Summary
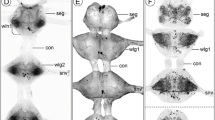
The distribution patterns of serotonin-immunoreactive somata in the cerebral and subpharyngeal ganglion, and in the head and tail ganglia of the nerve cord of Lumbricus terrestris are described from whole-mount preparations. A small number of serotonin-immunoreactive neurons occurs in the cerebral ganglion, in contrast to the large population of serotonin-immunoreactive neurons that exists in all parts of the ventral nerve cord. From the arrangement of serotonin-immunoreactive somata in the subpharyngeal ganglion, we suggest that this ganglion arises from the fusion of two primordial ganglia. In head and tail ganglia, the distribution of serotonin-immunoreactive somata resembles that in midbody segments. Segmental variations in the pattern and number of serotonin-immunoreactive somata in the different body regions are discussed on the background of known developmental mechanisms that result in metameric neuronal populations in annelids and arthropods.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CG1, CG2 :
-
cerebral soma group 1, 2
- CNS :
-
central nervous system
- GINs :
-
giant interneurons
- 5-HT :
-
5-hydroxytryptamine, serotonin
- 5-HTi :
-
5-HT-immunoreactive
- N :
-
side nerve
- SG19 :
-
subpharyngeal soma group 1–9
- SN :
-
segmental nerve
References
Aros B, Vigh B (1961) Neurosecretory activity of the central and peripheral nervous system in the earthworm. Acta Biol Hung 12:169–186
Bate M, Goodman CS, Spitzer NC (1981) Embryonic development of identified neurons: segment specific differences in the H cell homologues. J Neurosci 1:103–106
Beltz BS, Kravitz EA (1983) Mapping of serotonin-like immunoreactivity in the lobster nervous system. J Neurosci 3:585–602
Bishop CA, O'Shea M (1983) Serotonin immunoreactive neurons in the central nervous system of an insect (Periplaneta americana). J Neurobiol 14:251–269
Blue J (1976) Effect of anterior ganglia removal on phototaxis in the earthworm (Lumbricus terrestris). Bull Psychon Soc 7:257–259
Bullock TH (1945) Functional organization of the giant fiber system of Lumbricus. J Neurophysiol 8:57–71
Doolittle JH (1972) The role of anterior ganglia in phototaxis and thigmotaxis in the earthworm. Psychon Sci 27:151–152
Flanagan T, Schley C, Zipser B (1985) Antibody staining reveals novel aspects of segmentation within the leech central nervous system. Brain Res 345:147–152
Friedländer B (1888) Beiträge zur Kenntnis des Centralnervensystems von Lumbricus. Z Wiss Zool 47:47–84
Günther J (1969) Zur Struktur und Funktion der Riesenfaser-Systeme beim Regenwurm Lumbricus terrestris L., mit Hinweisen auf die nervöse Organisation des Bauchmarks. Dissertation, Göttingen
Günther J (1971a) Der cytologische Aufbau der dorsalen Riesenfasern von Lumbricus terrestris L. Z Wiss Zool 183:51–70
Günther J (1971b) Mikroanatomie des Bauchmarks von Lumbricus terrestris L. Z Morphol Tiere 70:141–182
Günther J, Walther JB (1971) Funktionelle Anatomie der dorsalen Riesenfaser-Systeme von Lumbricus terrestris L. (Annelida, Oligochaeta). Z Morphol Tiere 70:253–280
Harris WA (1981) Neural activity and development. Ann Rev Physiol 43:689–710
Henry LM (1947) The nervous system and the segmentation of the head in the annulata. Microentomology 12:83–110
Hess WN (1925) The nervous system of the earthworm Lumbricus terrestris L. J Morphol 40:235–259
Koritsánszky S (1975) Regeneration monoaminhaltiger Nervenzellen und Fasersysteme im Oberschlundganglion des Regenwurms Allolobophora caliginosa. Verh Anat Ges, Fischer, Stuttgart 69:617–624
Koritsánszky S, Hartwig HG (1974) The regeneration of the monoaminergic system in the cerebral ganglion of the earthworm, Allolobophora caliginosa. Cell Tissue Res 151:171–186
Laverack MS (1963) The physiology of earthworms. Pergamon Press, Oxford
Lent CM (1981) Morphology of neurons containing monoamines within leech segmental ganglia. J Exp Zool 216:311–316
Longley AJ, Longley RD (1986) Serotonin immunoreactivity in the nervous system of the dragonfly nymph. J Neurobiol 17:329–338
Marsden CA, Kerkut GA (1969) Fluorescence microscopy of the 5-HT- and catecholamine-containing cells in the CNS of the leech Hirudo medicinalis. J Comp Biochem Physiol 31:851–862
McMahan D (1974) Chemical messengers in development: a hypothesis. Science 185:1012–1021
McManus FE, Wyers EJ (1979) Differentiating ganglionic function in the earthworm. J Comp Physiol Psychol 93:1136–1144
McManus FE, Mendelson T, Wyers EJ (1982) The brain and central control in the earthworm. Behav Neural Biol 35:1–16
Meinhardt H (1977) A model of pattern formation in insect embryogenesis. J Cell Sci 23:117–139
Meinhardt H (1984) Models for positional signalling, the threefold subdivision of segments and the pigmentation pattern of molluscs. J Embryol Exp Morphol [Suppl] 83:289–311
Mittenthal JE, Wine JJ (1978) Segmental homology and variation in flexor motoncurons of the crayfish abdomen. J Comp Neurol 177:311–334
Moment GB (1946) A study of growth limitation in earthworms. J Exp Zool 103:487–506
Myhrberg HE (1967) Monoaminergic mechanisms in the nervous system of Lumbricus terrestris (L.). Z Zellforsch 81:311–343
Myhrberg HE (1972) Ultrastructural localisation of monoamines in the central nervous system of Lumbricus terrestris (L.) with remarks on ncurosecretory vesicles. Z Zellforsch 126:348–362
Nevmyvaka GA (1967) The nervous system of the earthworm. (English translation) National Lending Library for Science and Technology, Boston
Ogawa F (1939) The nervous system of earthworm (Pheretima comunissima) in different ages. Sci Rep Tohoku Univ Ser 4, 13:395–488
Prosser CL (1934) The nervous system of the earthworm. Q Rev Biol 9:182–200
Retzius G (1892) Das Nervensystem der Lumbricinen. Biol Untersuch 3:1–16
Rude S (1969) Monoamine-containing neurons in the nerve cord and body wall of Lumbricus terrestris. J Comp Neurol 128:397–412
Rude S (1966) Monoamine-containing neurons in the central nervous system and peripheral nerves of the leech Hirudo medicinalis. J Comp Neurol 136:349–372
Smith PH, Mittenthal JE (1980) Intersegmental variation of afferent pathways to giant interneurones of the earthworm, Lumbricus terrestris L. J Comp Physiol 140:351–363
Spörhase-Eichmann U, Gras H, Schürmann FW (1987) Patterns of serotonin-immunoreactive neurons in the central nervous system of the earthworm Lumbricus terrestris L. I Ganglia of the ventral nerve cord. Cell Tissue Res 249:601–614
Stewart RR, Macagno ER (1984) The development of segmental differences in cell number in the CNS of the leech. Soc Neurosci Abstr 10:152.5
Stuart DK, Glover JC, Blair SS, Weisblatt DA (1983) Development of leech serotonin neurons examined with serotonin antibody, cell lineage tracer, and cell killing. Soc Neurosci Abstr 9:179.7
Taghert PH, Goodman CS (1984) Cell determination and differeniation of identified serotonin-immunoreactive neurons in the grasshopper embryo. J Neurosci 4:989–1000
Tomkins GM (1975) The metabolic code. Science 189:760–763
Tyrer NM, Turner JD, Altmann JS (1984) Identifiable neurons in the locust central nervous system that react with antibodies to serotonin. J Comp Neurol 227:313–330
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Spörhase-Eichmann, U., Gras, H. & Schürmann, FW. Patterns of serotonin-immunoreactive neurons in the central nervous system of the earthworm Lumbricus terrestris L.. Cell Tissue Res. 249, 625–632 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00217334
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00217334