Summary
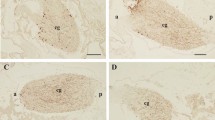
A gastric peptide from the Dungeness crab (Cancer magister), extracted and characterized previously (Larson and Vigna 1983b), was localized in the foregut (stomach) of this species by immunocytochemistry using antisera specific for the bioactive carboxy-terminal amino acid sequence common to gastrins and cholecystokinins (CCKs). Immunoreactivity was found in all gastric epithelial cells and in the procuticle. Electron microscopy revealed an absence of peptidergic secretory granules in the gastric epithelial cells. The pattern of immunostaining suggests that the gastric epithelial cells secrete this peptide apically where it is incorporated into the cuticle lining the lumen. Specific immunostaining could not be demonstrated in various neural ganglia or in the hypodermis. The distribution of this peptide is different from that of gastrin/CCK in vertebrates and other invertebrates. This suggests that the crab gastric peptide is sufficiently similar to gastrin/CCK to react with C-terminal specific antisera, but may be anatomically, functionally, and possibly phylogenetically otherwise unrelated.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barker PL, Gibson R (1977) Observations on the feeding mechanism, structure of the gut, and digestive physiology of the European lobster Homarus gammarus. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 26:297–324
Buchan AMJ, Polak JM, Solcia E, Pearse AGE (1979) Localization of intestinal gastrin in a distinct endocrine cell type. Nature 277:138–140
Dockray GJ (1980) Cholecystokinin in rat cerebral cortex: identification, purification and characterization by immunochemical methods. Brain Res 188:155–166
Dockray GJ (1982) The physiology of cholecystokinin in brain and gut. Br Med Bull 38:253–258
Dockray GJ, Hopkins CR (1975) Caerulein secretion by dermal glands in Xenopus laevis. J Cell Biol 64:724–733
Dockray GJ, Duve H, Thorpe A (1981a) Immunochemical characterization of gastrin/cholecystokinin-like peptides in the brain of the blowfly, Calliphora vomitoria. Gen Comp Endocrinol 45:491–496
Dockray GJ, Williams RG, Zhu W-Y (1981b) Development of region-specific antisera for the C-terminal tetrapeptide of gastrin/cholecystokinin and their use in studies of immunoreactive forms of cholecystokinin in rat brain. Neurochem Int 3:281–288
Factor JR (1981) Development and metamorphosis of the digestive system of larval lobsters, Homarus americanus. J Morphol 169:225–242
Falkmer S, Carraway RE, El-Salhy M, Emdin SO, Grimelius L, Rehfeld JF, Reinecke M, Schwartz TW (1981) Phylogeny of the gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine system: A review. In: Grossman MI, Brazier MAB, Lechago J (eds) Cellular basis of chemical messengers in the digestive system. Academic Press, New York, p 21
Fritsch HR, Van Noorden S, Pearse AGE (1978) Localization of somatostain- and gastrin-like immunoreactivity in the gastrointestinal tract of Ciona intestinalis. Cell Tissue Res 180:181–185
Grimmelikhuijzen CJP, Sundler F, Rehfeld JF (1980) Gastrin/ CCK-like immunoreactivity in the nervous system of coelenterates. Histochemistry 69:61–68
Hackman RH (1971) The integument of Arthropoda. In: Florkin M, Scheer BT (eds) Chemical zoology, Volume 6, Part B. Academic Press, New York, p 1
Iwanaga T, Fujita T, Nishiitsutsuji-Uwo J, Endo Y (1981) Immunohistochemical demonstration of PP-, somatostatin-, enteroglucagon-, and VIP-like immunoreactivities in the cockroach midgut. Biomed Res 2:202–207
Kramer KJ, Speirs RD, Childs CN (1977) Immunochemical evidence for a gastrin-like peptide in insect neuroendocrine system. Gen Comp Endocrinol 32:423–426
Larsson L-I, Rehfeld JR (1977) Evidence for a common evolutionary origin of gastrin and cholecystokinin. Nature 269:335–338
Larson BA, Vigna SR (1983a) Species and tissue distribution of cholecystokinin/gastrin-like substances in some invertebrates. Gen Comp Endocrinol 50:469–475
Larson BA, Vigna SR (1983b) Gastrin/cholecystokinin-like immunoreactive peptides in the Dungeness crab, Cancer magister (Dana): Immunochemical and biological characterization. Regul Pept 7:155–170
Larson BA Scalise FW, Reeve JR Jr., Vigna SR (1982) Immunochemical characterization and localization of gastrin/cholecystokinin-like immunoreactants in the Dungeness crab, Cancer magister. Am Zool 22:949
Locke M (1976) The role of plasma membrane plaques and Golgi complex vesicles in cuticle deposition during the moult/intermoult cycle. In: Hepburn HR (ed) The insect integument. Elsevier, Amsterdam, p 237
Mykles DL (1979) Ultrastructure of alimentary epithelia of lobsters, Homarus americanus and H. gammarus, and crab, Cancer magister, Zoomorphology 92:201–215
Nishiitsutsuji-Uwo J, Endo Y (1981) Gut endocrine cells in insects: The ultrastructure of the endocrine cells in the cockroach midgut. Biomed Res 2:30–44
Polak JM, Pearse AGE (1970) Anti-gastrin immunofluorescence in the skin of Hyla crepitans and the cytochemistry of the cells involved. Experientia 26:288–289
Rzasa P, Kaloustian KV, Prokop EK (1982) Immunochemical evidence for a gastrin-like peptide in the intestinal tissues of the earthworm Lumbricus terrestris. Comp Biochem Physiol 71A:631–634
Steiner DF, Peterson JD, Tager H, Emdin S, Ostberg Y, Falkmer S (1973) Comparative aspects of proinsulin and insulin structure and biosynthesis. Am Zool 13:591–604
Sternberger LA (1979) Immunocytochemistry, 2nd edition. Wiley, New York
Straus E, Yalow RS, Gainer H (1975) Molluscan gastrin: concentration and molecular forms. Science 190:687–689
Thorndyke MC (1982) Cholecystokinin(CCK)/gastrin-like immunoreactive neurones in the cerebral ganglion of the protochordate ascidians Styela clava and Ascidiella aspersa. Regul Pept 3:281–288
Van Noorden SE, Pearse AGE (1976) The localization of immunoreactivity to insulin, glucagon and gastrin in the gut of Amphioxus (Branchiostoma) lanceolatus. In: Grillo TAI, Liebson L, Epple A (eds) The evolution of pancreatic islets. Pergamon, New York, p 163
Walsh JH (1981) Gastrointestinal hormones and peptides. In: Johnson LR (ed) Physiology of the gastrointestinal tract. Raven Press, New York, p 59
Walsh JH, Lamers CB, Valenzuela JE (1982) Cholecystokinin-octapeptidelike immunoreactivity in human plasma. Gastroenterology 82:438–444
Warner GF (1977) The biology of crabs. Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, pp 1–21, 125–127
Zacharuk RY (1976) Structural changes of the cuticle associated with moulting. In: Hepburn HR (ed) The insect integument. Elsevier, Amsterdam, p 299
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Scalise, F.W., Larson, B.A. & Vigna, S.R. Localization of a peptide identified by antibodies to gastrin/CCK in the gut of Cancer magister . Cell Tissue Res. 238, 113–119 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00215151
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00215151