Summary
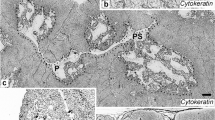
Interdigitating cells are non-lymphoid elements in the thymus and peripheral, secondary lymphoid organs of higher vertebrates. Their origin and functional significance are a matter of controversy. In the present investigation we analyze, for the first time, the nature of presumptive interdigitating cells of the thymus of an ectothermic vertebrate, the turtle Mauremys caspica. This model is specially useful because of the seasonal variations that affect the reptilian lymphoid organs. Immature pro-interdigitating cells and phagocytosing mature interdigitating cells are described with special emphasis on their ultrastructural characteristics and possible relationships with monocytes and macrophages.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Duijvestijn AM, Hoefsmit ECM (1981) Ultrastructure of the rat thymus: the microenvironment of T-lymphocyte maturation. Cell Tissue Res 218:279–292
Duijvestijn AM, Köhler YG, Hoefsmit ECM (1982a) Interdigitating cells and macrophages in the acute involuting rat thymus. An electron microscopy study on phagocytic activity and population development. Cell Tissue Res 224:291–301
Duijvestijn AM, Sminia T, Köhler YG, Janse EM, Hoefsmit ECM (1982b) Rat thymus micro-environment. An ultrastructural and functional characterization. In: Nieuwenhuis P, van der Broek AA, Hanna Jr MG (eds) In vivo immunology. Histophysiology of the lymphoid system. Plenum Publ, New York, p 441
Fonfria J, Barrutia MG, Villena A, Zapata A (1982) Ultrastructural study of interdigitating cells in the thymus of the spotless starling Sturnus unicolor. Cell Tissue Res 225:687–691
Gaudecker B von, Müller-Hermelink HK (1980) Ontogeny and organization of the stationary non-lymphoid cells in the human thymus. Cell Tissue Res 207:287–306
Gaudecker B von, Müller-Hermelink HK (1982) The development of the human tonsilla palatina. Cell Tissue Res 224:579–600
Groscurth P (1980) Non-lymphatic cells in the lymph node cortex of the mouse. I. Morphology and distribution of the interdigitating cells and the dendritic retuclar cells in the mesenteric node of the adult IRC mouse. Pathol Res Pract 169:212–234
Hoefsmit ECM, Kamperdijk EWA, Hendrichs HR, Beelen RHI, Balfour BM (1980) Lymph node macrophages. In: Carr I, Daems WT (eds) The reticulo-endothelial system. A comprehensive treatise, vol 1 Morphology. Plenum Publ, New York, p 417
Kaiserling E, Lennert K (1974) Die interdigitierenden Reticulumzellen im menschlichen Lymphknoten. Virchows Arch B 16:51–61
Kaiserling E, Stein H, Müller-Hermelink HK (1974) Interdigitating reticulum cells in the human thymus. Cell Tissue Res 155:47–55
Kamperdijk EWA (1980) Lymph node macrophages and reticulum cells in the immune response. PhD Thesis, University of Amsterdam, The Netherlands
Kamperdijk EWA, Raaymakers EM, de Leeuw JHS, Hoefsmit ECM (1978) Lymph node macrophages and reticulum cells in the immune response. I. The primary response to paratyphoid vaccine. Cell Tissue Res 192:1–23
Rausch E, Kaiserling E, Goos M (1977) Langerhans cells and interdigitating reticulum cells in the thymus-dependent regions in human dermatophic lymphoadenitis. Virchows Arch B 25:327–343
Veerman AJP (1974) On the interdigitating cells in the thymusdependent area of the rat spleen: a relationship between the mononuclear phagocyte system and T-lymphocytes. Cell Tissue Res 148:247–257
Veerman AJP, Ewijk W van (1975) White pulp compartments in the spleen of rat and mice. Cell Tissue Res 156:416–441
Veldman JE (1970) Histophysiology and electron microscopy of the immune response. Part 1 and 2. PhD Thesis, Groningen, The Netherlands
Veldman JE, Kaiserling E (1980) Interdigitating cells. In: Carr I, Daems WT (eds) The reticulo-endothelial system. A comprehensive treatise, vol 1 Morphology. Plenum Publ, New York, p 381
Villena A, Zapata A, Rivera-Pomar JM, Barrutia MG, Fonfria J (1983) Structure of the non-lymphoid cells during the postnatal development of the rat lymph nodes. Fibroblastic reticulum cells and interdigitating cells. Cell Tissue Res 229:219–232
Zapata A, Fernandez J (1983) The thymus of reptiles: emphasizing Lacerta hispanica and Elaphe scalaris with comparison to other vertebrates. Dev Comp Immunol, in press
Zapata A, Garrido E, Leceta J, Gomariz RP (1983) Relationships between neuroendocrine and immune systems in amphibians and reptiles. Dev Comp Immunol, 7: sup 3, 347–351
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Leceta, J., Villena, A., Razquin, B. et al. Interdigitating cells in the thymus of the turtle Mauremys caspica . Cell Tissue Res. 238, 381–385 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00217311
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00217311