Summary
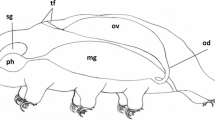
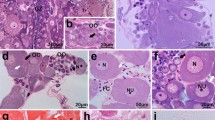
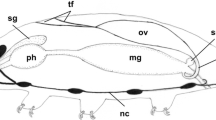
Oogenesis in Typosyllis pulchra begins with a short proliferative gonial phase. Gonial clusters, consisting of six to eight syncytial sibling cells, are surrounded by gonial peritoneum and are eventually liberated into the coelom. At about the same time as the onset of the coelomic phase, one gonial cell in each cluster differentiates, begins to accumulate yolk and increases in size, eventually to become a mature oocyte. Yolk is composed of lipid droplets and membranebound protein granules. The protein component appears to be at least partially synthesized by the oocyte although there are some signs of endocytosis. Nurse cells and peritoneal cells are apparently able to manufacture some protein that may also be utilized by the oocyte. The nurse cells maintain cytoplasmic continuity with the oocyte, and mitochondria and ribosomes are often seen within the intercellular bridges between oocyte and nurse cell. Immediately prior to spawning, oocytes undergo prematuration and cytoplasmic reorganization. Ultrastructural changes which occur during oocyte growth and maturation are described.
Similar content being viewed by others
Reference
Allen MJ (1964) Embryological development of a syllid, Autolytus fasciatus (Bosc). (Class Polychaeta). Biol Bull 127:187–205
Allen MJ (1967) Nucleic acid and protein synthesis in the developing oocytes of the budding form of the syllid Autolytis edwardsi (Polychaeta). Biol Bull 133:287–302
Anderson E (1968) Cortical alveoli formation and vitellogenesis during oocyte differentiation in the pipefish Syngnathus fuscus and the killifish Fundulus heteroclitus. J Morphol 125:53–60
Anderson E, Huebner E (1968) Development of the oocyte and its accessory cells of the polychaete Diopatra cuprea (Bosc). J Morphol 126:163–197
Anderson L, Telfer WH (1969) A follicle cell contribution to the yolk spheres of moth oocytes. Tissue and Cell 1:633–644
Beams HW Kessel RG (1969) Synthesis and deposition of oocyte envelopes (vitelline membrane, chorion) and the uptake of yolk in the dragonfly (Odonata: Aeschnidae). J Cell Sci 4:241–264
Bier K (1963) Autoradiographische Untersuchungen über die Leistungen des Follikelepithels und der Nährzellen bei der Dotterbildung und Eiweißsynthese im Fliegenovar. Wilhelm Roux Arch. Entwicklungsmech. Organismen 154:552–575
Bier K (1969) Oogenesetypen bei Insekten und Vertebraten, ihre Bedeutung für die Embryogenese und die Phylogenese. Zool Anz Suppl 33:7–29
Bilinski S (1977) Oogenesis in Acerentomon gallicum Jonescu (Protura). Previtellogenic and vitellogenic stages. Cell Tissue Res 179:401–412
Cloney RA, Florey E (1968) Ultrastructure of cephalopod chromatophore organs. Z Zellforsch 89:250–280
Cognetti-Varriale AM (1965) Ricerche sulla biologia riproduttiva dei Policheti. 1. Gli ovari delle Exogoninae. Arch Zool Ital 50:26–28
Daly JM (1972) The maturation and breeding biology of Harmothoe imbricata (Polychaeta: Polynoidae). Mar Biol 12:53–66
Dhainaut A (1966) Étude ultrastructurale de l'évolution des éléocytes chez Nereis pelagica L. (Annélide Polychète), à l'approche de maturité sexuelle. C R Acad Sci (Paris) 262 D: 2740–2743
Dhainaut A (1967) Étude de la vitellogenèse chez Nereis diversicolor (Müller OF) (Annélide Polychète) par autoradiographie à haute résolution. CR Acad Sci Paris 265 D: 434–436
Dhainaut A (1968) Étude par autoradiographie à haute résolution de l'élaboration des mucopolysaccharides acides au cours de l'ovogenèse de Nereis pelaqica L. (Annélide Polychète). J Microsc 7:1075–1080
Dhainaut A (1970a) Étude cytochimique et ultrastructurale de l'évolution ovocytaire de Nereis pelagica L. (Annélide Polychète). I. Ovogenèse naturelle. Z Zellforsch 104:375–390
Dhainaut A (1970b) Étude cytochimique et ultrastructurale de l'évolution ovocytaire de Nereis pelagica L. (Annélide Polychète). II. Évolution expérimentale en l'absence d'hormone cérébrale. Z Zellforsch 104:390–405 (1970b)
tDumont JN (1969) Oogenesis in the annelid Enchytraeus albidus with special reference to the origin and cytochemistry of the yolk. J Morphol 129:317–344
Dumont JN, Anderson E (1967) Vitellogenesis in the horseshoe crab Limulus polyphemus J Microsc 6:791–806
Durchon M (1959) Contributions à l'étude de la stolonisation chez les Syllidiens (Annélides Polychètes). I. Syllinae Bull. Biol Fr Belg 93:155–219
Eckelbarger KJ (1975) A light and electron microscope investigation of gametogenesis in Nicolea zostericola (Grube 1860) (Polychaeta: Terebellidae). Mar Biol 31:116–134
Eckelbarger KJ (1979) Ultrastructural evidence for both autosynthetic and heterosynthetic yolk formation in the oocytes of an annelid (Phragmatopoma lapidosa: Polychaeta). Tissue and Cell 11:425–443
Eckelbarger KJ (1980) An ultrastructural study of oogenesis in Streblospio benedicti (Spionidae), with remarks on diversity of vitellogenic mechanisms in Polychaeta. Zoomorphologie 94:241–263
Eckelbarger KJ, Chia F-S (1978) Morphogenesis of larval cuticle in the polychaete Phragmatopoma lapidosa. A correlated scanning and transmission electron microscopic study from egg envelope formation to larval metamorphosis. Cell Tissue Res 186:187–201
Emanuelsson H (1971) Electron microscope observations on yolk and yolk formation in Ophryotrocha labronica La Greca and Bacci. Z Zellforsch 95:19–36
Fawcett DW (1961) Intercellular bridges. Exp Cell Res 22, Suppl 8:174–187
Fischer A (1975) The structure of symplasmis early oocytes and their sheath cells in the polychaete, Platynereis dumerilii. Cell Tissue Res 160:327–343
Fischer A (1979) A vitellin-like antigen in the coelomic fluid of maturing Nereis virens females. Naturwissenschaften 66:316–317
Franke H-D (1979) Experimentelle Untersuchungen zur Steuerung des Fortpflanzungsrhythmus und der sexuellen Differenzierung an Laborkulturen des Polychaeten Typosyllis prolifera (Krohn 1852). Dissertation, Technische Universität zu Braunschweig
Franklin LE (1966) An egg cell-membrane derivative on the vitelline membrane of annelid eggs. Exp Cell Res 43:673–675
Gidholm L (1963) The sexual organs in the budding form of Autolytus. Zool Bidr Uppsala 35:529–544
Gidholm L (1965) On the morphology of the sexual stages, mating and egg-laying in Autolytus (Polychaeta). Zool Bidr Uppsala 19:135–142
Gwynn I, Jones PCT (1971) On the egg investments and fertilization reaction in Pomatoceros triqueter L. Z Zellforsch 113:388–395
Heacox AE (1980) Reproduction, ultrastructure of gametogenesis and endocrine control of gametogenesis and sex determination in Typosyllis pulchra (Polychaeta: Syllidae). Dissertation, Washington State University, Pullman, Washington
Heacox AE, Schroeder PC (1981) A light and electron microscopic investigation of gametogenesis in Typosyllis pulchra (Berkeley and Berkeley) (Polychaeta: Syllidae). I. Gonad structure and spermatogenesis. Cell Tissue Res 218:623–639
Hill RS, Bowen ID (1976) Studies on the ovotestis of the slug Agriolimax reticulatus (Müller), 1. The oocyte. Cell Tissue Res. 173:465–483
Howie DID (1963) Experimental evidence for the hormonal stimulation of ripening of the gametes and spawning in the polychaete Arenicola marina (L.). Gen Comp Endocrinol 3:660–668
Huebner E, Anderson E. (1970) The effects of vinblastine sulfate on the microtubular organization of the ovary of Rhodnius prolixus. J Cell Biol 46:191–198
Huebner E, Anderson E (1972) A cytological study of the ovary of Rhodnius prolixus. II. Oocyte differentiation. J Morphol 137:385–416
Humphrey DC, Pittman FE (1974) A simple methylene blue-azure II-basic fuchsin stain for epoxyembedded tissue sections. Stain Technol 49:9–14
Jouin C (1968) Sexualité et biologie de la réproduction chez Mesonerilla Remane et Meganerilla Boaden (Archiannélides, Nerillidae). Cal Biol Mar 9:31–52
King PE, Bailey JH, Babbage PC (1969) Vitellogenesis and formation of the egg chain in Spirorbis borealis (Serpulidae). J Mar Biol Ass UK 49:141–151 (1969)
Longo JF, Anderson E (1974) Gametogenesis In: Lash J, Whittaker JR (eds) Concepts of development. Sinauer Associates, Stanford, pp 3–47
Luft JH (1961) Improvements in epoxy resin embedding methods. J Biophys Biochem Cytol 9:409–414 (1961)
Malaquin A (1893) Recherches sur les Syllidiens. Morphologie, anatomie, réproduction, développement. Mem Soc Sci Arts Lille, pp 1–477
Olive PJW, Clark RB (1978) Physiology of reproduction. In: Mill PJ (ed) Physiology of Annelids, Academic Press, New York
Pasteels JJ (1965) Étude au microscope électronique de la réaction corticale. II. La réaction corticale de l'œuf vierge de Sabellaria alveolate. J Embryol Exp Morphol 13:327–339
Potswald HE (1972) Cytological observations on the so called neoblasts in the serpulid Spirorbis borealis. J Morphol 135:215–229
Potts FA (1911) Methods of reproduction in the syllids. Ergeb Fortschr Zool 3:1–72
Rasmussen E (1973) Systematics and ecology of the Isefjord marine fauna (Denmark). Ophelia 11:1–507
Ruthmann A (1964) Zellwachstum und RNS-Synthese im Ei-Nährzellverband von Ophryotrocha puerilis. Z Zellforsch 63:816–829
Schroeder PC, Hermans CO (1975) Annelida: Polychaeta. In: Giese AC, Pearse JS (eds) Reproduction of Marine invertebrates, Vol 3, Annelida and Echiurans. Academic Press, New York
Sichel G (1966) Modificazioni ultrastrutturali dell'ooplasma in rapporto alla vitellogenesi in Mercierella enigmatica Fauvel. Atti Accad Gioenia Sci Natur Catania 18:21–32
Spornitz UM, Kress A (1971) Yolk platelet formation in oocytes of Xenopus laevis (Daudin). Z Zellforsch 117:235–251
Tyler A (1965) The biology and chemistry of fertilization. Am Naturalist 99:309–334
Wartenberg H (1964) Experimentelle Untersuchungen über die Stoffaufnahme durch Pinocytose während der Vitellogenese des Amphibienoocyten. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat 63:1004–1019
Wiren A (1907) Macellicephala violacea Levinsen, nebst Bemerkungen über deren Anatomie. Zoologiska Studier Tillagnade Prof. I. Tullberg, Uppsala, pp 289–308
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Heacox, A.E., Schroeder, P.C. A light- and electron-microscopic investigation of gametogenesis in Typosyllis pulchra (Berkeley and Berkeley) (Polychaeta: Syllidae). Cell Tissue Res. 218, 641–658 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00210121
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00210121