Abstract
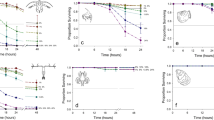
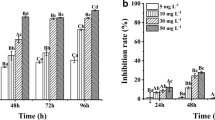
Alum sludges from ten water treatment plants throughout North America were subjected to a battery of toxicity tests which included the S. capricornutum growth test, the fathead minnow survival and growth test, a protozoan mortality test, and the Microtox® test. S. capricornutum was more sensitive than any other test species to sludge extracts. Algal growth inhibition was observed in extracts obtained at pH 5 but generally not in circumneutral solutions. Alum sludge extracts prepared with natural receiving waters were toxic to S. capricornutum at all extract pH levels tested if receiving water hardness was less than 35 mg CaCO3/L. These results indicate that water-soluble constituents from alum sludges discharged into receiving waters may affect algal growth.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Water Works Association [AWWA] (1986) Water Utility Operating Data. AWWA, Denver, CO
Baker P, Schofield CL (1979) Aluminum toxicity to fish in acidic waters. Water Air Soil Pollut 18:289–309
Beckman Instruments, Inc. (1982) Microtox® System Operating Manual. Beckman Instruments, Inc, Microbics Operations, Carlsbad, CA
Bloom PR, Erich MS (1989) The quantitation of aqueous aluminum. In: Sposito G (ed) The Environmental Chemistry of Aluminum. CRC Press, Inc, Boca Raton, FL, pp 1–27
Boyd CE (1979) Aluminum sulfate (alum) for precipitating clay turbidity from fish ponds. Transactions American Fishery Society 108:307–313
Buckler DR, Mehrle PM, Cleveland L, Dwyer FJ (1987) Influence of pH on the toxicity of aluminum and other inorganic contaminants to East Coast striped bass. Water Air Soil Pollut 35:97–106
Burrows WD (1977) Aquatic aluminum: Chemistry, toxicity, and environmental prevalence. CRC Critical Reviews in Environmental Control, CRC Press, Inc, Boca Raton, FL
Carter JW, Cameron IL (1973) Toxicity bioassay of heavy metals in water using Tetrahymena pyriformis. Water Research 7:951–961
DeGraeve GM, Cooney JD (1987) Ceriodaphnia: An update on effluent toxicity testing and research needs. Environ Toxicol Chem 6:331–333
Dougan WK, Wilson AL (1974) The absorptiometric determination of aluminum in water: A comparison of some chromogenic reagents and the development of an improved method. Analyst 99:413–430
Driscoll CT (1984) A procedure for the fractionation of aqueous aluminum in dilute acidic waters. Int J Environ Anal Chem 16:267–283
Freeman RA, Everhart WH (1971) Toxicity of aluminum hydroxide complexes in neutral and basic media to rainbow trout. Trans Amer Fish Soc 100:644
Goenaga X, Williams DJA (1988) Aluminum speciation in surface waters from a Welsh upland area. Environ Pollut 52:131–149
Gulley DD, Boelter AM, Bergman HL (1988) Toxstat Release 2.1. Fish Physiology and Toxicology Laboratory, University of Wyoming, Laramie, WY
Hall WS, Hall LW Jr (1989) Toxicity of alum sludge to Ceriodaphnia dubia and Pimephales promelas. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 42:791–798
Havas M (1985) Aluminum bioaccumulation and toxicity to Daphnia magna in soft water at low pH. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 42:1741–1748
Havas M, Hutchinson TC (1982) Aquatic invertebrates from the Smoking Hills, N.W.T.: Effect of pH and metals on mortality. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 39:890–903
McCauley DJ, Brook LT, Call DJ, Lindberg CA (1986) Acute and chronic toxicity of aluminum to Ceriodaphnia dubia at various pH's. University of Wisconsin—Superior, Superior, WI
Miller WE, Greene JC, Shioryama T (1978) The S. capricornutum Printz algal assay bottle test. EPA-600/9–78–018, Corvallis Environmental Research Lab, EPA, Corvallis, OR
Muniz IP, Leivestad H (1980) Toxic effects of aluminum on the brown trout, Salmo trutta L. In: Drablos D, Tollam A (eds) Ecological Impact of Acid Precipitation. Johs. Grefslie Press A/S, Mysen, Norway, pp 320–321
Nelson WO, Lutz TG, Orvig C (1987) The chemistry of neurologically active, neutral, and water soluble aluminum complexes. 194th National Meeting of the American Chemical Society, New Orleans, LA
Novak JT (1979) Historical and technical perspective of sludge treatment and disposal. Proceedings, AWWA Seminar, Recent Advances in Sludge Treatment and Disposal, AWWA, Denver, CO
Ohio River Valley Water Sanitation Commission (ORSANCO) (1981) Wastewater discharges from water treatment plants. Internal Report
Roberts RO, Berk SG (1990) Development of a protozoan chemoattraction inhibition assay for aquatic toxicity evaluation. Toxicity Assess 5:279–292
Rogeberg EJS, Henriksen A (1985) An automatic method for fractionation and determination of Al species in freshwaters. Vatten 41:48–53
SAS Institute Inc (1988) SAS User's Guide: Basics, Version 5 Edition. SAS Institute Inc, Cary, NC, p 1290
Schofield C, Trojnar JR (1980) Aluminum toxicity to brook trout (Salvelinus fontinalis) in acidified waters. In: Toribara TY, Miller MW, Morrow PE (eds) Polluted Rain. Plenum Press, NY, pp 341–363
Sposito G (1989) The environmental chemistry of aluminum. CRC Press Inc., Boca Raton, FL
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency [EPA] (1979) Handbook for analytical quality control in water and wastewater laboratories. Office of Research & Development, Environmental Monitoring and Support Laboratory, USEPA, Cincinnati, OH
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency [EPA] (1985) Short-term methods for estimating the chronic toxicity of effluents and receiving waters to freshwater organisms. EPA/600/4–85/014, Environmental Monitoring and Support Laboratory, USEPA, Cincinnati, OH
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency [EPA] (1988) Ambient water quality criteria for aluminum. EPA/440/5–86/008. USEPA, Washington, DC
Vicory AH, Weaver L (1984) Controlling discharges of water plant waste to the Ohio River. AWWA J 76(4):122–125
Witters H, Vangenechten JHD, Van Puymbroeck S, Vanderborght OLJ (1984) Interference of aluminum and pH on the Na-influx in an aquatic insect Corixa punctata (Illig.). Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 32:575–579
Wong SL (1989) Algal assays to interpret toxicity guidelines for natural waters. J Environ Sci Health A24(8):1001–1010
Wood CM, McDonald DG (1987) The physiology of acid/aluminum stress in trout. In: Witters, J and Vanderborght O (eds) Ecophysiology of acid stress in aquatic organisms. Soc R Zool Belg 117:399–410
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
George, D.B., Berk, S.G., Adams, V.D. et al. Toxicity of alum sludge extracts to a freshwater alga, protozoan, fish, and marine bacterium. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 29, 149–158 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00212964
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00212964