Summary
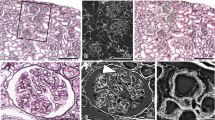
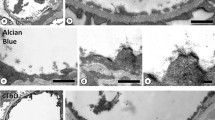
The rat kidney was perfused with saline and glutaraldehyde, treated with Murakami's tannin-osmium impregnation method, ethanol-freeze cracked and dried by the critical point method. Gold-palladium evaporated specimens were observed in a field-emission scanning electron microscope. The glomerular filtration membrane, fractured in different planes was observed with the following results:
-
1.
Adjacent pedicles originate from different podocytes. No interpedicular bridges of apparent cytoplasmic nature could be found.
-
2.
The basement membrane, in grazing fractures shows a horizontally layered architecture.
-
3.
The attenuated endothelial sheet (lamina fenestrata) is divided into compartments, which we suggest should be called “areolae fenestratae”, by cytoplasmic crests radiating from the nucleated portion of the endothelial cell. A crest also occurs along the cell margin, which contacts a similar crest at the margin of the adjacent cell.
-
4.
The pores in the areolae fenestratae are variable in size (30−150 nm diameter). A knob-like projection from the apparently naked basement membrane is found in a portion of the pores.
-
5.
Numerous microvilli may occur on the endothelium. Some of them anastomose and fuse with one another to form a net whose meshes appear identical with the endothelial pores. Domes and shelves formed of a fenestrated cytoplasmic sheet also occur above the ordinary level of the endothelial lining. A hypothesis implicating microvilli in partial renewal of the endothelial sheet is proposed.
This study was assisted by Mr. K. Adachi of the SEM Laboratory at the Niigata University School of Medicine.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrews, P.M., Porter, K.R.: A scanning electron microscopic study of the nephron. Amer. J. Anat. 140, 81–116 (1974)
Arakawa, M.: A scanning electron microscopy of the glomerulus of normal and nephrotic rats. Lab. Invest. 23, 489–496 (1970)
Arakawa, M., Tokunaga, J.: Further scanning electron microscope studies of the human glomerulus. Lab. Invest. 31, 436–440 (1974)
Bloom, W., Fawcett, D.W.: A textbook of histology, 9th ed., p. 657. Philadelphia-London-Toronto: W.B. Saunders 1974
Burkholder, P.M.: Atlas of human glomerular pathology. New York-Evanston-San Francisco-London: Harper & Row 1974
Buss, H., Krönert, W.: Zur Struktur des Nierenglomerulum der Ratte. Rasterelektronenmikroskopische Untersuchungen. Virchows Arch. Abt. B 4, 79–92 (1969)
Friederici, H.H.R.: The tridimensional ultrastructure of fenestrated capillaries. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 23, 444–456 (1968)
Friederici, H.H.R.: On the diaphragm across fenestrae of capillary endothelium. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 27, 373–375 (1969)
Fourman, J., Moffat, D.B.: The blood vessels of the kidney. Oxford and Edinburgh: Blackwell Sci. Publ. 1971
Fujita, T., Tokunaga, J., Miyoshi, M.: Scanning electron microscopy of the podocytes of renal glomerulus. Arch. histol. jap. 32, 99–113 (1970)
Groniowski, J., Biczyskowa, W., Walski, M.: Electron microscope studies on the surface coat of the nephron. J. Cell Biol. 40, 585–601 (1969)
Hall, B.V.: Studies of normal glomerular structure by electron microscopy. In: Proc. 5th Ann. Conf. on the Nephrotic syndrome, p. 1–39. New York: National Nephrosis Foundation 1953
Ham, A.W.: Histology, 7th ed., p. 760. Philadelphia and Toronto: J.B. Lippincott Co. 1974
Hamano, M., Otaka, T., Nagatani, T., Tanaka, K.: A frozen liquid cracking method for high resolution scanning electron microscopy. (Abstract). J. Electron Micr. 22, 298 (1973)
Humphreys, W.J., Spurlock, B.O., Johnson, J.S.: Critical point drying of ethanol-infiltrated, cryofractured biological specimens for scanning electron microscopy. In: Scanning electron microscopy 1974 (O. Johari, I. Corvin, eds.), p. 275–282. Chicago: IIT Res. Inst. 1974
Kobayashi, S.: Occurrence of unique colloidal particles in snake blood and their transport across the capillary wall. A proposal of a new hypothesis on the permeability of the blood capillaries. Arch, histol. jap. 31, 511–528 (1970)
Latta, H.: Ultrastructure of the glomerulus and juxtaglomerular apparatus. In: Handbook of physiology, Sect. 8: Renal physiology. (J. Orloff, R.W. Berliner, eds.), p. 1–29. Washington: American Physiological Society 1973
Majno, G.: Ultrastructure of the vascular membrane. In: Handbook of physiology, Sect. 2: Circulation (W.F. Hamilton, ed.), vol. III, p. 2293–2375. Washington: American Physiological Society 1965
Miyoshi, M., Fujita, T., Tokunaga, J.: The differentiation of renal podocytes. A combined scanning and transmission electron microscope study in rats. Arch. histol. jap. 33, 161–178 (1971)
Murakami, T.: A revised tannin-osmium method for non-coated scanning electron microscope specimens. Arch. histol. jap. 36, 189–193 (1974)
Pearse, D.C.: Fine structures of the kidney seen by electron microscopy. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 3, 295–308 (1955)
Rhodin, J.A.G.: The diaphragm of capillary endothelial fenestration. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 6, 171–185 (1962)
Simon, G.T., Chatelenat, F.: Ultrastructure of the normal and pathological glomerulus. In: The kidney (C. Rouiller, A.F. Muller, eds.), vol. 1, p. 261–349. New York-London: Academic Press 1969
Suzuki, Y.: An electron microscopy of the renal differentiation. II. Glomerulus. Keio J. Med. 8, 129–144 (1959)
Tokunaga, J., Edanaga, M., Fujita, T., Adachi, K.: Freeze cracking of scanning electron microscope specimens. A study of the kidney and spleen. Arch. histol. jap. 37, 165–182 (1974)
Trump, B.F., Benditt, E.P.: Electron microscopic studies of human renal disease. Observations of normal visceral glomerular epithelium and its modification in disease. Lab. Invest. 11, 753–781 (1962)
Wolff, J.: Elektronenmikroskopische Untersuchungen über die Vesikulation im Kapillarenendothel. Lokalisation, Variation und Fusion der Vesikel. Z. Zellforsch. 73, 143–164 (1966)
Wolff, J., Merker, H.J.: Ultrastruktur und Bildung von Poren im Endothel von porösen und geschlossenen Kapillaren. Z. Zellforsch. 73, 174–191 (1966)
Yamada, E.: The fine structure of the renal glomerulus of the mouse. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol. 1, 551–566 (1955)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This paper is dedicated to Prof. Dr. med. W. Bargmann, my (T.F.) teacher in cell and tissue research and one of the pioneer microscopists in the study of renal glomerulus, on the occasion of his 70th birthday.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fujita, T., Tokunaga, J. & Edanaga, M. Scanning electron microscopy of the glomerular filtration membrane in the rat kidney. Cell Tissue Res. 166, 299–314 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00220127
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00220127