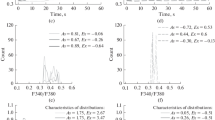
Abstract
Cadmium and nickel stimulate the early spontaneous adherence of peripheral human polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMNs). Formyl-methionylleucylphenylalanine (fMLP) at 0.25 nM inhibited the PMN adherence but was stimulated at 10 or 100 nM. Cadmium or nickel, nullified the fMLP inhibitory effect, and enhanced the adherence. No clear additive effect was noticed for either metal with fMLP. Blockade of CD11/CD18 receptors abolished the adherence modulatory effect of both fMLP and metals. p-Chloromercuriphenyl sulfonate (PCMPS), at a concentration that blocks peripheral SH groups, did not affect spontaneous adherence, but completely prevented the adherence enhancement caused by cadmium or nickel. Removal of extracellular calcium diminished both the spontaneous and the metal-stimulated adherence. Ryanodine, at a concentration that persistently inactivates ryanodine-sensitive intracellular channels, inhibited spontaneous PMN adherence, but had no effect on the cadmium or nickel induced adherence enhancement. Therefore, the results indicate that cadmium and nickel adherence stimulation depends on constitutive peripheral SH groups, CD11/CD18 integrins and extracellular calcium, but not on intracellular stored-calcium release through ryanodine-sensitive channels (RyRs). In contrast, spontaneous adherence greatly depends on the release of stored calcium through RyRs, and only slightly on extracellular calcium.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abramson JJ, Trimm JL, Weden L, Salama G (1983) Heavy metals induce rapid calcium release from sarcoplasmic reticulum vesicles isolated from skeletal muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 80:1526–1530
Anderson DC, Miller LJ, Schmalstieg FC, Rothlein R, Springer TA (1986) Contributions of the Mac-1 glycoprotein family to adherence-dependent granulocyte functions: structure-function assessments employing subunit-specific monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol 137:15–27
Andersson T, Dahlgren C, Pozzan T, Stendahl O, Lew DP (1986) Characterization of fMet-Leu-Phe receptor-mediated Ca2+ influx across the plasma membrane of human neutrophils. Mol Pharmacol 30:437–443
Berridge MJ (1993) Inositol trisphosphate and calcium signalling. Nature 361:315–325
Binah O, Berke G, Rosen D, Hoffman BF (1994) Calcium channel blockers modify electrophysiological effects induced by lytic granules from cytotoxic T lymphocytes in guinea pig ventricular myocytes. J Pharmacol Exp Therap 268:1581–1587
Carlos TM, Harlan JM (1990) Membrane proteins involved in phagocyte adherence to endothelium. Immunol Rev 114:5–28
Clapham DE (1995) Calcium signaling. Cell 80:259–268
Cifone MG, Alesse E, Procopio A, Paolini R, Morrone S, Di Eugenio R, Santoni G, Santoni A (1989) Effects of cadmium on lymphocyte activation. Biochim Biophys Acta 1011:25–32
Fergusson JE (1990) The toxicity of heavy elements to human being. In: The heavy elements: chemistry, environmental impact and health effects. Pergamon Press, Oxford, pp:533–568
Giordano GF, Lichtman MA (1973) The role of sulfhydryl groups in human neutrophil adhesion, movement and particle ingestion. J Cell Physiol 82:387–396
Hechtenberg S, Beyersmann D (1991) Inhibition of sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase activity by cadmium, lead and mercury. Enzyme 45:109–115
Hernández M, Macia M, Conde JL, de la Fuente M (1991) Cadmium and nickel modulation of adherence capacity of murine peritoneal macrophages and lymphocytes. Intersexual comparisons. Int J Biochem 23:541–544
Hogg N (1992) Roll, roll, roll your leucocyte gently down the vein ... Immunol Today 13:113–115
Hoover RL, Briggs RT, Karnovsky MJ (1978) The adhesive interaction between polymorphonuclear leukocytes and endothelial cells in vitro. Cell 14:423–428
Horiguchi H, Mukaida N, Okamoto S, Teranishi H, Kasuya M, Matsushima K (1993) Cadmium induces interleukin-8 production in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells with the concomitant generation of superoxide radicals. Lymphokine Cytokine Res 12(6):421–428
Jaconi MEE, Theler JM, Schlegel W, Appel RD, Wright SD, Lew PD (1991) Multiple elevations of cytosolic-free Ca2+ in human neutrophils: initiation by adherence receptors of the integrin family. J Cell Biol 112:1249–1257
Krause KH, Campbell KP, Welsh MJ, Lew DP (1990) The calcium signal and neutrophil activation. Clin Biochem 23:159–166
Krause KH, Demaurex N, Jaconi M, Lew DP (1993) Ion channels and receptor-mediated Ca2+ influx in neutrophil granulocytes. Blood Cells 19:165–175
Lawrence MB, Smith CW, Eskin SG, McIntire LV (1990) Effect of venous shear stress on CD18-mediated neutrophil adhesion to cultured endothelium. Blood 75:227–237
Liu G, Pessah IN (1994) Molecular interaction between ryanodine receptor and glycoprotein triadin involves redox cycling of functionally important hyperreactive sulfhydryls. J Biol Chem 269(52):33028–33034
Liu S-H, Lin-Schiau S-Y (1994) Potentiation by metal ions of ryanodine contracture of the mouse diaphragm. Eur J Pharmacol 251:61–68
Macia M, Hernández M (1995) Modulation of the adherence of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes by cadmium and nickel. Sexual differences. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 29:15–19
Malech HL, Gallin JI (1987) Neutrophils in human diseases. N Engl J Med 317:687–694
Merian E (ed) (1991) Metals and their compounds in the environment. Occurrence, analysis and biological relevance. VCH, Weinheim
Muller WA, Weigl SA, Deng X, Phillips DM (1993) PECAM-1 is required for transendothelial migration of leukocytes. J Exp Med 178:449–460
Omann GM, Allen RA, Bokoch GM, Painter RG, Traynor AE, Sklar LA (1987) Signal transduction and cytoskeletal activation in the neutrophil. Physiol Rev 67:285–322
Perry I, Buttrum SM, Nash GB (1993) Effect of activation on adhesion of flowing neutrophils to cultured endothelium: time course and inhibition by a calcium channel blocker (nitrendipine). Br J Pharmacol 110:1630–1634
Petersen M, Williams JD, Hallett MB (1993) Cross-linking of CD11b or CD18 signals release of localized Ca2+ from intracellular stores in neutrophils. Immunol 80:157–159
Salama G, Abramson JJ, Pike GK (1992) Sulphydryl reagents trigger Ca2+ release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum of skinned rabbit psoas fibres. J Physiol 454:389–420
Schwartz BR, Harlan JM (1989a) Neutrophil membrane sulfhydryl groups are involved in stimulated neutrophil adherence to endothelium. J Leukocyte Biol 45:177–182
—, — (1989b) Sulfhydryl reducing agents promote neutrophil adherence without increasing surface expression of CD11b/CD18 (Mac-1, Mol). Biochem Biophy Res Commu 165:51–57
Shankar VS, Bax CMR, Bax BE, Alam ASMT, Moonga BS, Simon B, Pazianas M, Huang CL-H, Zaidi M (1993) Activation of the Ca2+ “Receptor” on the osteoclast by Ni2+ elicits cytosolic Ca2+ signals: evidence for receptor activation and inactivation, intracellular Ca2+ redistribution, and divalent cation modulation. J Cell Physiol 155:120–129
Smith JB, Smith L, Pijuan V, Zhuang Y, Chen YC (1994) Transmembrane signals and prooncogene induction evoked by carcinogenic metals and prevented by zinc. Environ Health Perspect 102(3):181–189
Silvennoinen-Kassinen S, Ikäheimo I, Karvonen J, Kauppinen M, Kallioinen M (1992) Mononuclear cell subsets in the nickel-allergic reaction in vitro and in vivo. J Allergy Clin Immunol 89(4):794–800
Southwick FS, Dabiri GA, Paschetto M, Zigmond SH (1989) Polymorphonuclear leukocyte adherence induces actin polymerization by a transduction pathway which differs from that used by chemoattractants. J Cell Biol 109:1561–1569
Talbott GA, Sharar SR, Harlan JM, Winn RK (1994) Leukocyte-endothelial interactions and organ injury: the role of adhesion molecules. New-Horiz 2(4):545–554
Thorn P, Brady P, Llopis J, Gallacher DV, Petersen OH (1992) Cytosolic Ca2+ spikes evoked by the thiol reagent thimerosal in both intact and internally perfused single pancreatic acinar cells. Pflügers Arch 422:173–178
Wassem M, Bajpai R, Kaw JL (1993) Reaction of pulmonary macrophages exposed to nickel and cadmium in vitro. J Environ Pathol Toxicol Oncol 12(1):47–54
Zimányi I, Buck E, Abramson JJ, Mack MM, Pessah IN (1992) Ryanodine induces persistent inactivation of the Ca2+ release channel from skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. Mol Pharmacol 42:1049–1057
Zimmerman GA, Prescott SM, McIntyre TM (1992) Endothelial cell interactions with granulocytes: tethering and signaling molecules. Immunol Today 13:93–100
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hernández, M., Macia, M. Free peripheral sulfhydryl groups, CD11/CD18 integrins, and calcium are required in the cadmium and nickel enhancement of human-polymorphonuclear leukocyte adherence. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 30, 437–443 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00213393
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00213393