Abstract
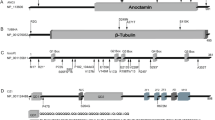
The current hypothesis that the Duchenne/Becker muscular dystrophy locus encodes a single 2000 kb gene is analyzed. The apparent encoding efficiency, the individual and total exon/intron ratios, and the heterogeneity of deletions associated with the disease, which are currently interpreted as supporting the single gene hypothesis, are also consistent with the alternative hypothesis that this locus is a portion of a complex of related gene clusters which include syntenic transcriptional units of enzymes and ligand transport proteins of one or more convergent metabolic pathways. The high recombination frequency and high rate of deletions are consistent with a locus that has recently evolved from pseudoautosomal origin. The propositions that nebulin or dystrophin is the product of the DMD locus, and that the mdx locus in the mouse is homologous to that of DMD, are critically evaluated. Several lines of evidence support the contention that developmental and tissue-specific enzymes of acyl-specific phospholipid synthesis are encoded in these clusters. Phenotypic variability not accountable for by deletion heterogeneity is postulated to arise from epistatic interactions with other loci within or outside these putative clusters. Some testable predictions of these hypotheses are suggested.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rowland LP: Biochemistry of muscle membranes in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Muscle & Nerve 3:3–20, 1980
Walton JN, Gardner-Medwin D: Progressive muscular dystrophy and the myotonic disorders. In: JN Walton (ed) Disorders of Voluntary Muscle. Churchill Livingstone, 4th edition, Edinburgh, 1981, pp 481–524
Moser H: Duchenne muscular dystrophy: pathogenic aspects and genetic prevention. Hum Genet 66:17–40, 1984
Infante JP: Impaired biosynthesis of highly unsaturated phosphatidylcholines: a hypothesis on the molecular etiology of some muscular dystrophies. J Theor Biol 116:65–88, 1985
Emery AEH: Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. Oxford University Press, New York, 1987, p 1, 149, 166
Monaco AP, Kunkel LM: A giant locus for the Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophy gene. TIG 3:33–37, 1987
Monaco AP, Neve RL, Colleti-Feener C, Bertelson CJ, Kurmit DM, Kunkel LM: Isolation of candidate cDNAs for portions of the Duchenne muscular dystrophy gene. Nature 323:646–650, 1986
Moser H: Duchenne muscular dystrophy: pathogenic aspects and genetic prevention. Hum Genet 66:17–40, 1984
Boyd Y, Buckle UJ: Cytogenetic heterogeneity of translocations associated with Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Clin Genet 29:108–115, 1986
Ray PN, Belfall B, Duff C, Logan C, Kean V, Thompson MW, Sylvester JE, Gorski JL, Schmickel RD, Worton RG: Cloning of the breakpoint of an X;21 translocation associated with Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Nature 318:672–675, 1985
Kunkel LM: Analysis of deletions in the DNA of patients with Becker and Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Nature 322:73–77, 1986
Koenig M, Hoffman EP, Bertelson CJ, Monaco AP, Feener C, Kunkel LM: Complete cloning of the Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) cDNA and preliminary genomic organization of the DMD gene in normal and affected individuals. Cell 50:509–517, 1987
Fischbeck K, Ritter AW, Tirscwell DL, Kunkel LM, Bertelson CJ, Monaco AP, Hejmanik JF, Bohem C, Ionasescu R, Vance MP, Kandt R, Roses AD: Recombination with PERT87(DXS164) in families with X-linked muscular dystrophy. Lancet ii:104 only, 1986
Burghes AHM, Logan C, Hu X, Belfall B, Worton RG, Ray PN: A cDNA clone from the Duchenne/Becker muscular dystrophy gene. Nature 328:434–437, 1987
Naora H, Deacon NJ: Relationship between the total size of exons and introns in protein-coding genes of higher eukaryotes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 79:6196–6200, 1982
Wood DS, Zeviani M, Prelle A, Bonilla E, Salviati G, Miranda AT, DiMauro S, Rowland LP: Is nebulin the defective gene product in Duchenne muscular dystrophy? N Engl J Med 316:107–108, 1987
Naora H, Deacon NJ: Clustered genes require extragenic territorial DNA sequences. Differ 21:1–6, 1982
Orkin SH: Reverse genetics and human disease. Cell 47:845–850, 1986
Campuzano S, Caramolino L, Cabrera CV, Ruiz-Gomez M, Villares R, Boronat A, Modolell J: Molecular genetics of the achaete-scute gene complex of D. melanogaster. Cell 40:327–338, 1985
Villares R, Cabrera CU: The achaete-scute gene complex of D. melanogaster: conserved domains in a subset of genes required for neurogenesis and their homology to myc. Cell 50:415–424, 1987
Antonarakis S, Kazazian HH, Orkin SH: DNA polymorphism and molecular pathology of the human globin clusters. Hum Genet 69:1–14, 1985
Yen PH, Allen E, Marsh B, Mohandas T, Wang N, Taggart RT, Shapiro LJ: Cloning and expression of steroid sulfatase cDNA and the frequent occurrence of deletions in STS deficiency: implications for XY interchange. Cell 49:443–454, 1987
Gillard EF, Attara NA, Yates JRW, Goudel DR, Lambert J, Aitken DA, Ferguson-Smith MA: Deletion of a DNA sequence in eight of nine families with X-linked ichthyosis (steroid sulphatase deficiency). Nucl Acids Res 15:3977–3985, 1987
Rouyer F, Simmler MC, Johnsson C, Vergnaud G, Cooke JH, Weissenbach J: A gradient of sex linkage in the pseudoautosomal region of the human sex chromosomes. Nature 319:291–295, 1986
Burgoyne PS: Mammalian X and Y crossover. Nature 319:258–259, 1986
Keitges E, Rivest M, Siniscalco M, Gartler SM: X-linkage of steroid sulfatase in the mouse is evidence for a functional Ylinked allele. Nature 315:226–227, 1985
Harbers K, Soriano P, Muller U, Jaenisch R: High frequency of unequal recombination in pseudoautosomal regions shown by proviral insertion in transgenic mouse. Nature 324:682–685, 1987
Goodfellow PJ, Darling SM, Thomas NS, Goodfellow PN: A pseudoautosomal gene in man. Science 243:740–743, 1986
Bengston BO, Goodfellow PN: The effect of recombination between the X and Y chromosomes of mammals. Ann Hum Genet 52:57–64, 1987
Moses MJ, Counce SJ, Paulson DF: Synaptonemal complex complement of man in spreads of spermatocytes with details of the sex chromosome pair. Science 187:363–365, 1975
Tres LL: Extensive pairing of the XY bivalent in mouse spermatocytes as visualized by whole mount electron microscopy. J Cell Sci 25:1–15, 1977
Raman R, Nauda I, Singh AP: Mammalian sex chromosomes. II. Pairing and alignment of the X and Y chromosomes of the pygmy mouse, Mus dunni. Cytogenet Cell Genet 45:38–43, 1987
Winter RM, Penbray ME: Does unequal crossing over contribute to the mutation rate in Duchenne muscular dystrophy? Am J Med Genet 12:437–441, 1982
Bertelson CJ, Bartley J, Monaco AP, Colletti-Feener C, Fischbeck K, Kunkel LM: Localisation of Xp21 meiotic exchange points in Duchenne muscular dystrophy families. J Med Genet 23:531–535, 1986
Smith GP: Evolution of repeated DNA sequences by unequal crossover. Science 191:528–535, 1976
Polani PA: Pairing of X and Y chromosomes, noninactivation of X-linked genes, and the maleness factor. Hum Genet 60:207–211, 1982
Brockdorff N, Cross GS, Cavanna JS, Fisher EMC, Lyon MF, Davies KE, Brown SDM: The mapping of a cDNA from the human X-linked Duchenne muscular dystrophy gene to the mouse X-chromosome. Nature 328:166–170, 1987
Soriano P, Keitges EA, Schorderet DF, Harbers K, Gartler SM, Jaenisch R: High rate of recombination and double crossovers in the mouse pseudoautosomal region during male meiosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:7218–7220, 1987
Mohandas T, Shapiro LJ, Sparkes RS, Sparkes MC: Regional assignment of the steroid sulfatase-X-linked ichthyosis locus; implications for a non inactivated region in the short arm of the human X-chromosome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 76:5779–5783, 1979
Craig IW, Goodfellow PN: Biology of disease. Molecular genetics of the X-chromosome and X-linked diseases. Lab Invest 54:241–253, 1986
Hoffman EP, Monaco AP, Feener CC, Kunkel LM: Conservation of the Duchenne muscular dystrophy gene in mice and humans. Science 238:347–350, 1987
Leff SE, Rosenfeld MG, Evenas RM: Complex transcriptional units: diversity in gene expression by alternative RNA processing. Ann Rev Biochem 55:1091–1117, 1986
Breitbart RE, Andreadis A, Naudl-Girard B: Alternative splicing: a ubiquitous mechanism for the generation of multiple protein isoforms from single genes. Ann Rev Biochem 56:467–495, 1987
Smith TJ, Wilson L, Kenwrick SJ, Forrest SM, Speer A, Coutelle C, Davies KE: Isolation of a conserved sequence in Duchenne muscular dystrophy patients. Nucl Acids Res 15:2167–2174, 1987
Worton RG: Molecular analysis of Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophy. BioAssays 7:57–62, 1987
Boyd Y, Buckle VJ, Holt SM, Munro EA, Hunter D, Craig IW: Muscular dystrophy in girls with X:autosome translocations. J Med Genet 23:484–490, 1986
Hammonds R: Protein sequence of DMD gene is related to actin-binding domain of alpha-actinin. Cell 51:1 only, 1987
Richardson JS: The anatomy and taxonomy of protein structure. Adv Prot Chem 34:167–339, 1981
Perutz MF: X-ray analysis, structure and function of enzymes. Eur J Biochem 8:455–456, 1969
Blake CCF, Koenig DF, Mair GA, North ACT, Phillips DC, Sarma VR: Structure of hen egg-white lysozyme. Nature 206:757–761, 1965
Perutz MF: Structure and mechanism of haemoglobin. Brit Med Bull 32:195–208, 1976
Wistow GJ, Mulders WN, de Jang WW: The enzyme lactate dehydrogenase as a structural protein in avian and crocodilian lenses. Nature 326:622–624, 1987
Kurosky A, Barnett DR, Lee TH, Touchstone B, Hay RE, Arnot MS, Bowman BH, Fitch WM: Covalent structure of human haptoglobin: a serine protease homolog. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 77:3388–3392, 1980
McLean JW, Tomlinson Je, Kuang WJ, Eaton DL, Chen EY, Fless GM, Scanu AM, Lawn RM: cDNA sequence of human apolipoprotein (a) is homologous to plasminogen. Nature 330:132–137, 1987
Infante JP: Impaired glycerophosphorylcholine synthesis in murine muscular dystrophy. Med Biol 63:81–87, 1985
Busch WA, Stromer MH, Goll DE, Suzuki A: Ca2+-specific removal of the Z lines from rabbit skeletal muscle. J Cell Biol 52:367–381, 1972
Sugita H, Nonak I, Itoh Y, Asakura A, Hu DH, Kimura S, Maruyama K: Is nebulin the product of Duchenne muscular gene? Proc Japan Acad 6313:107–108, 1987
Hoffman EP, Knudson CM, Campbell KP, Kunkel LM: Subeellular fractionation of dystrophin to the triads of skeletal muscle. Nature 330:754–758, 1987
Hoffman EP, Brown RH, Kunkel LM: Dystrophin: the protein product of the Duchenne muscular dystrophy locus. Cell 51:919–928; 1987
East JM, Colyer J, Lee AG: Inhibition of sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium pump by monoclonal antibodies. Biochem Soc Trans 15:464–465, 1987
Lev AA, Feener CC, Kunkel LM, Brown RH: Expression of the Duchenne muscular dystrophy gene in cultured muscle cells. J Biol Chem 262:15817–15820, 1987
Bulfield G, Siller WG, Wight PA, Moore KJ: X-hromosome-linked muscular dystrophy (mdx) in the mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81:1189–1192, 1984
Henry EW Cowan JS, Sidman RL: Comparison of trembler and trembler-J mouse phenotypes: varying severity of peripheral hypomyelination. J Neuropath Exp Neurol 42:688–706, 1983
Bridges LR: The association of cardiac muscle necrosis and inflamation with the degenerative and persistent myopathy of MDX mice. J Neurol Sci 72:147–157, 1986
Chamberlain JS, Reeves AA, Mullins LJ, Stephenson DA, Hoffman EP, Monaco AP, Kunkel LM, Caskey CT, Chapman VW: Regional localization of the murine muscular dystrophy gene on the mouse X chromosome. Somatic Cell Mol Genet 13:671–678, 1987
Beam KG, Knudson CM, Powell JA: A lethal mutation in mice eliminates the slow calcium current in skeletal muscle cells. Nature 320:168–170, 1986
Rieger F, Bournaud R, Shimahara T, Garcia L, Ninco-Raymond M, Romey G, Lazdunski M: Restoration of dysgenic muscle contraction and calcium channel function by co-culture with normal spinal cord neurons. Nature 330:563–566, 1987
Mitchell RD, Palade P, Fleischer SJ: Purification of morphologically intact triad structures from skeletal muscle. J Cell Biol 96:1008–1016, 1983
Max SR, Garbus J, Wehman HJ: Simple rapid procedure for rapid isolation of functionally intact mitochondria from human and rat skeletal muscle. Anal Biochem 46:576–584, 1972
de Duve C: The mitochondrial fraction. Biochem Soc Trans 7:823–835, 1979
Hedman R: Properties of isolated skeletal-muscle mitochondria from rat: Exp Cell Res 38:1–12, 1965
Busch HFM, Scholte HR: Early changes of muscle mitochondria in Duchenne dystrophy. J Neurol Sci 45:217–234, 1980
Palmer JW, Tandler B, Hoppel CL: Biochemical properties of subsarcolemmal and interfibrillar mitochondria isolated from cardiac muscle. J Biol Chem 252:8731–8739, 1977
Okano G, Matsuzaka H, Shimojo T Study of the lipid composition of white, intermediate, red and heart muscle in rats. Biochim Biophys Acta 619:167–175, 1982
Infante JP: De novo CDP-choline-dependent glycerophosphorylcholine synthesis and its involvement as an intermediate in phosphatidylcholine synthesis. FEBS Lett 214:149–152, 1987
Tinoco J: Dietary requirements and functions of alphalinolenic acid in mammals. Prog Lipid Res 21:1–45, 1982
Infante JP: Biosynthesis of acyl-specific glycerophospholipids in mammalian tissues. Postulation of new pathways. FEBS Lett 170:1–14, 1984
Infante JP: Docosahexaenoate-containing phospholipids in sarcoplasmic reticulum and retinal photoreceptors. A proposal for a role in Ca2+-ATPase calcium transport. Mot Cell Biochem 74:111–116, 1987
Kenwrick S, Patterson M, Speer A, Fischbeck K, Davies K: Molecular analysis of the Duchenne muscular dystrophy region using pulsed field gel electrophoresis. Cell 48:351–357, 1987
Benam FJ, Hodgkinson S, Davies KE: A glyceraldehyde-3phosphate dehydrogenase pseudogene on the short arm of the human X chromosome defines a multigene family. EMBO J 3:1635–1640, 1984
Hanauer A, Mandel JL: The glyceraldehyde 3 phosphate dehydrogenase gene family: structure of a human cDNA and of an X chromosome linked pseudogene; amazing complexity of the gene family. EMBO J 3:2627–2633, 1984
Otto J, Argos P, Rossman G: Prediction of secondary structural elements in glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase by comparison with other dehydrogenases. Eur J Biochem 109:325–330, 1980
Boer PH, Adra CN, Lau YF, McBurney MW: The testesspecific phosphoglycerate kinase gene pgk-2 is a recruited retroposon. Mol Cell Biol 7:3107–3112, 1987
Dunger DB, Pembry M, Pearson P, Whitfield A, Davies KE, Lake B, Williams D, Dillon MJD: Deletion on the X chromosome detected by direct DNA analysis in one of two unrelated boys with glycerol kinase deficiency, adrenal hypoplasia, and Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Lancet i:585–587, 1986
Renier WO, Nabbel FAE, Hustinx TWJ, Veerkamp JH, Orten BJ, Ter Laak HJ, Ter Haar BGA, Gabreels FJM: Congenital adrenal hypoplasia, progressive muscular dystrophy, and severe mental retardation, in association with glycerol kinase deficiency, in male sibs. Clin Genet 24:243–251, 1983
McCabe ERB: Human glycerol kinase deficiency: an inborn error of compartmental metabolism. Biochem Med 30:215–230, 1983
Infante JP: De novo sn-glycerol-3-phosphorylcholine synthesis activity in lung and muscle and its subcellular location. Mol Cell Biochem 71:135–137, 1986
Burt CT, Pluskal MG, Sreter FA: Generation of phosphodiesters during fast-to-slow muscle transformation. Biochim Biophys Acta 721:492–494, 1982
Gutmann E: The multiple regulation of muscle fiber pattern in cross striated muscle. Nova Acta Leopold 38:193–218, 1973
Villa-Moruzzi E, Locci-Cubbeddu T, Bergamini E: Developmental changes in glycogen enzymes in fast and slow muscles of the rat. Growth 43:73–79, 1979
Mann WS, Salafsky B: Enzyme and physiological studies on normal and diseased developing fast and slow cat muscles. J Physiol 20B:33–47, 1970
lonasescu V, Monaco L, Sandra A, Ionasescu R, Burmeister L, Deprosse C, Stern LZ: Alterations in lipid incorporation in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. J Neurol Sci 50:249–257, 1981
Ohno S: Ancient linkage groups and frozen accidents. Nature 244:259–262, 1967
Lundin LG: Evolutionary conservation of large chromosomal segments in mammalian gene maps. Clin Genet 16:72–81, 1979
Hagve TA, Christopherson BO: Sex-related differences in desaturation and chain elongation of essential fatty acids studied in isolated rat hepatocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta 920:149–154, 1987
Bjornstad P, Bremer J: In vivo studies on pathways for the biosynthesis of lecithin in the rat. J Lipid Res 7:38–45, 1966
Lyman RL, Hopkins SM, Sheehan G, Tinoco J: Effects of estradiol and testerone on the incorporation and distribution of [Me-14C]methionine methyl in rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta 152:197–207, 1968
Panagia V, Okumura K, Makino N, Dhalla NS: Stimulation of Ca2+-pump in heart rat sarcolemma by phosphatidylethanolamine N-methylation. Biochim Biophys Acta 856:383–387, 1986
Boyle DM, Suarez CP, Dean WL: Effect of in vivo changes in phospholipid composition on liver microsomal calcium transport. Cell Calcium 5:475–485, 1984
Hyser CL, Province M, Griggs RC, Mendell JR, Fenichel GM, Brooke MH, Miller JP, Palakowska R, Doherty RA, Quirk SQ: Genetic heterogeneity in Duchenne dystrophy. Ann Neurol 22:553–555, 1987
Cross GS, Speer A, Rosenthal A, Forrest SM, Smith TJ, Edwards Y, Flint T, Hill D, Davies KE: Deletions of fetal and adult muscle cDNA in Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophy patients. EMBO J 6:3277–3283, 1987
Thompson MW, Ludvigsen B, Monkton G: Some problems in genetics of muscular dystrophy. Rev Canad Biol 21:543–550, 1962
Beckman R, Jerusalem F: Male carriers of Duchenne-type muscular dystrophy? Lancet ii:1138–1139, 1966
Forrest SM, Cross GS, Speer A, Gardner-Medwin D, Burns J, Davies KE: Preferential deletion of exons in Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophies. Nature 329:638–640, 1987
Koh J, Pericak-Vance MA, Yamaoka LH, Hung WY, Worton RG, Lee JE, Kandt RS, Bartlett RJ, Speer MC, Phillips K, Ray PN, Gilbert JR, Siddique T, Roses AD: Inherited deletion at Duchenne dystrophy locus in normal male. Lancet ii:1154–1155, 1987
Darras BT, Franke U: A partial deletion of the muscular dystrophy gene transmitted twice by an unaffected male. Nature 329:556–558, 1987
Zatz M, Betti RTB, Levy JA: Benign Duchenne muscular dystrophy in a patient with growth hormone deficiency. Am J Med Genet 10:301–304, 1986
Zata M, Betti RTB, Frotapessoa O: Treatment of Duchenne muscular dystrophy with growth hormone inhibitors. Am J Med Genet 24:549–566, 1986
Totsuka T, Watanabe K, Kiyono S: Masking of a dystrophic symptom in genotypically dystrophic-dwarf mice. Proc Japan Acad 5713:109–113, 1981
Karpati G, Jacob P, Carpenter S, Prescott S: Hyophysectomy mitigates skeletal muscle fiber damage in hamster dystrophy. Ann Neurol 17:60–64, 1985
Totsuka T, Watanabe K: Some evidence for concurrent involvement of the fore- and hindleg muscles in murine muscular dystrophy. Exp Anim 30:465–470, 1981
McKusick VA: Heritable Disorders of Connective Tissue, 4th ed. Mosby, St. Louis, 1972, pp 1–5
Kuhn TS: The Structure of Scientific Revolutions. University of Chicago Press, Chicago, 1970, p 66
Lakatos I: Falsification and the methodology of scientific research programmes. In: I Lakatos and A Musgrave (eds) Criticism and the Growth of Knowledge. Cambridge University Press, New York, 1970, p 91
Popper KR: The Logic of Scientific Discovery. Harper & Row, New York, 1968, p 106
Bunge M: Scientific Research. I. The Search for System. Springer-Verlag, New York, 1967, p 222
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Infante, J.P., Huszagh, V.A. On the nature of the Duchenne muscular dystrophy locus: a portion of a complex of related gene clusters of recent pseudoautosomal origin?. Mol Cell Biochem 81, 103–119 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00219313
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00219313