Summary
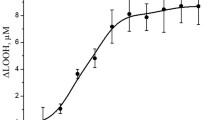
Cultured mouse (J774.1) macrophages accumulated triacylglycerol, but no cholesteryl ester or cholesterol, when incubated in albumin-poor medium with serum-activated lipid particles containing 84 mol% trioleoylglycerol and 9 mol% cholesteryl oleate. Accumulation of triacylglycerol by cells was associated with hydrolysis of particulate triacylglycerol to fatty acid and glycerol. Both acyl and glyceryl moieties of particulate triacylglycerol were recovered in cellular triacylglycerol with a molar ratio of 3.6. The cells also accumulated fatty acid and monoacylglycerol. Whether acylglycerol was taken up as a single molecular species, such as monoacylglycerol, or as several species can not be determined by the present findings. Macrophages incubated with lipid particles for 24 h had many lipid particles attached to cell surfaces and numerous intracellular lipid droplets. The surface film of attached particles was continuous with the outer leaflet of plasma membrane of the cells. Particles partially depleted of core triacylglycerol and collapsed surface films were found attached to surfaces of macrophages. There was no morphological evidence that lipid particles were taken up intact by cells, through endocytosis or phagocytosis. Macrophages incubated with lipid particles also contained intracellular lamellar structures. They varied in size and shape, and were located in the periphery of cells, sometimes near lipid droplets and endoplasmic reticulum. Only 3% of the lamellar structures were associated with lysosomes, indicating they probably were not of lysosomal origin. Lipid particles attached to cells decreased in size and number, and lamellar structures developed at the surface of particles, or replaced the particles, when glutaraldehyde-fixed specimens were incubated at 25° C, demonstrating lipolytic activity at the surface of macrophages. Our findings suggest that particulate triacylglycerol was hydrolyzed by lipoprotein lipase at the surface of macrophages, and that fatty acid and monoacylglycerol formed by lipolysis were transported directly into the cells to be reesterified. When lipolytic products were taken up faster than they could be utilized, they accumulated as lamellar structures in the cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- α MEM:
-
Eagle's alpha modification of minimum essential medium
References
Barka T, Anderson PJ (1983) Histochemistry. Theory, practice, and bibliography. Harper & Row, Publ New York, p 605
Beifrage P, Fredrickson G, Stralfors P, Tornquist H (1984) Adipose tissue lipase. In: B Borgstrom, HL Brockman (eds) Lipases Elsevier, New York, p 365–416
Bieberdorf FD, Chernick SS, Scow RO (1970) Effect of insulin and acute diabetes on plasma FFA and ketone bodies in the fasting rat. J Clin Invest 49:1685–1693
Blanchette-Mackie EJ, Scow RO (1971) Sites of lipoprotein lipase activity in adipose perfused with chylomicrons. Electron microscope cytochemical study. J Cell Biol 51:1–25
Blanchette-Mackie EJ, Scow RO (1973) Effects of lipoprotein lipase on the structure of chylomicrons. J Cell Biol 58:689–708
Blanchette-Mackie EJ, Scow RO (1976) Retention of lipolytic products in chylomicrons incubated with lipoprotein lipase: electron microscope study. J Lipid Res 17:57–67
Blanchette-Mackie EJ, Scow RO (1981) Lipolysis and lamellar structures in white adipose tissue of young rats: Lipid movement in membranes. J Ultrastruct Res 77:295–318
Blanchette-Mackie EJ, Scow RO (1983) Movement of lipolytic products to mitochondria in brown adipose tissue of young rats: an electron microscope study. J Lipid Res 24:229–244
Chait A, Iveruis PH, Brunzell JD (1982) Lipoprotein lipase secretion by human monocyte-derived macrophages. J Clin Invest 69:490–493
Chernick SS (1969) Determination of glycerol in acyl glycerols. Methods Enzymol 14:627–630
Day AJ (1960) Oxidation of 14C-labeled chylomicron fat and 14Clabeled unesterified fatty acids by macrophages in vitro and the effect of clearing factor. Quart J Exp Physiol 45:220–228
Day AJ (1964) The macrophage system, lipid metabolism and antherosclerosis. J Atheroscler Res 4:117–130
Day AJ (1967) Lipid metabolism by macrophages and its relationship to atherosclerosis. Adv Lipid Res 5:185–207
Fredrickson DS, Goldstein JL, Brown MS (1978) The familial hyperlipoproteinemias. In: JG Stanbury, JB Wyngaarden, DS Fredricksen (eds) The metabolic basis of inherited disease. McGraw Hill Book Co., Inc, New York 4th ed. pp 604–655
Gamble W, Vaughan M, Kruth HS, Avigan J (1978) Procedure for determination of free and total cholesterol in microor namogram amounts suitable for studies with cultured cells. J Lipid Res 19:1068–1070
Gianturco SH, Bradley WA, Gotto AM, Morrisett JD, Peary DL (1982) Hypertriglyceridemic very low density lipoproteins induce triglyceride synthesis and accumulation in mouse peritoneal macrophages. J Clin Invest 70:168–178
Hinegardner RT (1971) An improved fluorometric assay for DNA. Anal Biochem 39:197–201
Khoo JC, Mahoney E, Witztum JL (1981) Secretion of lipoprotein lipase by macrophages in culture. J Biol Chem 256:7105–7108
Linder C, Chernick SS, Fleck TR, Scow RO (1976) Lipoprotein lipase and uptake of chylomicron triglyceride by skeletal muscle of rats. Am J Physiol 231:860–864
Lindquist P, Ostlund-Linquist AM, Witzum JL, Steinberg D, Little JA (1983) The role of lipoprotein lipase in the metabolism of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins by macrophages. J Biol Chem 258:9086–9092
Mahoney EM, Khoo JC, Steinberg D (1982) Lipoprotein lipase secretion by human monocytes and rabbit alveolar macrophages in cultures. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 79:1639–1642
Mendelson CR, Scow RO (1972) Uptake of chylomicron-triglyceride by perfused mammary tissue of locating rats. Am J Physiol 23:1418–1423
Nilsson-Ehle P, Egelrud T, Beifrage P, Olivecrona T, Borgstrom B (1973) Positional specificity of purified lipoprotein lipase. J Biol Chem 248:6734–6737
Ostlund-Linquist A-M, Gustafson S, Lindquist P, Witztum JL, Little JA (1983) Uptake and degradation of human chylomicrons by macrophages in culture. Arteriosclerosis 3:433–440
Ralph P, Nakoinz I (1975) Phagocytosis and cytolysis by a macrophage tumour and its cloned cell line. Nature 257:393–394
Ralph P, Prichard J, Cohn M (1975) Reticulum cell sarcoma: an effector cell in antibody-dependent cell-mediated immunity. J Immunol 114:898–905
Schaffner T, Taylor K, Bartucci EJ, Fischer-Dzoga K, Beeson JH, Glagov S, Wissler RW (1980) Arterial foam cells with distinctive immunomorphologic and histochemical features of macrophages. Am J Pathol 100:57–73
Scow RO, Olivecrona T (1977) Effect of albumin on products formed from chylomicron triacylglycerol by lipoprotein lipase in vitro. Biochim Biophys Acta 487:472–486
Scow RO, Hamosh M, Blanchette-Mackie EJ, Evans AJ (1972) Uptake of blood triglyceride by various tissues. Lipids 7:497–505
Scow RO, Blanchette-Mackie EJ, Smith LC (1976) Role of capillary endothelium in the clearance of cylomicrons. A model for lipid transport from blood by lateral diffusion in cell membranes. Circ Res 39:149–162
Scow RO, Blanchette-Mackie EJ, Smith LC (1980) Transport of lipid across capillary endothelium. Fed Proc 39:2610–2617
Spooner PM, Chernick SS, Garrison MM, Scow RO (1979) Development of lipoprotein lipase activity and accumulation of triacylglycerol in differentiating 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J Biol Chem 254:1305–1311
Stein O, Scow RO, Stein Y (1970) FFA-3H uptake by perfused adipose tissue: electron microscopic autoradiographic study. Am J Physiol 219:510–518
Steinberg D (1983) Lipoproteins and atherosclerosis. A look back and a look ahead. Arteriosclerosis 3:283–301
Stoeckenius W, Schulman JH, Prince LM (1960) The structure of myelin figures and microemulsions as observed with the electron microscope. Kollid K 169:110–180
Strunk RC, Payne CM, Nagle RB, Kunke K (1976) Alteration of the structure and function of guinea pig peritoneal macrophages by a soybean oil emulsion. Am J Pathol 96:753–765
Takaski S, Emling F, Leive L (1984) Variants deficient in phagocytosis of latex beads isolated from the murine macrophage-like cell line J774. J Cell Biol 98:2198–2202
Wetzel MG, Scow RO (1984) Lipolysis and fatty acid transport in rat heart: electron microscopic study. Am J Physiol 246: C467-C485
Zinder O, Mendelson CR, Blanchette-Mackie EJ, Scow RO (1976) Lipoprotein lipase and uptake of chylomicron triacylglycerol and cholesterol by perfused rat mammary tissue. Biochem Biophys Acta 431:526–537
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Blanchette-Mackie, E.J., Briggs, T., Chernick, S.S. et al. Lipolysis of serum-activated triacylglycerol at the surface of J774.1 macrophages. Cell Tissue Res. 244, 95–105 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00218386
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00218386