Abstract
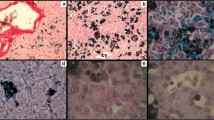
Embryos of Rana perezi were kept under laboratory conditions and treated with carbamate ZZ-Aphox® at chronic doses of 0.02‰ and 0.14‰ for 9 weeks. Both the histological study and the analysis of mortality show a direct relationship between the dosage and the effects of the pesticide. The histological study of the survivors over 56 days show damages in gills, liver, gall-bladder, heart, and notochord. Damages on the epithelia of gills (on their distal portion) and gall-bladder recover over a few days, whereas those provoked on the compacting of the hepatic parenchyma and the hepatocytes, the auricle and the perinotochordal collagenic fibers alter their structure in a lasting way. Potentials of such alterations are discussed, with special reference to the possible interference of the pesticide on the successful synthesis of the supporting connective sheaths.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvarez R (1988) Influencia del fotoperiodo y de la glándula pineal sobre el sistema immune de Rana perezi. Resumen tesis doctoral. Publicaciones de la Universidad de León
Antunes-Madeira MC, Carvalho AP, Madeira VMC (1981) Interactions of insecticides with erythrocyte membranes. Pestic Biochem Physiol 15(1):79–89
Brown HR, Sharma ML (1976) Synaptosomal adenosine triphosphatase (ATP-ase) inhibition by organophosphates. Experientia 32(12):1540–1544
Cossarini-Dunier M, Demael A, Siwicki AK (1990) In vivo effect of the organophosphorous insecticide Tricholrphon on the immune response of carp (Cyprinus carpio). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 19:93–98
Dawson DA, McCormick CA, Bantle JA (1985) Detection of teratogenic substances in acidic mine water samples using the frog embryo teratogenesis assay-Xenopus (FETAX). J Appl Toxicol 5(4):234–243
Deli E, Kiss Z (1988) Effect of parathion and methylparathion on protein content of chicken embryo muscle in vivo. Biochem Pharmacol 37(17):3251–3256
Domenech CE, Domenech EM, Balengo HF, Mendoza D, Farias RN (1977) Pesticide action and membrane fluidity: Allosteric behavior of rat erythrocyte membrane-bound acetylcholinesterase in the presence of organophosphorus compounds. FEBS Lett 74(2):243–246
Edery H, Schatzberg-Porath G (1960) Studies on the effects of organophosphorus insecticides on amphibians. Arch Int Pharmacodyn 124:212–224
Fawcett DW (1987) Tratado de histología. Ed. Interamericana-McGraw Hill, Madrid
Fikes JD (1990) Organophosphorous and carbamate insecticides. Vet Clin North Am: Small Anim Pract 20(2):353–367
Garrison JC, Wyttenbach CR (1985) Teratogenic effects of the organophosphate insecticide dicrotophos (Bidrin): Histological characterization of defects. Anat Rec 213:464–472
Ghosh P, Bhattacharya S, Bhattacharya S (1989) Impact of non lethal levels of Metacid-50 and Carbaryl on thyroid function and cholinergic system of Chana punctatus. Biomed Environ Sci 2:92–97
Gosner KL (1960) A simplified table for staging anuran embryos and larvae with notes on identification. Herpetologica 16:183–190
Hall RJ, Kolbe E (1980) Bioconcentration of organophosphorous insecticides to hazardous levels by amphibians. J Toxicol Environ Healt 6:853–860
Hanke W, Lange C, Weindel K (1990) The metabolic situation of the liver during development in respect to corticosteroid function. In: Hanke W (ed) Biology and Physiology of amphibians. Gustav Fischer Verlag 1990, Stuttgart, pp 167–176
Haya K (1989) Toxicity of pyrethroid insecticides to fish. Environ. Toxicol Chem 8:381–391
Honegger RE (1978) Amphibiens el reptiles menacés en Europe. Conseil de l'Europe 15, Strasbourg
Huckle KR, Millburn P (1990) Metabolism, bioconcentration and toxicity of pesticides in fish. In: Hutson DH, Roberts TR (eds) Environmental fate of pesticides. John Wiley and Sons, Chichester, 1990, pp 175–244
Laurent P, Perry SF (1991) Environmental effects on fish gill morphology. Physiol Zool 64(1):4–25
Lima SL, Agostinho CA (1984) Técnicas e propostas para alimentaçao de rãs. Universidade Federal de Viçosa, Informe Técnico 50, Viçosa
Marian MP, Arul V, Pandian TJ (1983) Acute and chronic effects of Carbaryl or survival, growth and metamorphosis in the bullfrog Rana tigrina. Arch Envirom Contam Toxicol 12:217–275
Meeks RL (1968) The accumulation of 36Cl ring-labeled DDT in a fresh water marsh. J Wildl Manage 32:376–398
Meerdink GL (1989) Organophosphorous and carbamate insecticide poisoning large animals. Vet Clin North Am: Food Anim Pract 5(2):375–389
Meneely CA, Wyttenbach CR (1989) Effects of the organophosphate insecticides diazinon and parathion on bobwhite quail embryos: skeletal defects and acetyl-cholinesterase activity. J Exp Zool 252:60–70
Moreno AJM, Madeira VMC (1990) Interference of parathion with mitochondrial bioenergetics. Biochim Biophys Acta 1015:361–367
Nayak PL, Bender ML (1978) Organophosphorus compounds as active site-directed inhibitors of lastase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 83(3):1178–1183
Phillips K (1990) Where have all the frogs and toads gone? BioScience 40(6):422–424
Powell GVN, De Weese LR, Lamont TG (1982) A field evaluation of frogs as a potential source of secondary organophosphorous insecticide poisoning. Can J Zool 60:2233–2235
Richmonds C, Dutta HM (1989) Histophathological changes induced by Malathion in the gills of bluegill Lepomis macrochirus. Bull Environ Toxicol 43:123–130
Riggin GW, Schultz TW (1986) Teratogenic effects of Benzoil Hydrazine on frog embryos. Trans Am Microsc Soc 105:197–210
Roy PK, Munshi JSD (1991) Malathion induced structural and morphometric changes of gills of a fresh water major carp, Cirrhinus mrigala (Ham.) J Envirom Biol 12(1):79–87
Schultz TW, Dumont JN, Epler RG (1985) The embryotoxic and osteolathyrogenic effects of semicarbazide. Toxicology 36(2): 183–198
Schuytema GS, Nebeker AV, Griffis WL, Wilson KN (1991) Teratogenesis, toxicity and bioconcentration in frogs exposed to dieldrin. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 21:332–350
Snawder JE, Chambers JE (1989) Toxic and developmental effects of organophosphorous insecticides embryos of the south african clawed frog. J Environ Sci Health B24(3):205–218
—, — (1990) Critical time periods and the effect of tryptophan in malathion-induced developmental defects in Xenopus embryos. Life Sci 46:1635–1642
Studnicka M (1970) Investigations on the remnants of the phospho-organic compound foschlor in tissues of fishes subjected to the treatment with this preparation. Pol Arch Weter 13(3):107–121
Sultatos LG, Shao M, Murphy SD (1984) The role of hepatic biotransformation in mediating the acute toxicity of the phosphorothionate insecticide chlorpyrifos. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 73:60–68
Szubartowska E, Gromysz-Kalkowska K, Wójcik K (1990) Behavior of the formed blood elements in Rana esculenta L. after repeated contacts of the animal with a therapeutic dose of Foschlor. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 45:796–803
Tucker RK, Crabtree DG (1970) Handbook of toxicity of pesticides to wildlife. U.S. Fish and Wildl. Serv Resour Publ 84, Washington, DC
Wyttenbach CR, Thompson SC (1985) The effects of the organophosphate insecticide malathion on very young chick embryos: Malformations detected by histological examination. Am J Anat 174: 187–202
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Honrubia, M.P., Herráez, M.P. & Alvarez, R. The carbamate insecticide ZZ-Aphox® induced structural changes of gills, liver, gall-bladder, heart, and notochord of Rana perezi tadpoles. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 25, 184–191 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00212129
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00212129