Summary
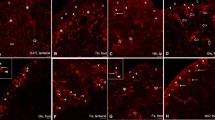
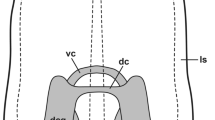
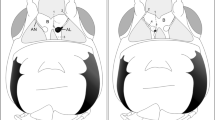
Part of the sensory cells of the earthworm (Lumbricus terrestris) epidermis stain immunocytochemically with enkephalin antisera of different region specificities. The immunocytochemical results suggest the existence of peptides identical with or closely resembling met- and leu-enkephalin in these cells. The processes of enkephalin-immunoreactive cells become collected to form sensory nerves before entering the ventral ganglionic chain where they project as enkephalin-immunoreactive sensory bundles. Injections of the opiate receptor antagonist naloxone in earthworms inhibit their touch-induced withdrawal reflex. Recovery occurs within 2 hours. Moreover, anaesthesia of earthworms in dilute ethanol brings about abolishment of the withdrawal reflex as well as disappearance of enkephalin immunoreactivity from the cell bodies, but not from the sensory hairs. Together, these data suggest that opioid peptides, possibly enkephalins, act as sensory transmitters or modulators in earthworms.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chapman A, Gonzales G, Burrowes WR, Assanah P, Iannone B, Leung MK, Stefano GB (1984) Alterations in high-affinity binding characteristics and levels of opioids in invertebrate ganglia during aging: evidence for an opioid compensatory mechaism. Cell Mol Neurobio 4, 2:143–155
Gesser BP, Larsson L-I (1985) Changes from enkephalin-like to gastrin/cholecystokinin-like immunoreactivity in snail neurons. J Neurosci 5, 6:1412–1417
Gubler U, Seeburg P, Hoffman BJ, Gage LP, Udenfriend S (1982) Molecular cloning establishes proenkephalin as precursor of enkephalin-containing peptides. Nature 295:206–208
Haynes LW (1980) Peptide neuroregulators in invertebrates. Prog Neurobiol 15:205–245
Kakidani H, Furutani Y, Takahashi H, Noda M, Morimoto Y, Hirose T, Asai M, Inayama S, Nakanishi S, Numa S (1982) Cloning and sequence analysis of cDNA for porcine β-neoendorphin/dynorphin precursor. Nature 298:245–249
Kavaliers M, Hirst M, Teskey GC (1983) A functional role for an opiate system in snail thermal behavior. Science 220:99–101
Knapp MF, Mill PJ (1971) The fine structure of ciliated sensory cells in the epidermis of the earthworm Lumbricus terrestris. Tissue Cell 3:623–626
Langdon FE (1895) The sense-organs of Lumbricus agricola. J Morphol 11:193–234
Larsson L-I (1981) Peptide Immunocytochemistry. Prog Histochem Cytochem 13:1–85
Larsson L-I, Rehfeld JF (1977) Evidence for a common evolutionary origin of gastrin and cholecystokinin. Nature 269:335–338
Larsson L-I, Stengaard-Pedersen K (1981) Enkephalin/endorphin related peptides in antropyloric gastrin cells. J Histochem Cytochem 29:1088–1098
Larsson L-I, Stengaard-Pedersen K (1982) Immunocytochemical and ultrastructural differentiation between met-enkephalin, leu-enkephalin and met/leu-enkephalin immunoreactive neurons of feline gut. J Neurosci 2:861–878
Laverack MS (1961) Tactile and chemical perception in earthworms. II Response to acid pH solutions. Comp Biochem Physiol 2:22–34
Leung M, Stefano GB (1983) Isolation of molluscan peptides. Life Sci [Suppl I] 33:77–80
Myhrberg HE (1967) Monoaminergic mechanisms in the nervous system of Lumbricus terrestris L. Z Zellforsch 81:311–343
Noda M, Teranishi Y, Takahashi H, Toyosato M, Notake M, Nakanishi S, Numa S (1982a) Isolation and structural organization of the human preproenkephalin gene. Nature 297:431–434
Noda M, Furutani Y, Kakahashi H, Toyosato M, Hirose T, Inayama S, Nakanishi S, Numa S (1982b) Cloning and sequence analysis of cDNA for bovine adrenal preproenkephalin. Nature 295:202–206
Retzius G (1892) Das Nervensystem der Lumbricinen. Biol Unters N F 3:1–16
Rzasa PJ, Kaloustian KV, Prokop EK (1984) Immunochemical evidence for met-enkephalin-like and leu-enkephalin-like peptides in tissues of the earthworm Lumbricus terrestris. Comp Biochem Physiol 77C: 345–350
Scharrer B (1978) Peptidergic neurons: facts and trends. Gen Comp Endocrinol 34:50–62
Snyder SH (1980) Brain peptides as neurotransmitters. Science 209:976–983
Stefano GB (1982) Comparative aspects of opioid-dopamine interactions. Cell Mol Neurobiol 2:167–178
Stefano GB, Leung M (1984) Presence of Met-enkephalin-Arg6-Phe7 in molluscan neuronal tissue. Brain Res 298:362–365
Stefano GB, Kream RM, Zukin RS, Catapane EJ. Seasonal variation of stereospecific enkephalin binding and pharmacological activity in marine molluscs nervous tissue. Adv Physiol Sci 22:453–458
Sternberger LA (1979) Immunocytochemistry. 2nd edition, Wiley & Sons, New York
Uhler M, Herbert E (1983) Complete amino acid sequence of mouse pro-opiomelanocortin derived from the nucleotide sequence of pro-opiomelanocortin cDNA. J Biol Chem 258:257–261
Viveros OH, Diliberto EJ, Daniels AJ (1983) Biochemical and functional evidence for the cosecretion of multiple messengers from single and multiple compartments. Fed Proc 42:2923–2928
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gesser, B.P., Larsson, LI. Enkephalins may act as sensory transmitters in earthworms. Cell Tissue Res. 246, 33–37 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00218995
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00218995