Abstract
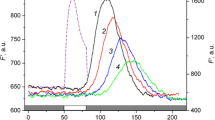
The fluorescent calcium-sensitive dye 1-[2-amino-5-(6-carboxyindol-2-yl)-phenoxy]-2-(2′-amino-5′-methylphenoxy)-ethane-N,N,N′,N′-tetraacetic acid (indo-1) was loaded by a transplasmalemma pH gradient into filamentous cells and protoplasts of Mougeotia scalaris, such that most of the indo-1 fluorescence originated from the cytoplasm. Incubation of M. scalaris filaments in ethylene glycol-bis(β-aminoethyl ether)-N,N,N′,N′-tetraacetic acid (EGTA)-buffered media (-log [Ca2+] (=pCa) 8 versus pCa 3) caused a consistent and significant decrease in the cytoplasmic free [Ca2+]. Pulses of the fluorescence excitation light (UV-A 365 nm, 0.7 s) caused an increase in cytoplasmic free [Ca2+] in M. scalaris that was nearly independent of the external [Ca2+] and of chloroplast dislocation by centrifugation. This calcium flux, highest in UV-A light, compared with blue or red light, probably resulted from a release of Ca2+ from intracellular stores. Increased cytoplasmic [Ca2+] may affect the velocity of chloroplast rotation since UV-A-light-mediated chloroplast movement was faster than in blue or red light. Consistently, the calcium ionophore A23187 and the calcium-channel agonist Bay-K8644 both increased the velocity of the red-light-mediated chloroplast rotation. Based on these and other observations, a Ca2+-induced decrease in cytoplasmic viscosity in Mougeotia is presumed to occur.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- EGTA:
-
ethylene glycol-bis-(β-aminoethyl ether)N,N,N′,N′-tetraacetic acid
- indo-1:
-
1-[2-amino-5-(6-carboxyindol-2-yl)-phenoxy]-2-(2′-amino-5′-methylphenoxy)-ethane-N,N,N′,N′tetraacetic acid
- pCa:
-
log [Ca2+]
- Pfr :
-
far-red-absorbing form of phytochrome
- Pr :
-
red-absorbing form of phytochrome
- xG :
-
geometric mean
References
Berkelman, T., Lagarias, J.C. (1990) Calcium transport in the green alga Mesotaenium caldariorum — Preliminary characterization and subcellular distribution. Plant Physiol. 93, 748–757
Brownlee, C., Wood, J.W. (1986) A gradient of cytoplasmic free calcium in growing rhizoid cells of Fucus serratus. Nature 320, 624–626
Bush, D.S., Jones, R.L. (1987) Measurement of cytoplasmic calcium in aleurone protoplasts using Indo-1 and Fura-2. Cell Calcium 8, 455–472
Bush, D.S., Jones, R.L. (1990) Measuring intracellular Ca2+ levels in plant cells using the fluorescent probes, Indo-1 and Fura-2 progress and prospects. Plant Physiol. 93, 841–845
Cork, R.J., Strautman, A.F., Robinson, K.R. (1989) Measuring cytoplasmic calcium: a review of three methods with emphasis on the practical aspects of their use. Biol. Bull. 176, Suppl., 25–30
Dorée, M., Picard, A. (1980) Release of Ca2+ from intracellular pools stops cytoplasmic streaming in Tradescantia staminal hairs. Experientia 36, 1291–1292
Felle, H. (1988) Cytoplasmic free calcium in Riccia fluitans L. and Zea mays L.: Interaction of Ca2+ and pH? Planta 176, 248–255
Felle, H. (1989) a2+-selective microelectrodes and their application to plant cells and tissues. Plant Physiol. 91, 1239–1242
Foos, K. (1970) Mikrotubuli bei Mougeotia spec. Z. Pflanzenphysiol. 62, 201–203
Galway, M.E., Hardham, A.R. (1986) Microtubule reorganization, cell wall synthesis and establishment of the axis of elongation in regenerating protoplasts of the alga Mougeotia. Protoplasma 135, 130–143
Gilroy, S., Hughes, W.A., Trewavas, A.J. (1989) A comparison between Quin-2 and Aequorin as indicators of cytoplasmic calcium levels in higher plant cell protoplasts. Plant Physiol. 90, 482–491
Grolig, F., Wagner, G. (1987) Vital staining permits isolation of calcium vesicles from the green alga Mougeotia. Planta 171, 433–437
Grolig, F., Wagner, G. (1988) Light-dependent chloroplast reorientation in Mougeotia and Mesotaenium: Biased by pigmentregulated plasmalemma anchorage sites to actin filaments? Bot. Acta 101, 2–6
Grolig, F., Wagner, G. (1989) Characterization of the isolated calcium-binding vesicles from the green alga Mougeotia scalaris, and their relevance to chloroplast movement. Planta 177, 169–177
Grynkiewicz, G., Poenie, M., Tsien, R.Y. (1985) A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J. Biol. Chem. 260, 3440–3450
Haupt, W. (1970) Hellrotund Dunkelrot-Wechselwirkungen bei der Chloroplastendrehung von Mougeotia. Wiss. Z. Ernst-Moritz-Arndt-Univ. Greifswald, Math. Naturwiss. Reihe 19, 47–54
Haupt, W. (1982) Light-mediated movement of chloroplasts. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. 33, 205–233
Haupt, W. (1987) Phytochrome control of intracellular movement. In: Phytochrome and photoregulation in plants, pp. 225–237, Furuya, M., ed. Academic Press, London
Haupt, W., Trump, K. (1975) Licht-orientierte Chloroplastenbewegung bei Mougeotia: Die Größe des Phytochromgradienten steuert die Bewegungsgeschwindigkeit. Biochem. Physiol. Pflanz. 168, 131–140
Hepler, P.K., Wayne, R.O. (1985) Calcium and plant development. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. 36, 397–439
Kakimoto, T., Shibaoka, H. (1986) Calcium-sensitivity of cortical microtubules in the green alga Mougeotia. Plant Cell Physiol. 27, 91–101
Kauss, H. (1987) Some aspects of calcium-dependent regulation in plant metabolism. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. 38, 47–72
Kraml, M., Büttner, G., Haupt, W., Herrmann, H. (1988) Chloroplast orientation in Mesotaenium: the phytochrome effect is strongly potentiated by interaction with blue light. Protoplasma Suppl. 1, 172–179
Kuroda, R., Hatano, S., Hiramoto, Y., Kuroda, H. (1988) Change of cytosolic Ca-ion concentration in the contraction and relaxation cycle of Physarum microplasmodia. Protoplasma Suppl. 1, 72–80
Martell, A.E., Smith, R.M. (1974) Critical stability constants. Plenum Press, New York
Minta, A., Kao, J.P.Y., Tsien, R.Y. (1989) Fluorescent indicators for cytosolic calcium based on rhodamine and fluorescein chromatophores. J. Biol. Chem. 264, 8171–8178
Neuscheler-Wirth, H. (1970) Wachstumsgeschwindigkeit und Wachstumsrhythmik bei Mougeotia. Z. Pflanzenphysiol. 63, 352–369
Owen, C.S., Shuler, R.L. (1989) Spectral evidence for non-calcium interactions of intracellular Indo-1. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 163, 328–333
Popov, E.G., Gavrilov, I.Y., Pozin, E.Y., Gabbasov, Z.A. (1988) Multiwavelength method for measuring concentration of free cytosolic calcium using the fluorescent probe indo-1. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 261, 91–96
Quader, H. (1990) Formation and disintegration of cisternae of the endoplasmic reticulum visualised in live cells by conventional fluorescence and confocal laser scanning microscopy: evidence for the involvement of calcium and the cytoskeleton. Protoplasma 155, 166–175
Roberts, D.M. (1989) Detection of a calcium-activated protein kinase in Mougeotia by using synthetic peptide substrates. Plant Physiol. 91, 1613–1619
Russ, U., Grolig, F., Wagner, G. (1988) Differentially absorbed vital dyes inhibit chloroplast movement in Mougeotia scalaris. Protoplasma Suppl. 1, 180–184
Schönbohm, E. (1987) Movement of Mougeotia chloroplasts under continuous weak and strong light. Acta Physiol. Plant 9, 109–135
Schönbohm, E., Hellwig, H. (1979) Zum Photorezeptorproblem der Schwachlichtbewegung des Mougeotia-Chloroplasten im Blau bzw. Hellrot bei niedrigen Temperaturen. Ber. Dtsch. Bot. Ges. 92, 749–762
Serlin, B.S., Ferrell, S. (1989) The involvement of microtubules in chloroplast rotation in the alga Mougeotia. Plant Sci. 60, 1–8
Stabenau, H. (1978) Wachstum von Mougeotia in der Durchlüftungskultur. Ber. Dtsch. Bot. Ges. 91, 251–255
Stern, M.D., Spurgeon, H.A., Hansford, R., Lakatta, E.G., Capogrossi, M.C. (1989) Optimum spectral windows to minimize quantum noise of ratiometric intracellular fluorescent probes. Cell Calcium 10, 527–534
Tretyn, A., Kendrick, R.E., Bossen, M.E. (1990) The effect of a calcium-channel antagonist, nifedipin and agonist, Bay K-8644, on the phytochrome-controlled swelling of etiolated wheat protoplasts. Physiol. Plant. 78, 230–235
Wagner, G., Grolig, F., Altmüller, D. (1987) Transduction chain of low irradiance response of chloroplast reorientation in Mougeotia in blue or red light. Photobiochem. Photobiophys. Suppl., 183–189
Wagner, G., Valentin, P., Dieter, P., Marmé, D. (1984) Identification of calmodulin in the green alga Mougeotia and its possible function in chloroplast reorientational movement. Planta 162, 62–67
Weisenseel, M. (1968) Vergleichende Untersuchungen zum Einfluß der Temperatur auf lichtinduzierte Chloroplastenverlagerungen. Z. Pflanzenpysiol. 59, 56–69 and 153–171
Williamson, R.E. (1984) Calcium and the plant cytoskeleton. Plant Cell Environ. 7, 431–440
Williamson, R.E., Ashley, C.C. (1982) Free Ca2+ and cytoplasmic streaming in the alga Chara. Nature 296, 647–651
Zhang, D.H., Callaham, D.A., Hepler, P.K. (1990) Regulation of anaphase chromosome motion in Tradescantia stamen hair cells by calcium and related signaling agents. J. Cell Biql. 111, 171–182
Zurzycki, J. (1955) Chloroplast arrangement as a factor in photosynthesis. Acta Soc. Bot. Pol. 24, 27–63
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Dedicated to Professor Wolfgang Haupt on the occasion of his 70th birthday
This paper is part of the Ph.D. thesis of U. Russ at the Justus-Liebig-Universitat Giessen (FRG). Part of this work has been presented at a meeting on “Calcium and intracellular signalling in plants” in Plymouth, UK, Dec. 1990
We are indebted to Dr. G. Seibold and Dipl. Phys. H. Weintraut for their advice on the technique of microspectrofluorometry and for allowing access to the microspectrophotometric facilities in the Strahlenzentrum der Justus-Liebig-Universität, Giessen, FRG. We thank Mrs. A. Quanz for reliable culture of the algae and evaluation of the videotapes. Bay-K8644 was a generous gift of Bayer AG, Wuppertal, FRG. U. russ was supported by a scholarship according to the Hessisches Graduierten Förderungsgesetz. This work was supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Russ, U., Grolig, F. & Wagner, G. Changes of cytoplasmic free Ca2+ in the green alga Mougeotia scalaris as monitored with indo-1, and their effect on the velocity of chloroplast movements. Planta 184, 105–112 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00208243
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00208243