Summary
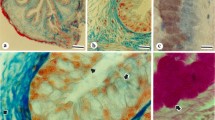
Light-microscopic autoradiography was used to localize the cellular sites for neutral amino acid uptake in submandibular and sublingual salivary gland epithelia. The vasculature of isolated glands was perfused for 3–5 min with either L-(3-3H)serine or L-(4-3H)phenylalanine and then fixed by perfusion with buffered glutaraldehyde. In the submandibular gland the small neutral amino acid L-serine and the aromatic amino acid L-phenylalanine were localized to central acinar cells, demilunar cells and ductal cells. In the sublingual gland silver grains associated with each of these tritiated amino acids were localized to central acinar and ductal cells. Perfusion of both submandibular and sublingual glands with unlabelled L-serine (25 mM) or L-phenylalanine (30 mM) resulted in a significant decrease in the silver grain density associated with each labelled amino acid. The absence of silver grains in the lumina of acinar and ductal cells and the presence of tight junctions near the apical surface of the epithelium strongly suggest that the initial uptake of these amino acids was mediated by basolateral plasma membrane carriers.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bustamante JC, Mann GE, Yudilevich DL (1981) Specificity of neutral amino acid uptake at the basolateral side of the epithelium in the cat salivary gland in situ. J Physiol 313:65–79
Christensen HN (1979) Exploiting amino acid structure to learn about membrane transport. Adv Enzymol 49:41–101
Hirji KN (1982) Autoradiographic observations on the incorporation of amino acids into esophageal, gastric and pancreatic glands in the leopard frog Rana pipiens. Cell Tissue Res 226:195–200
Hopwood D (1972) Theoretical and practical aspects of glutaraldehyde fixation. Histochem J 4:267–303
Lindsay RH, Catanzaro OL, Ueha T, Hanson RW (1969) Site of amino acid transfer in dog parotid glands. Am J Physiol 217:1025–1029
Mann GE, Yudilevich DL (1984) Discrimination of parallel neutral amino acid transport systems in the basolateral membrane of cat salivary epithelium. J Physiol 347:111–127
Mann GE, Møller M, Poulsen J, Hedemark (1982) Autoradiographic localization of L-serine uptake at the basolateral interface of acinar and ductal epithelium in the cat salivary gland. J Physiol 332:75P
Mann GE, Smaje EH, Yudilevich DE (1979) Permeability of the fenestrated capillaries in the cat submandibular gland to lipidinsoluble molecules. J Physiol 297:335–354
Mann GE, Wilson SM Yudilevich DE (1984) Characteristics of a cationic amino acid transport system in the basolateral membrane of the cat salivary epithelium. J Physiol 351:123–134
Oxender DE, Christensen HN (1963) Distinct mediating systems for the transport of neutral amino acids by the Ehrlich cell. J Biol Chem 237:3686–3699
Snedcor GW, Cochran WG (1969) Statistical methods. Iowa State University Press, Iowa, p 128
Yudilevich DL, Mann GE (1982) Unidirectional uptake of substrates at the blood side of secretory epithelia: stomach, salivary gland and pancreas. Fed Proc 41:3045–3053
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mann, G.E., Møller, M., Hedemark Poulsen, J. et al. Autoradiographic localization of transported neutral amino acids in epithelia of cat submandibular and sublingual salivary glands. Cell Tissue Res. 246, 353–358 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00215897
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00215897