Abstract
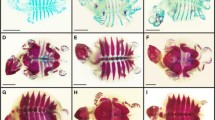
Tadpoles of Rana perezi were kept for 14 weeks in water containing two sublethal levels of the carbamate insecticide ZZ-Aphox® or the organophosphate Folidol®. Approximate concentrations of their active ingredients were 0.25 and 1 mg/L. Resulting malformations were studied by skeletal analysis and histological and histochemical investigation of the rear limbs of the tadpoles. The pesticides caused the animals to have malformations of the spinal column (scoliosis) and/or limbs (short and thick long bones with the epiphyses grossly twisted). Histochemical study showed differences in the composition of the connective matrix, and microscopic examination of the long bones indicated alterations in the thickness of the uncalcified bone matrix (osteoid) and the presence of abundant vascularised connective tissue in the region of the periosteum. The results confirmed changes in the composition of the connective tissue matrix as the cause of the defects observed in bone formation which are also discussed in relation to vitamin D absorption and calcium homeostasis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antunes-Madeira MC, Carvalho AP, Madeira VMC (1981) Interactions of insecticides with erythrocyte membranes. Pestic Biochem Physiol 15 1:79–89
Bright JE, Inns RH, Tuckwell NJ, Griffiths GD, Marrs TC (1991) A histochemical study of changes observed in the mouse diaphragm after organophosphate poisoning. Human Exp Toxicol 10:9–14
Brooks JA (1981) Otolith abnormalities in Limnodynastes tasmaniensis tadpoles after embryonic exposure to the pesticide dieldrin. Environ Pollut Ser A 25:19–25
Cooke AS (1972) The effects of DDT, dieldrin and 2,4-D on amphibian spawn and tadpoles. Environ Pollut 3:51–68
Cotran RS, Kumar V, Robbins SL (1990) Patologia Estructural y Funcional. McGraw-Hill-Interamericana de España S. A. Madrid, Spain
Dawson DA, McCormick CA, Bantle JA (1985) Detection of teratogenic substances in acidic mine water samples using the frog embryo teratogenesis assay-Xenopus (FETAX). J Appl Toxicol 54:234–243
Dawson DA, Wilke TS (1991) Initial evaluation of developmental malformation as an end point in mixture toxicity hazard, assessment for aquatic vertebrates. Ecotox Environ Safe 21:215–226
Fikes JD (1990) Organophosphorous and carbamate insecticides. Vet Clin N Am: Small Anim Pract 20 (2):353–367
Fulton MH, Chambers JE (1985) The toxic and teratogenic effects of selected organophosphorus compounds on the embryos of three species of amphibians. Toxicol Lett 26:175–180
Gabe M (1986) Techniques Histologiques. Ed. Masson, Paris
Garrison JC, Wyttenbach CR (1985) Teratogenic effects of the organophosphate insecticide dicrotophs (Bidrin): Histological characterization of defects. Anat Rec 213:464–472
Ghosh P, Bhattacharya S, Bhattacharya S (1989) Impact of non-lethal levels of Metacid-50 and Carbaryl on thyroid function and cholinergic system of Chana punctatus. Biomed Environ Sci 2:92–97
Gilbert SF (1991) Developmental Biology, Third Edition, Sinauer Associates Inc., Sunderland, MA
Gosner KL (1960) A simplified table for staging anuran embryos and larvae with notes on identification. Herpetologica 16:183–190
Hall RJ, Kolbe E (1980) Bioconcentration of organophosphorous insecticides to hazardous levels by amphibians. J. Toxicol Environ Health 6:853–860
Hall RJ (1990) Accumulation metabolism and toxicity of parathion in tadpoles. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 44:629–635
Hanken J, Wassersug R (1981) The Visible Skeleton. Funct Photog 16 4:22–44
Haya K (1989) Toxicity of pyrethroid insecticides to fish. Environ Toxicol and Chem 8:381–391
Honegger RE (1978) Amphibiens el reptiles menacés en Europe. Conseil de l'Europel5
Honrubia MP, Herráez MP, Alvarez R (1993) The Carbamate Insecticide ZZ-Alphox® Induced Structural Changes of Gills, Liver, Gallbladder, Heart, and Notochord of Rana perezi Tadpoles. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 25:184–191
Honrubia MP (1993) Estudio del efecto de los pesticidas Aphox® y Folidol® sobre el desarrollo embrionario y larvario de Rana perezi. Tesis de Licenciatura. Universidad de León. Spain
Kinebuchi H, Shiraishi N, Konishi Y (1992) Hypocalcemia in delayed neuropathy caused by organophosphates. Environ Sci 14:199–204
Kivirikko KI, Myllyla R (1985) Post-Translational Processing of Procollagens. Annals New York Acad Sci 460:187–201
Lima SL, Agostinho CA (1984) Técnicas e propostas para alimentacao de ras. Universidade Federal de Vicosa, Informe Técnico 50
Marian MP, Arul V, Pandian TJ (1983) Acute and chronic effects of Carboryl on survival, growth and metamorphosis in the bullfrog Rana tigrina. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 12:217–275
Martínez I, Alvarez R, Herráez I, Herráez MP (1992) Skeletal malformations in hatchery reared Rana perezi tadpoles. Anat Rec 233:314–320
Meerdink GL (1989) Organophosphorous and carbamate insecticide poisoning of large animals. Vet Clin N Amer Food Anim Pract 5(2):375–389
Meiniel R (1981) Neuromuscular blocking agents and axial teratogenesis in the avian embryo. Can axial morphogenetic disorders be explained by pharmacological action upon muscle tissue? Teratology 23:259–271
Montes GS, Junqueira LCU (1988) Histochemical localization of collagen and of proteoglycans in tissues. In: Collagen VII Biochemistry and Biomechanics. M.E. Nimni, ed. CRC Press, Inc. Boca Ratón, FL pp 41–72
Phillips K (1990) Where have all the frogs and toads gone? BioScience 40:6:422–424
Schultz TW, Dumont JN, Epler RG (1985) The embryotoxic and osteolathyrogenic effects of semicarbazide. Toxicology 36 2:183–198
Schuytema GS, Nebeker AV, Griffis WL, Wilson KN (1991) Teratogenesis, toxicity and bioconcentration in frogs exposed to dieldrin. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 21:332–350
Shirazi MA, Dawson DA (1991) Developmental malformation of frog embryos: An analysis of teratogenicity of chemical mixtures. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 21:117–182
Shirazi MA, Dawson DA, Snawder JE, Chambers JE (1989) Toxic and developmental effects of organophosphor insecticides in embryos of the South African clawed frog. J Environ Sci Health B24(3):205–218
Snawder JE, Chambers JE (1990) Critical time periods and the effect of tryptophan in malathion-induced developmental defects in Xenopus embryos. Life Sci 46:1635–1642
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alvarez, R., Honrubia, M.P. & Herráez, M.P. Skeletal malformations induced by the insecticides ZZ-Aphox® and Folidol® during larval development of Rana perezi . Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 28, 349–356 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00213113
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00213113