Summary
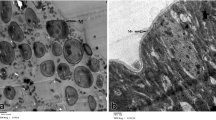
The ultrastructure of the epithelial cells in the posterior part of the midgut in female Aedes aegypti was partly changed after starvation periods of 5 or 8 days. Most obvious is a drastic reduction of the amount of rough endoplasmic reticulum (rer), which is responsible for the synthesis of enzymes for blood digestion. A similar influence on rer membranes is to be observed in mosquitoes fed on sucrose solution only, without additional blood meals.
Zusammenfassung
Nach einer Hungerperiode von 5 bzw. 8 Tagen ist die Ultrastruktur der Epithelzellen im hinteren Abschnitt des Mitteldarmes weiblicher A. aegypti teilweise verändert. So wird beispielsweise eine drastische Reduktion des rauhen endoplasmischen Retikulum (rer) gemessen, das für die Synthese der Enzyme zur Blutverdauung verantwortlich ist. Einen ähnlichen Einfluß auf das rer hat eine gleich lang dauernde Fütterung der Mücken mit Zuckerwasser.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bertram, D.S., Bird, R.G.: Studies on mosquito-borne viruses in their vectors. I. The normal fine structure of the midgut epithelium of the adult female Aedes aegypti L. and the functional significance of its modification following a blood meal. Trans. roy. Soc. trop. Med. Hyg. 55, 404–423 (1961)
Briegel, H., Kaiser, C.: Life-span of mosquitoes under laboratory conditions. Gerontologia 19, 240–249 (1973)
Christophers, R.: Aedes aegypti: The yellow fever mosquito: its life history, bionomics and structure, 739 pp. Cambridge: Cambridge Univ. Press 1960
Fisk, F.W., Shambaugh, G.F.: Protease activity in adult Aedes aegypti mosquitoes as related to feeding. Ohio J. Sci. 52, 80–88 (1952)
Gooding, R.H.: Digestive processes of haematophagous insects. I. A literature review. Quaestiones entomol. 8, 5–60 (1972)
Gooding, R.H.: The digestive processes of haematophagous insects. IV. Secretion of trypsin by Aedes aegypti (Diptera: Culicidae). Canad. Entomol. 105, 599–603 (1973)
Hecker, H., Brun, R.: Morphometric differences in midgut epithelial cells between strains of female Aedes aegypti (L.) (Insecta, Diptera). Cell Tiss. Res. 159, 91–99 (1975)
Hecker, H., Brun, R., Reinhardt, C., Burri, P.H.: Morphometric analysis of the midgut of female Aedes aegypti L. (Insecta, Diptera) under various physiological conditions. Cell Tiss. Res. 152, 31–49 (1974)
Hecker, H., Freyvogel, T.A., Briegel, H., Steiger, R.: Ultrastructural differentiation of the midgut epithelium in female Aedes aegypti L. (Insecta, Diptera) imagines. Acta trop. (Basel) 28, 80–104 (1971)
Rudin, W., Hecker, H.: Morphometric comparison of the midgut epithelial cells in male and female Aedes aegypti L. (Insecta, Diptera). Tissue and cell. 8 (3), 459–470 (1976)
Samish, M., Akov, S.: Influence of feeding on midgut protease activity in Aedes aegypti. Israel J. Entomol. 7, 41–48 (1972)
Weibel, E.R.: Stereological principles for morphometry in electron microscopic cytology. Int. Rev. Cytol. 26, 235–302 (1969)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
The authors thank Prof. T.A. Freyvogel and Dr. R. Brun for their critical reading and Miss A. Tiger for typing the manuscript
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bauer, P., Rudin, W. & Hecker, H. Ultrastructural changes in midgut cells of female Aedes aegypti L. (insecta, diptera) after starvation or sugar diet. Cell Tissue Res. 177, 215–219 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00221082
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00221082