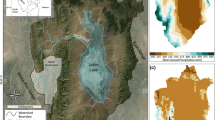
Abstract
A regional model of the atmosphere (version 4 of the NCAR mesoscale model, MM4) was used to assess whether lake-effect precipitation was a significant component of the late-Pleistocene hydrologic budgets of Lakes Lahontan and Bonneville. Control simulations for January and July of 1979 were made using MM4, and the Pleistocene highstand surface areas of the lakes were added to the model and the simulations repeated. In the January simulations, 18% of the moisture added to the modeled atmosphere by Lake Lahontan returned to the Lahontan basin as precipitation, while 32% of the water evaporated from Lake Bonneville fell as precipitation over the Bonneville basin. In the July simulations, 7% of the moisture added to the modeled atmosphere by Lake Lahontan returned to the Lahontan basin as precipitation, and 4% of the water evaporated from Lake Bonneville fell as precipitation over the Bonneville basin. An additonal January simulation was made with the lake surface areas set at onehalf their highstand extents (the average surface area 20 to 15 ka BP). Results from this simulation were similar to the simulation with the highstand lakes, indicating lake-effect precipitation could have been a significant component of the hyrologic budgets of the lakes before and during the highstand period.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antevs E (1948) The Great Basin, with emphasis on glacial and post-glacial times; climate changes and pre-white man. Bull Univ Utah Biolog Ser 19:168–191
Anthes RA, Warner TT (1978) Development of hydrodynamical models suitable for air pollution and other mesometeorological studies. Mon Wea Rev 106:1045–1078
Anthes RA, Hsie EY, Kuo YH (1987) Description of the Penn State/NCAR mesoscale model version 4 (MM4). NCAR Technical Note, NCAR/TN-282 + STR, National Center for Atmospheric Research, Boulder, Colorado
Benson LV, Thompson RS (1987a) Lake-level variation in the Lahontan basin for the past 50000 years. Quat Res 28:69–85
Benson LV, Thompson S (1987b) The physical record of lakes in the Great Basin. In: Ruddiman WF, Wright HE (eds) North America and adjacent oceans during the last deglaciation. Geol Soc Am, pp 241–260
Benson LV, Curry DR, Dorn RI, Lajoie KR, Oviatt CG, Robinson SW, Smith GI, Stine S, Thompson RS (1990) Variation in sizes of four Great Basin lake systems during the past 35 000 years. Paleogeog Paleoclim Paleoecol 78:241–286
Carpenter DM (1984) An introduction to Great Salt Lake effect snowfall. In: Kay PA, Diaz HF (eds) Problems of and prospects for predicting Great Salt Lake levels. Center Pub Affairs Admin, Univ Utah, Logan pp 155–165
Dickinson RE, Errico RM, Giorgi F, Bates GT (1989) A regional climate model for the western United States. Clim Change 15:383–422
Dohrenwend JC (1984) Nivation landforms in the western Great Basin and their paleoclimatic significance. Quat Res 19:231–324
Eichenlaub VL (1979) Weather and climate of the Great Lakes Region. Univ of Notre Dame Press, South Bend
Giorgi F, Bates GT (1989) The climatological skill of a regional model over complex terrain. Mon Wea Rev 117 (11):2325–2347
Giorgi F (1990) Simulation of reginal climate using a limited area model nested in a general circulation model. J Climate 3:941–963
Giorgi F (1991) Sensitivity of simulated summertime precipitation over the Western United States to different physics parameterizations. Mon Wea Rev 119 (12):2870–2888
Hostetler SW (1991) Simulation of lake ice and its effect on the late-Pleistocene evaporation rate of Lake Lahontan. Clim Dyn 6:43–48
Hostetler SW, Bartlein PJ (1990) Simulation of lake evaporation with application to modeling lake level variations of Harney-Malheur Lake, Oregon. Water Resourc Res 26 (10):2603–2612
Hostetler S, Benson LV (1990) Paleoclimatic implications of the high stand of Lake Lahontan derived from models of evaporation and lake level. Clim Dyn 4:207–217
Kutzbach JE, Guetter PJ (1986) The influences of changing orbital parameters and surface boundary conditions on climate simulations for the past 18000 years. J Atmos Sci 43:1726–1759
Manabe S, Broccoli AJ (1985) The influence of continental ice sheets on the climate of an ice age. Ann Glaciol 5:2167–2190
McCoy WD, Williams LD (1984) Application of an energy-balance model to the late Pleistocene Little Canyon glacier with implications regarding the paleohydrology of Lake Bonneville. In: Kay PA, Diaz HF (eds) Problems of and prospects for predicting Great Salt Lake levels. Center Pub Affairs Admin, Univ Utah, Logan, Utah, pp 40–53
Rind D (1987) Components of Ice Age circulation. J Geophys Res 92 (D4):4241–4281
Thompson RS (1984) Late Pleistocene and Holocene environments in the Great Basin. PhD Thesis, University of Arizona, Tucson
Thompson RS, Mead JI (1982) Late Quaternary environments and biogeography in the Great Basin. Quat Res 25:39–55
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
The National Center for Atmospheric Research is sponsored by the U.S. National Science Foundation
Offprint requests to: SW Hostetler
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hostetler, S.W., Giorgi, F. Use of a regional atmospheric model to simulate lake-atmosphere feedbacks associated with Pleistocene Lakes Lahontan and Bonneville. Climate Dynamics 7, 39–44 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00204820
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00204820