Abstract
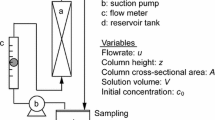
The adsorption of phenol, p-chlorophenol and mercuric ions onto activated carbon in fixed beds has been studied. The effects of process variables such as bed height and residence have been studied. The results have been used to predict optimum conditions for the systems based on the C exhaustion rate and the empty bed residence time (EBRT).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen, J. B., Joyce, R. S., and Kasch, R. H.: 1967, Journal WPCF 39, 217.
Bilello, L. J. and De John, P. B.: 1981, Total Process Design and Economics, Activated Carbon Adsorption for Wastewater Treatment, Perrich, J. R. (ed.), CRC Oress, pp. 177–200.
Erskine, D. B. and Schuliger, W. G.: 1971, A. 1. Ch. E. Symp Ser. — Water, pp. 185–190.
McKay, G. and Bino, M. J.: 1985, Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 63, 168.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McKay, G., Bino, M.J. Simplified optimisation procedure for fixed bed adsorption systems. Water Air Soil Pollut 51, 33–41 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00211501
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00211501