrads of lamellae (approximately 16 nm thickness) were seen associated with lipid droplets. If the lamellar bodies observed in this study were formed during fixation then the appearance of three different types after the same fixation procedure would indicate the presence of a similar number of pools of precursor materials which differ in their chemical composition and distribution in the embryo.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armstrong, P.B.: Unusual yolk platelets in embryos of Xenopus laevis (Amphibia). Z. Zellforsch. 129, 320–327 (1972)
Arnold, J.M.: Intercellular bridges in somatic cells: cytoplasmic continuity of blastoderm cells of Loligo pealei. Differentiation 2, 335–341 (1974)
Bangham, A.D., Horne, R.W.: Negative staining of phospholipids and their structural modification by surface-active agents as observed in the electron microscope. J. mol. Biol. 8, 660–668 (1964)
Beaulaton, J.A.: Modifications ultrastructurales des cellules sécrétrices de la glande prothoracique de vers à soie au cours des deux derniers âge larvaires. I. Le chondriome, et ses relations avec le réticulum agranulaire. J. Cell Biol. 39, 501–525 (1968)
Bluemink, J.G.: Cytokinesis and cytochalasin-induced furrow regression in the first cleavage zygote of Xenopus laevis. Z. Zellforsch. 121, 102–126 (1971)
Bluemink, J.G., De Laat, S.W.: New membrane formation during cytokinesis in normal and cytochalasin B-treated eggs of Xenopus laevis. I. Electron microscope observations. J. Cell Biol. 59, 89–108 (1973)
Curgy, J.J.: Influence du mode de fixation sur la possibilité d'observer des structures myéliniques dans les hepatocytes d'embryos de poulet. J. Microsc., Paris 7, 63–80 (1968)
Glauert, A.M., Lucy, J.A.: Globular micelles and the organization of membrane lipids. In: The Membranes (A.J. Dalton and F. Haguenau, eds.), p. 1–32. New York: Academic Press 1968
Kalt, M.R.: The relationship between cleavage and blastocoel formation in Xenopus laevis. II. Electron microscope observations. J. Embryol. Exp. Morph. 26, 51–66 (1971)
Kalt, M.R., Tandler, B.: A study of fixation of early amphibian embryos for electron microscopy. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 36, 633–645 (1971)
Leonard, R., Deamer, D.W., Armstrong, P.: Amphibian yolk platelet ultrastructure visualized by freeze-etching. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 40, 1–24 (1972)
Mercer, E.M.: The evolution of intracellular phospholipid membrane systems. In: The Interpretation of Ultrastructure (R.J.C. Harris, ed.), p. 369–384. New York: Academic Press 1962
Pannese, E.: Structures possibly related to the formation of new mitochondria in spinal ganglion neuroblasts. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 15, 57–65 (1966)
Robertson, J.D.: Unit membranes: A review with recent new studies of experimental alterations and a new subunit structure in synaptic membranes. In: Cellular Membranes in Development (M. Locke, ed.), p. 1–81. New York: Academic Press 1964
Ruby, J.R., Webster, R.M.: Origin of the Golgi complex in germ cells in the developing ovary of the bat. Z. Zellforsch. 133, 1–12 (1972)
Sanders, E.J.: Aspects of furrow formation in the cleaving Drosophila embryo. Cell Tiss. Res. 156, 463–474 (1975)
Sanders, E.J., Singal, P.K.: Visualization of the outer and interblastomeric surface of early embryos of Xenopus laevis by scanning electron microscopy. Micron 4, 156–162 (1973)
Sanders, E.J., Singal, P.K.: Furrow formation in Xenopus embryos: Involvement of the Golgi body as revealed by ultrastructural localization of thiamine pyrophosphatase activity. Exp. Cell Res. 93, 219–224 (1975)
Singal, P.K., Sanders, E.J.: An ultrastructural study of the first cleavage of Xenopus embryos. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 47, 433–451 (1974 a)
Singal, P.K., Sanders, E.J.: Cytomembranes in first cleavage Xenopus embryos. Interrelationship between Golgi bodies, endoplasmic reticulum and lipid droplets. Cell Tiss. Res. 154, 189–209 (1974 b)
Spornitz, U.M.: Lamellar bodies in oocytes of Xenopus laevis and their relation to the mode of fixation. Experientia (Basel) 29, 589–591 (1973)
Stoeckenius, W.: The molecular structure of the lipid water systems and cell membrane models studied with the electron microscope. In: The Interpretation of Ultrastructure (R.J.C. Harris, ed.), 1, p. 349–367. New York: Academic Press 1962
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work was supported by a grant from the Medical Research Council (MRC) of Canada to Dr. E.J. Sanders. The author is on a MRC fellowship.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singal, P.K. Types and distribution of lamellar bodies in first cleavage Xenopus embryos. Cell Tissue Res. 163, 215–221 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00221728
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00221728