Summary
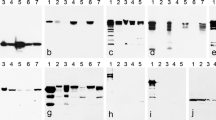
The occurrence of tight junctions between Sertoli cells, providing the structural basis of the blood-testis barrier, has been studied using hypertonic fixative and lanthanum tracer in the testes of seven species of vertebrates having different testicular organization. In all cases inter-Sertoli tight junctions, establishing an effective barrier, appear either when meiosis is complete (teleosts and amphibians, both with cystic testes) or immediately after the onset of meiosis (reptiles and birds, both having testes consisting of seminiferous tubules). In the cystic testes, tight junctions are regularly associated with desmosomes, whereas in testes with seminiferous tubules, cisternae of the endoplasmic reticulum are present beneath the junctions (subsurface cisternae). The avian testes examined have, in addition, septate-like junctions between the Sertoli cells but before the tight junctions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abraham M, Rahamin E, Tibika H, Golenser E, Kieselstein M (1980) The blood-testis barrier in Aphanius dispar (Teleostei). Cell Tissue Res 211:207–214
Baccetti B, Bigliardi E, Talluri MV, Burrini AG (1983) The Sertoli cell in lizards. J Ultrastruct Res 85:11–23
Bergmann M, Dierichs R (1983) Postnatal formation of the blood-testis barrier in the rat with special reference to the initiation of meiosis. Anat Embryol 168:269–275
Bergmann M, Greven H, Schindelmeiser J (1983) Observations on the blood-testis barrier in a frog and a salamander. Cell Tissue Res 232:189–200
Billard R (1970) La spermatogenése de Poecilia reticulata. III. Ultrastructure des cellules de Sertoli. Ann Biol Anim Biochim Biophys 10:37–50
Breucker H (1982) Seasonal spermatogenesis in the mute swan (Cygnus olor). In: Beck F, Hild W, van Limborgh J, Ortmann R, Pauli JE, Schiebler TH (ededs) Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol, Vol 72, 1–94
Brown NL, Baylé JD, Seanes CG, Follet BK (1975) Chicken gonadotrophins: their effects on the testis of immature and hypophysectomized Japanese quail. Cell Tissue Res 156:499–520
Camatini M, Franchi E, de Curtis I (1979) Sertoli junctions in human testes: a freeze fracture and lanthanum tracer study. J Submicrosc Cytol 11:511–516
Cavicchia JC, Moviglia GA (1983) The blood-testis barrier in the toad (Bufo arenarum Hensel): A freeze fracture and lanthanum tracer study. Anat Rec 205:387–396
Connell CJ (1978) A freeze fracture and lanthanum tracer study of the complex junction between Sertoli cells of the canine testis. J Cell Biol 76:57–75
Connell CJ (1980) Blood-testis barrier formation and the initiation of meiosis in the dog. In: Steinberger A, Steinberger E (eds) Testicular development, structure, and function. Raven Press, New York, pp 71–78
Cooksey EJ, Rothwell B (1973) The ultrastructure of the Sertoli cell and its differentiation in the domestic fowl (Gallus domesticus). J Anat 114:329–345
Dym M (1973) The fine structure of the monkey (Macaca) Sertoli cell and its role in maintaining the blood-testis barrier. Anat Rec 175:639–656
Dym M, Cavicchia JC (1977) Further observations on the blood-testis barrier in monkeys. Biol Reprod 17:390–403
Dym M, Cavicchia JC (1978) Functional morphology of the testis. Biol Reprod 18:1–5
Franchi E, Camatini M, de Curtis I (1982) Morphological evidence of a permeability barrier in urodele testis. J Ultrastruct Res 80:253–263
Lofts B (1974) Reproduction. In: Lofts B (ed) Physiology of the amphibia. Vol II. Academic Press, New York, pp 107–218
Marcaillou C, Szöllösi A (1980) The “blood-testis” barrier in a nematode and a fish: a generalizable concept. J Ultrastruct Res 70:128–136
Meyer R, Posalaky Z, McGinley D (1977) Intercellular junction development in maturing rat seminiferous tubules. J Ultrastruct Res 61:271–283
Nagano T, Suzuki F (1976) The postnatal development of junctional complexes of the mouse Sertoli cells as revealed by freeze fracture. Anat Rec 185:403–418
O'Rand MG, Romrell LJ (1977) Appearance of cell surface auto-and isoantigens during spermatogenesis in the rabbit. Dev Biol 55:347–358
Osman DI, Plöen L (1978) The terminal segment o the seminiferous tubules and the blood-testis barrier before and after efferent ductule ligation in the rat. Int J Androl 1:235–249
Osman DI, Ekwall H, Plöen L (1980) Specialized cell contacts and the blood-testis barrier in the seminiferous tubules of the domestic fowl (Gallus domesticus). Int J Androl 3:553–562
Russell L (1977) Movement of spermatocytes from the basal to the adluminal compartment of the rat testis. Am J Anat 148:313–328
Setchell BP, Waites GMH (1975) The blood-testis barrier. In: Greep RO, Astwood EB (eds) Handbook of physiology, endocrinology. Washington DC: Am Physiol Soc sect 7, vol V, chapt 6, pp 143–172
Tung PS, Fritz IV (1978) Specific surface antigens on rat pachytene spermatocytes and successive classes of germinal cells. Dev Biol 64:297–315
Vitale R, Fawcett DW, Dym M (1973) The normal development of the blood-testis barrier and effects of clomiphene and estrogen treatment. Anat Rec 176:333–344
Waites GMH, Gladwell RT (1982) Physiological significance of fluid secretion in the testis and blood-testis barrier. Physiol Rev 62:624–671
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Dedicated to Prof. Dr. H. Rollhäuser, Münster, on the occasion of his 65th birthday.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bergmann, M., Schindelmeiser, J. & Greven, H. The blood-testis barrier in vertebrates having different testicular organization. Cell Tissue Res. 238, 145–150 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00215155
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00215155