Summary
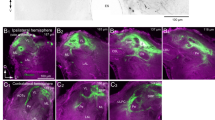
Within the central part of the brain in male crickets (Acheta domesticus) 150 local interneurons were recorded intracellularly and consequently stained with either Lucifer Yellow CH or cobaltous sulphide. The shapes of the injected cells were reconstructed from serial sections and drawn to scale using known brain regions as landmarks.
Several types of neurons were encountered, which differ in their topographical relationships to the mushroom bodies and the central body. Extensive branching was often found in the calyces or the lobes of the mushroom bodies, within the lateral protocerebral neuropil and in the columns of the central body.
These neurons connect different parts of the brain with the neuronal assemblies of the mushroom bodies and the central body, structures, which are considered to participate in the control of complex behavior. The role of the mushroom body with respect to its connectivity to other brain areas and various feedback loops is discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bacon J, Altman JS (1977) Silver intensification of cobalt filled neurons in intact ganglia. Brain Res 138:359–363
Bacon J, Tyrer NM (1978) The tritocerebral commissure giant: A bimodal interneuron in the locust. J Comp Physiol 126:317–325
Boyan GS (1980) Auditory neurons in the brain of the cricket Gryllus bimaculatus (de Geer). J Comp Physiol 140:81–93
Erber J (1978) Response characteristics and aftereffects of multimodal neurons in the mushroom body of the honey bee. Physiol Ent 3:77–89
Erber J, Masuhr T, Menzel R (1980) Localization of short-term memory in the brain of the bee Apis mellifera. Physiol Ent 5:343–358
Ernst KD, Boeckh J, Boeckh V (1977) A neuroanatomical study on the organization of the central antennal pathways in insects. Cell Tissue Res 176:285–308
Fraser-Rowell CH (1963) A general method for silvering invertebrate central nervous systems. Quart J Micr Sci 104:81–87
Goll W (1967) Strukturuntersuchungen am Gehirn von Formica. Morph Ökol Tiere 59:143–210
Hanström B (1928) Vergleichende Anatomie des Nervensystems der wirbellosen Tiere. Springer Berlin 1928
Homberg U (1981) Ableitungen und Lucifer-Yellow Markierungen von Neuronen des Tractus-olfactorius-globularis im Bienengehirn. Verh dt zool Ges 74:176
Homberg U, Erber J (1979) Response characteristics and identification of extrinsic mushroom body neurons of the bee. Z Naturforsch 340:612–615
Honegger HW, Schürmann FW (1975) Cobalt sulphide staining of optic fibers in the brain of the cricket Gryllus campestris. Cell Tissue Res 159:213–225
Huber F (1960) Untersuchungen über die Funktion des Zentralnervensystems und insbesondere des Gehirns bei der Fortbewegung und der Lauterzeugung der Grillen. Z vergl Physiol 44:60–132
Kenyon CF (1896) The brain of the bee. J Comp Neurol 6:133–210
O'Shea M, Rowell CHF (1977) Complex neural integration and identified interneurons in the locust brain. In: Hoyle G (ed) Identified neurons and behavior of arthropods. Plenum Press, New York, pp 307–328
Otto D (1971) Untersuchungen der zentralnervösen Kontrolle der Lauterzeugung der Grillen. Z vergl Physiol 44:60–132
Pearson L (1971) The corpora pedunculata of Sphinx ligustri L and other Lepidoptera. Phil Trans Roy Soc Lond B 259:477–516
Schildberger K (1981) Some physiological features of mushroom-body linked fibers in the house cricket brain. Naturwiss 67:623
Schildberger K (1982) Untersuchungen zur Struktur und Funktion von Interneuronen im Pilzkörperbereich der Hausgrille Acheta domesticus. Diss Göttingen
Schürmann FW (1970) Über die Struktur der Pilzkörper des Insektenhirns: I. Synapsen im Pedunculus. Z Zellforsch 103:365–381
Schürmann FW (1972) Über die Struktur der Pilzkörper des Insektenhirns: II. Synaptische Schaltungen im Alpha-Lobus des Heimchens. Z Zellforsch 127:240–257
Schürmann FW (1973) Über die Struktur der Pilzkörper des Insektenhirns: III. Die Anatomie der Nervenfasern in den Corpora pedunculata. Z Zellforsch 145:247–285
Schürmann FW (1974) Bemerkungen zur Funktion der Corpora pedunculata im Gehirn aus morphologischer Sicht. Exp Brain Res 19:406–432
Stewart WW (1978) Functional connections between cells as revealed by dye-coupling with a highly fluorescent naphtalimide tracer. Cell 14:741–759
Strausfeld NJ (1976) Atlas of an insect brain. Springer, New York Heidelberg Berlin
Vowles DM (1955) The structure and connections of the corpora pedunculata in bees and ants. Quart J Micr Sci 96:239–255
Wadepuhl M, Huber F (1979) Elicitation of singing and courtship movements by electrical stimulation of the brain of the grasshopper. Naturwiss 66:230
Weiss MJ (1974) Neuronal connections and the function of the corpora pedunculata of the American cockroach Periplaneta americana. J Morphol 142:21–69
Weiss MJ (1981) Structural patterns in the corpora pedunculata of Orthoptera: A reduced silver analysis. J Comp Neurol 203:515–553
Williams JLD (1975) Anatomical studies of the insect central nervous system: a ground plan of the midbrain and an introduction to the central complex in the locust Schistocerca gregaria. J Zool Lond 176:67–86
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schildberger, K. Local interneurons associated with the mushroom bodies and the central body in the brain of Acheta domesticus . Cell Tissue Res. 230, 573–586 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00216202
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00216202