Summary
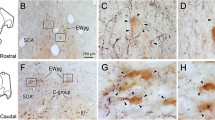
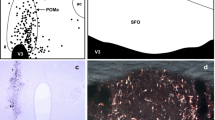
The octapeptide vasotocin, which is formed in the classical neurosecretory nuclei of lampreys (Petromyzonidae), is transported, bound to the carrier protein neurophysin, not only to the neurohypophysis but also to various other regions of the brain via exohypothalamic fibres. A target area of this exohypothalamic vasotocinergic system is, in the brook lamprey (Lampetra planeri Bloch), a relatively well circumscribed area in the isthmus region of the rhombencephalic tegmentum motoricum, which is called area lateralis tegmenti. In this area, which belongs to the reticular formation, the vasotocinergic fibres form synaptic contacts with nerve cell perikarya and processes. The vesicles contained in the fibres were identified, ultrahistochemically, as neurophysin vesicles. They correspond to the neurophysin vesicles observed in the neurohypophysis of the same species. The functional significance of the vasotocinergic supply to portions of the reticular formation in lampreys is open to discussion.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baker, B.L., Yu, Y.-Y.: Distribution of growth hormone-release-inhibiting hormone (somatostatin) in the rat brain as observed with immunocytochemistry. Anat. Rec. 186, 343 (1976)
Barker, J.L.: Peptides: roles in neuronal excitability. Physiol. Rev. 56, 435–452 (1976)
Barry, J.: Recherches morphologiques et expérimentales sur la glande diencéphalique et l'appareil hypothalamo-hypophysaire. Ann. sci. Univ. Besançon, Zool. Physiol., Sér. 2/5, 3–133 (1961)
Barry, J., Poulain, P., Carette, B.: Systématisation et éfférences des neurones à LRH chez les primates. Ann. d'Endocrinol. (Paris) 37, 227–234 (1976)
Baumgarten, H.G.: Biogenic monoamines in the cyclostome and lower vertebrate brain. Progress in Histochemistry and Cytochemistry (W. Graumann, Z. Lojda, A.G.E. Pearse, and T.H. Schiebler, eds.), Vol. 4, No. 1. Stuttgart: Fischer 1972
Bock, R.: Über die Darstellbarkeit neurosekretorischer Substanz mit Chromalaun-Gallocyanin im supraoptico-hypophysären System vom Hund. Histochemie 6, 362–369 (1966)
Brownfield, M.S., Kozlowski, G.P.: The hypothalamo-choroidal tract. I. Immunohistochemical demonstration of neurophysin pathways to telencephalic choroid plexuses and cerebrospinal fluid. Cell Tiss. Res. 178, 111–127 (1977)
Byck, R.: Peptide transmitters: A unifying hypothesis for euphoria, respiration, sleep, and the action of lithium. Lancet 1976 II, 72–73
Elde, R., Hökfelt, T., Johansson, O., Terenius, L.: Immunohistochemical studies using antibodies to leucine-enkephalin: Initial observations on the nervous system of the rat. Neuroscience 1, 349–351 (1976)
Follett, B.K., Heller, H.: The neurohypophysial hormones of bony fishes and cyclostomes. J. Physiol. (Lond) 172, 74–91 (1964)
Fuxe, K., Ganten, D., Hökfelt, T., Bolme, P.: Immunohistochemical evidence for the existence of angiotensin II-containing nerve terminals in the brain and spinal cord in the rat. Neurosci. Letters 2, 229–234 (1976)
Goossens, N., Dierickx, K., Vandesande, F.: Immunocytochemical demonstration of the hypothalamo-hypophysial vasotocinergic system of Lampetra fluviatilis. Cell Tiss. Res. 177, 317–323 (1977)
Heier, P.: Fundamental principles in the structure of the brain. A study of the brain of Petromyzon fluviatilis. Acta anat. (Basel), Suppl. 8, 1–213 (1948)
Helas, G.: frÉtude en fluorescence du système hypothalamo-hypophysaire de la grenouille verte (Rana esculenta) dans des conditions normales ou expérimentales. Bull. Ass. Anat. 152, 534–542 (1971)
Henderson, N.E.: Ultrastructure of the neurohypophysial lobe of the hagfish, Eptatretus stouti (Cyclostomata). Acta zool. (Stockh.) 53, 243–266 (1972)
Hökfelt, T., Efendić, S., Hellerström, C., Johansson, O., Luft, R., Arimura, A.: Cellular localization of somatostatin in endocrine-like cells and neurons of the rat with special references to the A1-cells of the pancreatic islets and to the hypothalamus. Acta endocr. (Kbh.) 80, Suppl. 200, 5–41 (1975c)
Hökfelt, T., Efendić, S., Johansson, O., Luft, R., Arimura, A.: Immunohistochemical localization of somatostatin (growth hormone release-inhibiting factor) in guinea pig brain. Brain Res. 80, 165–169 (1974)
Hökfelt, T., Elde, R., Johansson, O., Luft, R., Nilsson, G., Arimura, A.: Immunohistochemical evidence for separate populations of somatostatin-containing and substance P-containing primary afferent neurons in the rat. Neuroscience 1, 131–136 (1976a)
Hökfelt, T., Fuxe, K., Johansson, O., Jeffcoate, S., White, N.: Distribution of thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) in the central nervous system as revealed with immunohistochemistry. Europ. J. Pharmacol. 34, 389–392 (1975a)
Hökfelt, T., Fuxe, K., Johansson, O., Jeffcoate, S., White, N.: Thyrotropin releasing hormone (TRH)-containing nerve terminals in certain brain stem nuclei and in the spinal cord. Neurosci. Letters 1, 133–139 (1975b)
Hökfelt, T., Kellerth, J.O., Nilsson, G., Pernow, B.: Substance P: Localization in the central nervous system and in some primary sensory neurons. Science 190, 889–890 (1975d)
Hökfelt, T., Meyerson, B., Nilsson, G., Pernow, B., Sachs, C.: Immunohistochemical evidence for substance P-containing nerve endings in the human cortex. Brain Res. 104, 181–186 (1976b)
Kobayashi, H.: Median eminence of the hagfish and ependymal absorption in higher vertebrates. In: Brain-endocrine interaction. Median eminence: Structure and function (K.M. Knigge, D.E. Scott, and A. Weindl, eds.), pp. 67–78. Basel: Karger 1972
Kobayashi, H., Uemura, H.: The neurohypophysis of the hagfish, Eptatretus burgen (Girard). Gen. comp. Endocr. Suppl. 3, 114–124 (1972)
Kozlowski, G.P., Brownfield, M.S., Schultz, W.J.: Extrahypothalamic neurosecretory system: Immunocytochemical evidence for a neurosecretory innervation of the choroid plexus. Proc. VII Int. Symp. Neurosecretion, p. 93. Leningrad 1976
Larsson, L.-I., Fahrenkrug, J., Schaffalitzky de Muckadell, O., Sundler, F., Håkanson, R., Rehfeld, J.F.: Localization of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP) to central and peripheral neurons. Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. (Wash.) 73, 3197–3200 (1976)
Legait, H.: Les voies éfférentes des noyaux neurosécrétoires hypothalamiques chez les Oiseaux. C.R. Soc. Biol. (Paris) 150, 996–998 (1956)
Legait, H., Anatomie microscopique des noyaux hypothalamiques neurosécrétoires et de leur voies éfférentes chez la Poule Rhode-Island. Acta neuroveg. (Wien) 15, 252–262 (1957)
Legait, H., Legait, E.: Mise en évidence de voies neurosécrétoires extra-hypothalamo-hypophysaires chez quelques Batraciens et Reptiles. C.R. Soc. Biol. (Paris) 150, 1429–1431 (1956)
Legait, H., Legait, E.: Relations entre les noyaux hypothalamiques neurosécrétoires et les régions septale et habénulaire chez quelques Oiseaux. Acta neuroveg. (Wien) 17, 143–147 (1957a)
Legait, H., Legait, E.: Les voies extra-hypophysaires des noyaux neuro-sécrétoires hypothalamiques chez les Batraciens et les Reptiles. Acta anat. (Basel) 30, 429–443 (1957b)
Legait, H., Legait, E.: Présence d'une voie neurosécrétoire hypothalamo-habénulaire et mise en évidence d'une activité antidiuretique au niveau des ganglions de l'habénula chez la Poule. C.R. Soc. Biol. (Paris) 152, 828–830 (1958)
Marx, J.L.: Learning and behavior (I): Effects of pituitary hormones. Science 190, 367 (1975a)
Marx, J.L.: Learning and behavior (II): The hypothalamic peptides. Science 190, 544–545 (1975b)
Müller, H.: Zur Feinstruktur der “Neurohypophyse” des Bachneunauges Lampetra planeri (Bloch). Biol. Rdsch. 1, 228–230 (1964a)
Müller, H.: Elektronenmikroskopische Untersuchung der “Neurohypophyse” vom Bachneunauge Lampetra planeri (Bloch). In: Electron Microscopy 1964, Vol. Biology. Proc. III Europ. Reg. Conf., Prague 1964, p. 479–480 (1964)
Naumann, W., Sterba, G.: Ultrastructural studies on neurophysine-containing vesicles of the neurosecretory system of vertebrates. Cell Tiss. Res. 165, 545–553 (1976a)
Naumann, W., Sterba, G.: An ultrahistochemical method to identify neurophysin-containing vesicles of the neurosecretory system of vertebrates. Proc. VII Int. Symp. Neurosecretion, p. 115. Leningrad 1976 (b)
Nieuwenhuys, R.: Topological analysis of the brain stem of the lamprey, Lampetra fluviatilis. J. comp. Neurol. 145, 165–178 (1972)
Nilsson, G. Hökfelt, T., Pernow, B.: Distribution of substance P-like immunoreactivity in the rat central nervous system as revealed by immunohistochemistry. Medical Biol. 52, 424–427 (1974)
Percy, R., Leatherland, J.F., Beamish, F.W.H.: Structure and ultrastructure of the pituitary gland in the sea lamprey, Petromyzon marinus, at different stages in its life cycle. Cell Tiss. Res. 157, 141–164 (1975)
Polenov, A.L., Belenky, M.A., Konstantinova, M.S.: The hypothalamo-hypophysial system of the lamprey, Lampetra fluviatilis L. I. The neurohypophysis. Cell Tiss. Res. 150, 505–519 (1974)
Reith, M.E.A., Schotman, P., Gispen, W.H., de Wied, D.: Pituitary peptides as modulators of neuronal functioning. Trends in Biochem. Sci. 2, 56–58 (1977)
Reynolds, E.S.: The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J. Cell Biol. 17, 208–215 (1963)
Rodríguez, E.M.: The comparative morphology of neural lobes of species with different neurohypophysial hormones. Mem. Soc. Endocr. 19, 263–292 (1971)
Rudert, H.: Das Subfornikalorgan und seine Beziehungen zu dem neurosekretorischen System im Zwischenhirn des Frosches. Z. Zellforsch. 65, 790–804 (1965)
Rühle, H.-J., Sterba, G.: Zur Histologie der Hypophyse des Flußneunauges (Lampetra fluviatilis L.). Z. Zellforsch. 70, 136–168 (1966)
Sandman, C.A., Miller, L.H., Kastin, A.J.: Introduction to: The neuropeptides. Pharmacology, physiological substrates and behavioral effects. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 5, Suppl. 1, 1–2 (1976)
Sawyer, W.H.: Active neurohypophysial principles from a cyclostome (Petromyzon marinus) and two cartilaginous fishes (Squalus acanthias and Hydrolagus collei). Gen. comp. Endocr. 5, 427–439 (1965)
Schober, F., Naumann, W., Sterba, G.: Light and electron microscopic study of the oxytocinergic efferences of the hypothalamus in the medulla of rat and pigeon. Proc. VII Int. Symp. Neurosecretion, p. 144. Leningrad 1976
Schober, W., Vergleichend-anatomische Untersuchungen am Gehirn der Larven und adulten Tiere von Lampetra fluviatilis (Linné, 1758) und Lampetra planeri (Bloch, 1784). J. Hirnforsch. 7, 107–209 (1964)
Schwab, M.E.: Some new aspects about the prosencephalon of Lampetra planeri (L.): A cytoarchitectural and comparative study. Acta anat. (Basel) 86, 353–375 (1973)
Sterba, G.: Fluoreszenzmikroskopische Untersuchungen über die Neurosekretion beim Bachneunauge (Lampetra planeri Bloch). Z. Zellforsch. 55, 763–789 (1961)
Sterba, G.: Neuro- and gliasecretion. In: The biology of lampreys, Vol. 2 (M.W. Hardisty and I.C. Potters, eds.), pp. 69–89. London-New York: Academic Press 1972
Sterba, G.: Das oxytocinerge neurosekretorische System der Wirbeltiere. Beitrag zu einem erweiterten Konzept. Zool. Jb. Physiol. 78, 409–123 (1974a)
Sterba, G.: Ascending neurosecretory pathways of the peptidergic type. In: Neurosecretion — The final neuroendocrine pathway (F. Knowles and L. Vollrath, eds.), pp. 38–47. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer 1974b
Sterba, G.: The oxytocinergic exohypothalamic neurosecretory system of vertebrates and memory processes. Proc. VII Int. Symp. Neurosecretion, p. 158. Leningrad 1976
Sterba, G.: Morphologische Grundlagen einer humoralen Informationsübermittlung durch Peptide bei Wirbeltieren. Sitzungsber. der Akademie der Wissenschaften der DDR, 5 N, 40–61 (1977)
Sterba, G., Hoheisel, G., Rühle, H.-J., Engelmann, W.E.: Extrahypothalamische peptiderge Neurosecretion. I. Neurosekretion im Mittelhirn der Neunaugen. Z. Zellforsch. 142, 329–345 (1973)
Tsuneki, K., Adachi, T., Ishii, S., Oota, Y.: Morphometric classification of neurosecretory granules in the neurohypophysis of the hagfish, Eptatretus burgert. Cell Tiss. Res. 166, 145–157 (1976)
Tsuneki, K., Gorbman, A.: Ultrastructure of pars nervosa and pars intermedia of the lamprey, Lampetra tridentata. Cell Tiss. Res. 157, 165–184 (1975a)
Tsuneki, K., Gorbman, A.: Ultrastructure of the anterior neurohypophysis and the pars distalis of the lamprey, Lampetra tridentata. Gen. comp. Endocr. 25, 487–508 (1975b)
Wächtler, K.: The distribution of acetylcholinesterase in the cyclostome brain. I. Lampetra planeri (L.). Cell Tiss. Res. 152, 259–270 (1974)
Weber, W.: Entwicklung und Funktion des neurosekretorischen Systems von Salamandra salamandra. Z. Zellforsch. 66, 35–65 (1965)
Wegelin, R., Sterba, G., Hoheisel, G.: Licht- und elektronenmikroskopische Untersuchungen am exohypothalamischen oxytocinergen System von Pleurodeles waltli Michah. (Urodela). Biol. Zbl. 94, 633–660 (1975)
Weindl, A., Sofroniew, M.V.: Demonstration of extrahypothalamic peptide secreting neurons. A morphologic contribution to the investigation of psychotropic effects of neurohormones. Pharmacopsych. 9, 226–234 (1976)
Weindl, A., Sofroniew, M.V., Schinko, I.: Psychotrope Wirkungen hypothalamischer Hormone: Immunhistochemische Identifikation extrahypophysärer Verbindungen neuroendokriner Neurone. Arzneimittel-Forsch. (Drug Res.) 26, Nr. 6, 1191–1194 (1976a)
Weindl, A., Sofroniew, M.V., Schinko, I.: Vasopressin and LRH secreting systems: Identification and localization by immunohistochemistry. Proc. VII Int. Symp. Neurosecretion, p. 172. Leningrad 1976 (b)
Wied, D. de: Peptides and behavior. Life Sci. 20, 195–204 (1977)
Wied, D. de, Wimersma Greidanus, Tj.B. van, Bohus, B., Urban, I., Gispen, W.H.: Vasopressin and memory consolidation. In: Perspectives in Brain Research (M.A. Corner and D.F. Swaab, eds.), Progress in Brain Research, Vol. 45, pp. 181–194. Elsevier/North Holland: Biomedical Press 1976
Wimersma Greidanus, Tj. B. van, de Wied, D.: The physiology of the neurohypophysial system and its relation to memory processes. In: Biochemical correlations of brain structure and function (A.N. Davison, ed.), pp. 215–248. New York-London: Academic Press 1977
Wohlfarth-Bottermann, K.E.: Die Kontrastierung tierischer Zellen und Gewebe im Rahmen ihrer elektronenmikroskopischen Untersuchungen an ultradünnen Schnitten. Naturwissenschaften 44, 287–288 (1957)
Wolf, G.: Immunhistological identification of neurophysin and neurophysin-like substances in different vertebrates. Endokrinologie 68, 288–299 (1976a)
Wolf, G.: On the immunological relationship of the neurophysins of vertebrates. Proc. VII Int. Symp. Neurosecretion, p. 174. Leningrad 1976 (b)
Zetler, G.: The peptidergic neuron: A working hypothesis. Biochem. Pharmacol. 25, 1817–1818 (1976)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by grants from the Ministry for Science and Technology of the German Democratic Republic.
Acknowledgements: For skilled technical assistance the authors are indebted to their colleagues Mrs. S. Mehnert, E. Siebert, C. Schneider, and I. Seifert.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hoheisel, G., Rühle, H.J. & Sterba, G. The reticular formation of lampreys (Petromyzonidae) — A target area for exohypothalamic vasotocinergic fibres. Cell Tissue Res. 189, 331–345 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00209281
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00209281