Abstract
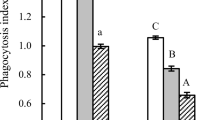
In vitro experiments were conducted to determine the effects of recombinant cytokines on phagocytic and oxidative burst activities of bovine neutrophils. Neutrophils were isolated (purity >91%, viability >97%) from EDTA-anticoagulated blood from healthy Holstein-Friesian heifers. Aliquots of neutrophils (10 × 106 cells/ml) were incubated for 1 h at 37 °C with equal volumes of recombinant human cytokines, namely, tumour necrosis factor-alpha (rhTNF-α, 0.5–1000 ng/ml), interleukin-1-alpha (rhIL-1-α, 0.001–10 ng/ml), interferon-gamma (rhIFN-γ, 0.01–100 ng/ml), granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (rhG-CSF, 25 ng/ml), and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (rhGM-CSF, 10 ng/ml). Then, the percentage phagocytosis and average number of intracellular bacteria per cell were evaluated by flow cytometry and/or fluorescent microscopy using FITC-labelled opsonised bacteria (Escherichia coli 0111:B4). Unlabelled opsonised bacteria and dichlorofluorescin diacetate were used to evaluate H2O2 production, a measure of oxidative burst, by flow cytometry. The results showed that all five cytokines significantly (p <0.05) increased percentage phagocytosis (52.4–86.1%), number of intracellular bacteria per cell (24.9–47.9%), and H2O2 production (31.3–58.2%) when compared to untreated neutrophils. A gradual increase in mean channel fluorescence but not in percentage phagocytosis was consistently seen with increasing concentrations of rhTNF-α, rhIL-1-α, and rhIFN-γ, thereby indicating a concentration-dependent stimulation of phagocytic capacity by these three cytokines.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amezaga MA, Bazzoni F, Sorio C et al. (1992) Evidence for the involvement of distinct signal transduction pathways in the regulation of constitutive and interferon gamma-dependent gene expression of NADPH oxidase components (gp91-phox, p47-phox, and p22-phox) and high affinity receptor for IgG (Fc gamma R-I) in human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Blood 79:735–744
Atkinson YH, Marasco WA, Lopez AF et al. (1988) Recombinant human tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Regulation of N-formylmethionylleucylphenylalanine receptor affinity and function on human neutrophils. J Clin Invest 81:759–765
Bajaj MS, Kew RR, Webster RO et al. (1992) Priming of human neutrophil functions by tumor necrosis factor; enhancement of superoxide anion generation, degranulation, and chemotaxis to chemoattractants C5a and F-Met-Leu-Phe. Inflammation 16:241–250
Balazovich KJ, Alrneida HI, Boxer LA (1991) Recombinant human G-CSF and GM-CSF prime human neutrophils for superoxide production through different signal transduction mechanisms. J Lab Clin Med 118:576–584
Baldwin GC, Fuller ND, Roberts RL et al. (1989) Granulocyte- and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factors enhance neutrophil cytotoxicity towards HIV-infected cells. Blood 74:1673–1677
Balkwill FR, Burke F (1989) The cytokine network [see comments]. Immunol Today 10:299–304
Bass DA, Parce JW, Dechatelet LIZ et al. (1983) Flow cytometric studies of oxidative product formation by neutrophils: a graded response to membrane stimulation. J Immunol 130:1910–1917
Berton G, Cassatella MA (1992) Modulation of neutrophil functions by interferon-gamma. In: Coffey RG (ed) Granulocyte responses to cytokines: basic and clinical research. Marcel Dekker Inc, New York, pp 437–456
Bienhoff SE, Allen GK, Berg JN (1992) Release of tumor necrosis factor-alpha from bovine alveolar macrophages stimulated with bovine respiratory viruses and bacterial endotoxins. Vet Immunol Immunopathol 30:341–357
Cairo MS (1991) Cytokines: a new immuotherapy. Clin Perinatol 18:343–359
Canning PC, Roth JA (1989) Effects of in vitro and in vivo administration of recombinant bovine interferon-gamma on bovine neutrophil responses to Brucella abortus. Vet Immunol Immunopathol 20:119–133
Capsoni F, Bonara P, Minonzio F et al. (1991) The effect of cytokines on human neutrophil Fc receptor-mediated phagocytosis. J Clin Lab Immunol 34:115–124
Carlson GP, Kaneko JJ (1973) Isolation of leukocytes from bovine peripheral blood. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 142:853–856
Cassatella MA, Hartman L, Perussia B et al. (1989) Tumor necrosis factor and immune interferon synergistically induce cytochrome b-245 heavy-chain gene expression and nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide phosphate hydrogenase oxidase in human leukemic myeloid cells. J Clin Invest 83:1570–1590
Curnutte JT (1992) Molecular basis of autosomal recessive forms of chronic granulomatous disease. Immunodefic Rev 3:149–154
Daifuku R, Andresen J, Morstyn G (1993) Recombinant methionyl human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor for the prevention and treatment of non-neutropenic infectious diseases. J Antimicrob Chemother 32 Suppl A:91–97
Ferrante A, Nandoskar M, Walz A et al. (1988) Effects of tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin-1 alpha and beta on human neutrophil migration, respiratory burst and degranulation. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol 86:82–91
Figari IS, Mori NA, Palladino MA, Jr (1987) Regulation of neutrophil migration and superoxide production by recombinant tumor necrosis factors-alpha and -beta: comparison to recombinant interferongamma and interleukin-1 alpha. Blood 70:979–984
Fujii M, Sugamura K, Sano K et al. (1986) High-affinity receptormediated internalization and degradation of interleukin 2 in human T cells. J Exp Med 163:550–562
Galizzi JP, Zuber CE, Cabrillat H et al. (1989) Internalization of human interleukin 4 and transient down-regulation of its receptor in the CD23-inducible Jijoye cells. J Biol Chem 264:6984–6989
Gallin JI (1984) Human neutrophil heterogeneity exists, but is it meaningful? Blood 63:977–983
Gasson JC (1991) Molecular physiology of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor. Blood 77:1131–1145
Gelfand JA, Fauci AS, Green I et al. (1976) A simple method for the determination of complement receptor-bearing mononuclear cells. J Immunol 116:595–599
Guthrie LA, McPhail LC, Henson PM et al. (1984) Priming of neutrophils for enhanced release of oxygen metabolites by bacterial lipopolysaccharide. Evidence for increased activity of the superoxide-producing enzyme. J Exp Med 160:1656–1671
Hengge UR, Brockmeyer NH, Goos M (1992) Granulocyte colonystimulating factor treatment in AIDS patients. Clin Invest 70:922–926
Jain NC (1986) Schalm's veterinary hematology, 4th edn. Lea and Febiger, Philadelphia, pp 20–86
Jain NC, Paape MJ, Berning L et al. (1991) Functional competence and monoclonal antibody reactivity of neutrophils from cows injected with Escherichia coli endotoxin. Comp Haematol Int 1:10–20
Kabbur MB, Jain NC (1995) Signal transduction pathways involved in phagocytic and oxidative burst activities of cytokine-treated bovine neutrophils. Comp Haematol Int (in press)
Kabbur MB, Jain NC, Zinkl JG et al. (1991) Heterogeneity in phagocytic and nitroblue tetrazolium reductive properties of neutrophils from cows. Am J Vet Res 52:2023–2028
Kaufman SE, DiPersio JF, Gasson JC (1989) Effects of human GMCSF on neutrophil degranulation in vitro. Exp Hematol 17:800–804
Kehrli ME, Schmalsteig FC, Anderson DC et al. (1990) Molecular definition of the bovine granulocytopathy syndrome: identification of deficiency of the Mac-1 (CD11b/CD18) glycoprotein. Am J Vet Res 51:1826–1836
Kehrli ME, Jr, Goff JP, Stevens MG et al. (1991) Effects of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor administration to periparturient cows on neutrophils and bacterial shedding. J Diary Sci 74:2448–2458
Kharazmi A, Nielsen H, Bendtzen K (1988) Modulation of human neutrophil and monocyte chemotaxis and superoxide responses by recombinant TNF-alpha and GM-CSF. Immunobiology 177:363–370
Khwaja A, Carver JE, Linch DC (1992) Interactions of granulocytemacrophage colony-stimulating factor (CSF), granulocyte CSF, and tumor necrosis factor alpha in the priming of the neutrophil respiratory burst. Blood 79:745–753
Kitagawa S, Yuo A, Souza LM et al. (1987) Recombinant human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor enhances superoxide release in human granulocytes stimulated by the chemotactic peptide. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 144:1143–1146
Klebanoff SJ, Vadas MA, Harlan JM et al. (1986) Stimulation of neutrophils by tumor necrosis factor. J Immunol 136:4220–4225
Krause PJ, Maderazo EG, Bannon P et al. (1988) Neutrophil heterogeneity in patients with blunt trauma. J Lab Clin Med 112:208–215
Kushner BH, Chung NK (1989) GM-CSF enhances 3178 monoclonal antibody-dependent cellular-cytotoxicity against human melanoma and neuroblastoma. Blood 73:1936–1941
Larrick JW, Graham D, Toy K et al. (1987) Recombinant tumor necrosis factor causes activation of human granulocytes. Blood 69:640–644
Le J, Vilcek J (1987) Tumor necrosis factor and interleukin 1: cytokines with multiple overlapping biological activities. Lab Invest 56:234–248
Livingston DH, Appel SH, Sonnenfeld G et al. (1989) The effect of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interferon-gamma on neutrophil function. J Surg Res 46:322–326
Lopez AF, Nicola NA, Burgess AW et al. (1983) Activation of granulocyte cytotoxic function by purified mouse colony-stimulating factors. J Immunol 131:2983–2988
Lowenthal JW, MacDonald HR (1986) Binding and internalization of interleukin 1 by T cells. Direct evidence for high- and low-affinity classes of interleukin 1 receptor. J Exp Med 164:1060–1074
Mason MJ, Van Epps DE (1989) In vivo neutrophil emigration in response to interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha. J Leukoc Biol 45:62–68
McPhail LC, Snyderman R (1984) Mechanisms of regulating the respiratory burst in leukocytes. Contemp Top Immunobiol 14:247–281
Metcalf D (1989) The molecular control of cell division, differentiation commitment and maturation in haemopoietic cells. Nature 339:27–30
Mizel SB, Kilian PL, Lewis JC et al. (1987) The interleukin 1 receptor. Dynamics of interleukin 1 binding and internalization in T cells and fibroblasts. J Immunol 138:2906–2912
Morrison CJ, Brummer E, Stevens DA (1989) In vivo activation of peripheral blood polymorphonuclear neutrophils by gamma interferon results in enhanced fungal killing. Infect Immun 57:2953–2958
Movat HZ, Burrowes CE, Cybulsky MI et al. (1987) Acute inflammation and a Shwartzman-like reaction induced by interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor. Synergistic action of the cytokines in the induction of inflammation and microvascular injury [published erratum appears in Am J Pathol 1988 Mar;130(3):642]. Am J Pathol 129:463–476
Nickerson SC, Owens WE, Watts JL (1989) Effects of recombinant granulocyte colony-stimulating factor on Staphylococcus aureus mastitis in lactating dairy cows. J Dairy Sci 72:3286–3294
Ohmann HB, Campos M, McDougall L et al. (1990) Expression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha receptors on bovine macrophages, lymphocytes and polymorphonuclear leukocytes, internalization of receptor-bound ligand, and some functional effects. Lymphokine Res 9:43–58
Ozaki Y, Ohashi T, Kume S (1987) Potentiation of neutrophil function by recombinant DNA-produced interleukin 1a. J Leukoc Biol 42:621–627
Paape MJ, Pearson RE, Schultze WD (1978) Variation among cows in the ability of milk to support phagocytosis and in the ability of polymorphonuclear leukocytes to phagocytose Staphylococcus aureus. Am J Vet Res 39:1907–1910
Perussia B, Kobayashi M, Rossi ME et al. (1987) Immune interferon enhances functional properties of human granulocytes: role of Fc receptors and effect of lymphotoxin, tumor necrosis factor, and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor. J Immunol 138:765–774
Platzer E, Welte K, Lu L et al. (1985) Biological activities of a human pluripotent hemopoietic colony-stimulating factor. Hamatol Bluttransfus 29:418–422
Qwarnstrom EE, Page RC, Gillis S et al. (1988) Binding, internalization, and intracellular localization of interleukin-1 beta in human diploid fibroblasts. J Biol Chem 263:8261–8269
Rapoport AP, Abboud CN, DiPersio JF (1992) Granulocytemacrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF): receptor biology, signal transduction, and neutrophil activation. Blood Rev 6:43–57
Reddy PG, McVey DS, Chengappa MM et al. (1990) Bovine recombinant granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor enhancement of bovine neutrophil functions in vitro. Am J Vet Res 51:1395–1399
Richter J, Andersson T, Olsson I (1989) Effect of tumor necrosis factor and granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor on neutrophil degranulation. J Immunol 142:3199–3205
Saad AM, Hageltorn M (1985) Flow cytometric characterization of bovine blood neutrophil phagocytosis of fluorescent bacteria and zymosan particles. Acta Vet Scand 26:289–307
Sahlin S, Hed J, Rundquist I (1983) Differentiation between attached and ingested immune complexes by a fluorescence quenching cytofluoremetric assay. J Immunol Methods 60:115–124
Samanta AK, Oppenheim JJ, Matsushima K (1990) Interleukin 8 (monocyte-derived neutrophil chemotactic factor) dynamically regulates its own receptor expression on human neutrophils. J Biol Chem 265:183–189
Sample AK, Czuprynski CJ (1991) Priming and stimulation of bovine neutrophils by recombinant human interleukin-1 alpha and tumor necrosis factor alpha. J Leukoc Biol 49:107–115
Sauder DN, Mounessa NL, Katz SI et al. (1984) Chemotactic cytokines: the role of leukocytic pyrogen and epidermal cell thymocyte-activating factor in neutrophil chemotaxis. J Immunol 132:828–832
Sayers TJ, Wiltrout TA, Bull CA et al. (1988) Effect of cytokines on polymorphonuclear neutrophil infiltration in the mouse. Prostaglandin- and leukotriene-independent induction of infiltration by IL-1 and tumor necrosis factor. J Immunol 141:1670–1677
Scala G, Kuang YD, Hall RE et al. (1984) Accessory cell function of human B cells. I. Production of both interleukin 1-like activity and an interleukin 1 inhibitory factor by an EB V-transformed human B cell line. J Exp Med 159:1637–1652
Scales WE (1992) Structure and function of interleukin-1. In: Kunkel SL, Remick DG (eds) Cytokines in health and disease. Marcel Deckker Inc, New York, pp 15–26
Schultz RM (1991) Effect of recombinant human granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor on neutrophil superoxide production. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol 13:183–198
Semani MJ, Kabbur MB, Jain NC (1993) Activation of bovine neutrophil functions by interferon-gamma, tumor necrosis factoralpha, and interleukin-1 alpha. Comp Haematol Int 3:81–88
Shalaby MR, Aggarwal BB, Rinderknecht E et al. (1985) Activation of human polymorphonuclear neutrophil functions by interferongamma and tumour necrosis factors. J Immunol 135:2069–2073
Shalaby MR, Palladino MA, Jr, Hirabayashi SE et al. (1987) Receptor binding and activation of polymorphonuclear neutrophils by tumor necrosis factor-alpha. J Leukoc Biol 41:196–204
Silva ID, Jain NC (1988) Phagocytic and nitroblue tetrazolium reductive properties of bovine neutrophils for mammary pathogens. J Dairy Sci 71:1625–1631
Simon PL, Willoughby WF (1981) The role of subcellular factors in pulmonary immune function: physicochemical characterization of two distinct species of lymphocyte-activating factor produced by rabbit alveolar macrophages. J Immunol 126:1534–1541
Smith RJ, Bowman BJ, Speziale SC (1986) Interleukin-1 stimulates granule exocytosis from human neutrophils. Int J Immunopharmacol 8:33–40
Sordillo LM, Peel J, Babiuk LA (1991) Potential role of cytokines in determining the outcome of acute coliform mastitis. National Mastitis Council, Arlington, pp 50–58
Steinbeck MJ, Roth JA (1989) Neutrophil activation by recombinant cytokines. Rev Infect Dis 11:549–568
Tiku K, Tiku ML, Skosey JL (1986) Interleukin 1 production by human polymorphonuclear neutrophils. J Immunol 136:3677–3685
Tsuji Y, Tori MF (1992) Tumor necrosis factor: Structure and function. In: Kunkel SL, Remick DG (eds) Cytokines in health and disease. Marcel Dekker, Inc, New York, pp 131–150
Utsumi T, Klostergaard J, Akimaru K et al. (1992a) Modulation of TNF-alpha-priming and stimulation-dependent superoxide generation in human neutrophils by protein kinase inhibitors. Arch Biochem Biophys 294:271–278
Utsumi T, Klostergaard J, Akimaru K et al. (1992b) Effect of tumor necrosis factor-alpha on the stimulus-coupled responses of neutrophils and their modulation by various inhibitors. Physiol Chem Phys Med NMR 24:77–88
Wankowicz Z, Megyeri P, Issekutz A (1988) Synergy between tumour necrosis factor alpha and interleukin-1 in the induction of polynuclear leukocyte migration during inflammation. J Leukoc Biol 43:349–356
Watson ED (1989) In vitro function of bovine neutrophils against Actinomyces pyogenes. Am J Vet Res 50:455–458
Weisbart RH, Golde DW, Clark SC et al. (1985) Human granulocytemacrophage colony-stimulating factor is a erythrocyte activator. Nature 314:361–363
Weisbart RH, Kacena A, Schuh A et al. (1988) GM-CSF induces human neutrophil IgA-mediated phagocytosis by an IgA Fc receptor activation mechanism. Naturek 332:647–648
Weissman AM, Harford JB, Svetlik PB et al. (1986) Only highaffinity receptors for interleukin 2 mediate internalization of ligand. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:1463–1466
Williams MR, Bunch KJ (1981) Variation among cows in the ability of their blood polymorphonuclear leucocytes to kill Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. Res Vet Sci 30:298–302
Worku M, Paape MJ, Marquardt WW (1994) Modulation of Fc receptors for IgG on bovine polymorphonuclear neutrophils by interferon-gamma through de novo RNA transcription and protein synthesis. Am J Vet Res 55:234–238
Yuo A, Kitagawa S, Ohsaka A et al. (1990) Stimulation and priming of human neutrophils by granulocyte colony-stimulating factor and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating qualitative and quantitative differences. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 171:491–497
Zoon KC, Arnheiter H, Zur Nedden D et al. (1983) Human interferon alpha enters cells by receptor-mediated endocytosis. Virology 130:195–203
Zoon KC, Zur Nedden D, Arnheiter H (1986) Procedures for studying the binding of interferon to human and bovine cells in monolayer culture. Methods Enzymol 119:312–315
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kabbur, M.B., Jain, N.C. & Farver, T.B. Modulation of phagocytic and oxidative burst activities of bovine neutrophils by human recombinant TNF-α, IL-1-α, IFN-γ, G-CSF, GM-CSF. Comparative Haematology International 5, 47–55 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00214490
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00214490