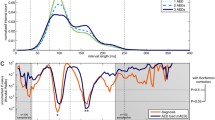
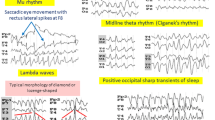
Abstract
Familial and twin studies have shown that the individual variability of the normal human electroencephalogram (EEG) is largely genetically determined. In epileptology, these genetic parameters of the EEG background activity are almost totally neglected. The aim of the present study has been to investigate whether a special genetic type of background activity might be related to the pathogenesis of epilepsy. EEG recordings of parents of 257 epileptic children were evaluated retrospectively. Some 156 healthy adults served as controls. Special attention was paid to alpha activity extending to the frontal region, both in bipolar and in referential recordings (Alpha I). Alpha I was found significantly more often in parents of children with primary generalized epilepsy (18%) compared with parents of children with focal epilepsy (8%) or controls (9%). In a second step, parental EEGs of children with different EEG patterns associated with epilepsy were studied. Alpha I was found significantly more often in parents of children with focal sharp waves and generalized spikes and waves (26%) than in parents of probands with focal sharp waves without additional generalized spikes and waves (8%) or in controls (9%). Parents of probands with theta rhythms and spikes and waves had alpha I significantly more often (18%) than parents of probands with theta rhythms without additional spikes and waves (8%) or controls (9%). The findings reveal a clear correlation between the type of EEG background activity in parents and the EEG characteristics in their children, thus pointing to common mechanisms.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams A (1959) Studies on the flat electroencephalogram in man. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 11:35–41
Anokhin A, Steinlein O, Fischer C, Yping M, Vogt P, Schalt E, Vogel F (1992) A genetic study of the human low-voltage electroencephalogram. Hum Genet 90:99–112
Baier WK, Doose H (1987) Interdependence of different genetic EEG patterns in siblings of epileptic patients. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 66:483–488
Barlow JS (1993) The electroencephalogram. Its patterns and origins. A Bradford Book, London / MIT Press Cambridge, Mass. pp 152–154
Dieker H (1967) Untersuchungen zur Genetik besonders regelmäßiger hoher Alpha-Wellen im EEG des Menschen. Humangenetik 4:189–216
Doose H, Baier WK (1987) Genetic factors in epilepsies with primarily generalized minor seizures. Neuropediatrics 18 [Suppl 1]:1–64
Doose H, Baier WK (1988) Theta rhythms in the EEG — a genetic trait in childhood epilepsy. Brain Dev 10:347–354
Doose H, Baier WK (1989) Generalized spikes and waves. In: Beck-Mannagetta G, Anderson VE, Doose H, Janz D (eds) Genetics of epilepsies. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 95–103
Doose H, Waltz S (1993a) Das monotone Alpha-EEG — ein prädisponierender Faktor in der Pathogenese generalisierter Epilepsien. In: Stefan H (ed) Epilepsie 92. Deutsche Sektion der Internationalen Liga gegen Epilepsie, Berlin, pp 189–195
Doose H, Waltz S (1993b) Photosensitivity — genetics and clinical aspects. Neuropediatrics 24:249–255
Doose H, Völzke E, Scheffner D (1965) Verlaufsformen kindlicher Epilepsien mit spike wave-Absencen. Arch Psychiat Nervenkr 207:394–415
Doose H, Gerken H, Hien-Voelpel KF, Völzke E (1969) Genetics of photosensitive epilepsy. Neuropädiatrie 1:56–73
Doose H, Gerken H, Völzke E (1972) On the genetics of EEG-anomalies. I. Abnormal theta rhythms. Neuropädiatrie 3:386–401
Dumermuth G (1968) Variance spectra of electroencephalograms in twins. In: Kellaway P, Petersén J (eds) Clinical electroencephalography of children. Almquist and Wiksell, Stockholm, pp 119–154
Gasser T, Jennen-Steinmetz C, Sroka L, Verleger R, Möcks I (1988) Development of the EEG of school-age children and adolescents. 11. Topography. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 69:100–110
Gloor P (1982) Towards a unifying concept of epileptogenesis. In: Akimoto H, et al (eds) Advances in epileptology: XIIIth Epilepsy International Symposium. Raven, New York, pp 83–86
Gundel A, Doose H (1986) Genetic EEG patterns in febrile convulsions — a multivariate analysis. Neuropediatrics 17:3–6
Inouye T, Sakamoto H, Shinosaki K, Toi S, Ukai S (1990) Analysis of rapidly changing EEGs before generalized spike and wave complexes. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 76:205–221
Janz D, Christian W (1957) Impulsiv-Petit mal. Dtsch Z Nervenheilkd 176:346–386
Lykken DT, Teilegen A, Thorkelson K (1974) Genetic determination of EEG frequency spectra. Biol Psychol 1:245–259
Matousek M, Petersén I (1973) Frequency analysis of the EEG in normal children and in normal adolescents. In: Kellaway P, Petersén J (eds) Automation of clinical electroencephalography. Raven, New York, pp 75–102
Michel CM, Lehmann D, Henggeler B, Brandeis D (1992) Localization of the sources of EEG delta, theta, alpha and beta frequency bands using the FFT dipole approximation. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 82:38–44
Ottman R, Hauser WA, Susser M (1985) Genetic and maternal influences on susceptibility to seizures. Am J Epidemiol 122:923–939
Ottman R, Annegers JF, Hauser WA, Kurland LT (1988) Higher risk of seizures in offspring of mothers than of fathers with epilepsy. Am J Hum Genet 43:257–264
Propping P (1977) Genetic control of ethanol action in the central nervous system. An EEG study in twins. Hum Genet 35:309–334
Propping P, Friedl W, Nebel B, Feige A (1979) Plasma DBH, platelet MAO and proteins of red blood cell membranes in individuals with variants of the normal EEG. Neuropsychobiology 5:309–316
Propping P, Friedl W, Pluto R (1980) Further evidence for a correlation between EEG synchronization and plasma DBH activity in normal subjects. J Neural Transm 49:167–178
Rodin EA, Ancheta O (1987) Cerebral electrical fields during petit mal absences. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 66:457–466
Simon O, Müllner E, Heinemann U (1976) Relationship between background activity and subclinical seizure pattern. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 40:449–455
Stassen HH, Lykken DT, Propping P, Bomben G (1988) Genetic determination of the human EEG. Hum Genet 80:165–176
Steinlein O, Anokhin A, Yping M, Schalt E, Vogel F (1992) Localization of a gene for the human low-voltage EEG on 10q and genetic heterogeneity. Genomics 2:227–237
Vogel F (1958) Über die Erblichkeit des normales EEG. Zwillingsuntersuchungen. Thieme, Stuttgart
Vogel F (1962a) Ergänzende Untersuchungen zur Genetik des menschlichen Niederspannungs-EEG. Dtsch Z Nervenheilkd 184:105–111
Vogel F (1962b) Untersuchungen zur Genetik der β-Wellen im EEG des Menschen. Dtsch Z Nervenheilk 184:137–173
Vogel F (1966) Zur genetischen Grundlage fronto-präzentraler βWellen-Gruppen im EEG des Menschen. Humangenetik 2:227–237
Vogel F (1970) The genetic basis of the normal human electroencephalogram (EEG). Humangenetik 10:91–114
Vogel F, Götze W (1959) Familienuntersuchungen zur Genetik des normalen Elektroenzephalogramms. Dtsch Z Nervenheilkd 178:668–700
Vogel F, Schalt E (1979) The electroencephalogram (EEG) as a research tool in human behavior genetics: psychological examinations in healthy males with various inherited EEG variants. III. Interpretation of the results. Hum Genet 57:81–111
Vogel F, Schalt E, Krüger J, Propping P, Lehnen KF (1979a) The electroencephalogram (EEG) as a research tool in human behavior genetics: psychological examinations in health males with various inherited EEG variants. I. Rationale of the study, material, methods, heritability of test parameters. Hum Genet 47:1–45
Vogel F, Schalt E, Krüger J (1979b) The electroencephalogram (EEG) as a research tool in human behavior genetics: psycholocical examinations in healthy males with various inherited EEG variants. II. Results. Hum Genet 47:47–80
Vogel F, Krüger J, Höpp H-P, Schalt E, Schnobel R (1986) Visually and auditory evoked EEG potentials in carriers of four hereditary EEG variants. Hum Neurobiol 5:49–58
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Doose, H., Castiglione, E. & Waltz, S. Parental generalized EEG alpha activity predisposes to spike wave discharges in offspring. Hum Genet 96, 695–704 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00210302
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00210302