Summary
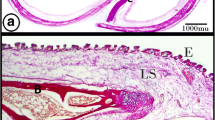
Tonsils of human fetuses at the 8th to the 28th gestational week (g.w.) were investigated by electron microscopy, enzyme histochemistry, and immunohistochemistry on cryostat sections. The development of the tonsilla palatina starts during the 14th g.w. when the mesenchyme underlying the mucous membrane of the tonsillar cavity becomes invaded by mononuclear wandering cells. In fetuses of about the 16th g.w. epithelial crypts grow down into the connective tissue and are infiltrated by T-lymphocytes. At the same time, precursors of interdigitating cells (IDC) can be identified among the epithelial cells. Frequently, lymphocytes and IDC-like cells are in close contact. From these findings it is concluded that the infiltrated crypt epithelium in the human tonsilla palatina represents a T-cell region. Primary follicles develop in earlier fetal stages than in all other secondary lymphoid organs. They contain precursors of dendritic reticulum cells and lymphoid cells that belong to the B-cell line. These primary follicles may be considered as the first assemblage of B-cell regions in human fetal lymphoid tissue. The present findings indicate that the formation of different stationary elements during the development of B-cell regions and T-cell regions is an important factor for the homing and antigen-dependent maturation of different subpopulations of immunocompetent lymphoid cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexopoulos C, Papayannis AG, Gardikas C (1976) Increased proportion of B-lymphocytes in human tonsils and appendices. Acta Haematol 55:95–98
Bailey D, Habershaw JA (1982; in press) Phenotypes of lymphoid cells constituting germinal centers and the lymphomas derived from them. Adv Exp Med Biol
Feller AC, Parwaresh MR (1980) Zytochemische Darstellung der Blasten bei akuter T-lymphoblastischer Leukämie mit Hilfe der Glycyl-prolyl-4-methoxy-beta-naphthylamid-Peptidase (DAP IV). Klin Pädiatrie 192:150
Gaudecker B von (1978) Ultrastructure of the age-involuted adult human thymus. Cell Tissue Res 186:507–525
Gaudecker B, Müller-Hermelink HK (1980) Ontogeny and organization of the stationary nonlymphoid cells in the human thymus. Cell Tissue Res 207:287–306
Grossi CE, Webb SR, Zicea A, Lydyard PM, Moretta L, Mingari MC, Cooper MD (1978) Morphological and histochemical analyses of two human T-cell subpopulations bearing receptors for IgM or IgG. J Exp Med 147:1405–1417
Heusermann U, Stutte HJ, Müller-Hermelink HK (1974) Inderdigitating cells in the white pulp of the human spleen. Cell Tissue Res 153:415–417
Jaffe ES, Shevach EM, Frank MM, Berard CW, Green J (1974) Nodular lymphoma-evidence for origin from follicular B-lymphocytes. New Engl J Med 290:813–819
Janossi G, Tidman N, Selby WS, Thomas JA, Granger S, Kung PC, Goldstein G (1980) Human T-lymphocytes of inducer and supressor type occupy different microenvironments. Nature 288:81–84
Kaiserling E, Lennert K (1974) Die interdigitierende Retikulumzelle im menschlichen Lymphknoten. Eine spezifische Zelle der thymusabhängigen Region. Virchows Arch B 16:51–61
Ledbetter JA, Evans RL, Lipinski M, Cunningham-Rundles C, Good RA, Herzenberg LA (1981) Evolutionary conservation of surface molecules that distinguish T-lymphocyte helper/inducer and T-cytotoxic/Supressor subpopulation in mouse and man. J Exp Med 153:310–323
Leder LD (1967) Der Blutmonozyt. Experimentelle Medizin Pathologie und Klinik. Springer Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg New York, Bd 23
Leene W (1971) Origin and fate of lymphoid cells in the developing palatine tonsil of rabbit. Z Zellforsch 116:502–522
Markgraf R, von Gaudecker B, Müller-Hermelink HK (1982: in press) The development of the human lymph node. Cell Tissue Res (accepted 5th April)
Mühlbach H (1977) Histochemische Darstellung der alkalischen Phosphatase und der 5′-Nucleotidase in der menschlichen Gaumentonsile. Inauguraldissertation zur Erlangung der Doktorwürde der Med Fak, Kiel
Müller-Hermelink HK, Gaudecker B von (1980) Ontogenese des lymphatischen Systems beim Menschen. Verh Anat Ges 74:235–259
Nduka-Agwo O (1981) Langerhanszellen und interdigitierende Retikulumzellen in der menschlichen Tonsille. Inauguraldissertation zur Erlangung der Doktorwürde der Med Fak, Kiel
Plum J, de Smedt M (1980) Enzymatic relationship between human T-lymphocytes and thymocytes. Cell Immunol 55:485
Poppema S (in press) Distribution of T-cell subsets in germinal centers of human lymph nodes. 7th International Conference of lymphatic tissues and germinal centers in immune reactions, Groningen 1981. Adv Exp Med Biol
Poppema S, Bhan AK, Reinherz EL, McCluskey RT, Schlossman SF (1981) Distribution of T-cell subsets in human lymph node. J Exp Med 153:30
Richardson KC, Jarell L, Finke EH (1960) Embedding in epoxy resins for ultrathin sectioning in electron microscopy. Stain Technol 35:313–323
Sesterhenn K, Krueger GRF, Uhlmann Ch (1979) Percent distribution of T- and B-cells in tonsils of children, juvenils and adults. Arch Otorhinolaryngol (NY) 218:37–44
Siegel G (1979) Evidence for selective proliferation and histological localization of B-lymphocytes in the human tonsil. ORL 41(3):147–157
Stein H, Bonk A, Tolksdorf G, Lennert K, Rodt H, Gerdes J (1980) Immunohistologic analysis of the organization of normal lymphoid tissue and non-Hodgkin's lymphomas. J Histochem Cytochem 28:746–760
Stutte HJ, Müller-Hermelink HK (1976) Lysosomen in Blutzellen als diagnostischer Parameter. Verh Dtsch Ges Path 50:155–175
Wolff K (1972) The Langerhans cell. Curr Probl Derm Vol 4:79–145
Zelickson AS, Mottaz JH (1968) Epidermal dendritic cells. A quantitative study. Arch Derm 98:652–659
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This investigation was supported by grants from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft, particularly the Sonderforschungsbereich 111
The authors appreciate the contribution of human fetal material from Dr. J. von Hollweg and Dr. J. Körner from the Hospital Heidberg c.o. Hamburg and the excellent technical assistance of Mrs. O.-M. Bracker, Mrs. H. Hansen, Mrs. I. Knauer, Mrs. R. Köpke, Mrs. I. König, Mrs. F. Müller, Mrs. H. Siebke and Mrs. H. Waluk
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
von Gaudecker, B., Müller-Hermelink, H.K. The development of the human tonsilla palatina. Cell Tissue Res. 224, 579–600 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00213754
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00213754