Abstract
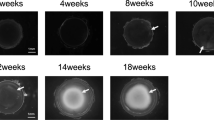
Aldose reductase (AR) mRNA concentration in rat lens was quantitated by hybridization of a RNA transcript from a previously described AR cDNA clone to mRNA found in epithelial and cortical cytosols. This was done on normal rat lens and on lens initially made cataractous by feeding of a diet of Purina Chow containing 50% galactose, followed by reversal of the cataracts due to the removal of the galactose from the diet. Recent data from this laboratory has shown that AR mRNA was increased in lens epithelial cells upon administration of galactose; while in the cortex it was reduced to insignificant levels when fiber cell damage became extensive by day 20 on galactose. Present data reveals that, upon removal of galactose from the diet, the lens epithelial AR mRNA was gradually reduced from the high levels found at day 20 of galactose feeding to low levels by day 30 of reversal. On the other hand, the cortex exhibited an initial sudden increase in AR mRNA at days 1 to 6 of reversal and by day 30 it was reduced to levels below those found in the untreated lens. DNA content in the epithelium also began to decrease to normal levels by day 16 following reversal of the cataracts. The data demonstrate that the concentration of AR mRNA in lens of reversed cataracts appears to faithfully reflect the loss of epithelial cellular need for AR mRNA in favor of enhanced differentiation of epithelial cells to secondary fiber cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hsu M-Y, Unakar NJ, Bekhor I: Differential gene expression in rat lens undergoing chemically induced cataractogenesis. Lens Res 3: 305–318, 1986
Hsu M-Y, Jaskoll TF, Unakar NJ, Bekhor I: Survival of fiber cells and fiber-cell messenger RNA in lens of rats maintained on a 50% galactose diet for 45 days. Exp Eye Res 44: 577–586, 1987
Shinohara T, Piatigorsky J, Carper DA, Kinoshita JH: Crystallin mRNAs in galactosemic rat lenses. Exp Eye Res 34:39–48,1982
Bekhor I: MP26 messenger RNA sequences in normal and cataractous lens. A molecular probe for abundance and distribution of a fiber cell-specific gene product. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 29: 802–813, 1988
Bekhor I: Progress in nonhistone protein research, Vol 3, CRC Press, Inc, Boca Raton, Florida, 1989, pp 157–166
Kinoshita JH, Merola LO and Dikmak E: Osmotic changes in experimental galactose cataracts. Exp Eye Res 1: 405–410,1962
Gabbay KH, Kinoshita JH: Mechanism of development and prevention of cataracts. Isr J Med Sci 8: 1557–1561, 1972
Kinoshita JH, Kador P, Datiles M: Aldose reductase in diabetic cataracts. J Am Med Assoc 246: 257–261, 1981
Srivastava SK, Ansari N: Prevention of sugar-induced cataractogenesis in rats by butylated hydroxytoluene. Diabetes, 37: 1505–1508, 1988
Trevithick JR, Creighton MO, Ross WM, Stewart-DeHaan PJ, Sanwal M: Mpdeling cortical cataractogenesis: in vitro effect on the lens of agents preventing glucose- and sorbitolinduced cataracts. Can J Ophthalmol 16: 32–38, 1981
Cheng HM, Gonzalez RG: The effect of high glucose and oxidative stress on lens metabolism, aldose reductase, and senile cataractogenesis. Metabolism, 35 (Suppl 1):10–14,1986
Cheng HM, Hirose K, Xiong H, Gonzalez RG: Polyol pathway activity in streptozotocin-diabetic rats. Exp Eye Res 49: 87–92, 1989
Kador PF, Kinoshita JH: Diabetic and galactosemic cataracts. In: Human cataract formation, Ciba Foundation Symposium 106. Pitman, London, 1984, pp 110–131
Varma SD, Kinoshita JH: Sorbitol pathway in diabetic rat lens and galactosemic rat lens. Biochim Biophys Acta 338: 632–640,1974
van Heyningen R: The sorbitol pathway in the lens. Exp Eye Res 1: 396–404, 1962
Agaki Y, Yajima Y, Kador PF, Kuwabara T, Kinoshita JH: Localization of aldose reductase in the human eye. Diabetes 33: 562–566, 1984
Bekhor I, Shi S, Carper D, Nishimura C, Unakar NJ: Relative abundance of aldose reductase mRNA in rat lens undergoing development of osmotic cataracts. Curr Eye Res, in press, 1989
Grimes P, von Sallman L: Lens epithelium proliferation in sugar cataracts. Invest Ophthalmol 7: 535–543, 1968
Unakar NJ, Weinseider A, Reddan JR: Ultrastructural changes associated with the induction and reversal of a chemically induced cataracts. Ophthal Res 9: 296–307,1977
White AB, Bancroft FL: Cytoplasmic dot hybridization. Simple analysis of relative mRNA levels in multiple small cell or tissue samples. J Biol Chem 257: 8569–8572, 1982
Carper D, Nishimura C, Shinohara T, Dietzchold B, Wistow G, Craft C, Kador P, Kinoshita JH: Aldose reductase and @-crystallin belong to the same protein superfamily as aldehyde reductase. FEBS Letts 230: 209–213, 1987
Thomas PS: Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci, USA 77: 5201–5205, 1980
Hentzen PC, Rho JH, Bekhor I: Nuclear matrix DNA from chicken erythrocytes contain -globin gene sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci, USA 81: 304–307, 1984
Hsu M-Y, Davis C, Jaskoll TF, Zeineh RA, Unakar NJ, Bekhor I: Crystallin mRNA product levels in lens undergoing reversal and inhibition of galactose cataracts. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 28: 1413–1421, 1987
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bekhor, I., Shi, S. & Unakar, N.J. Management of aldose reductase mRNA abundance in rat lens undergoing reversal of galactose induced cataracts. A model for gene response to changes in the environment. Mol Cell Biochem 95, 55–60 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00219530
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00219530