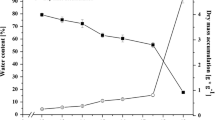
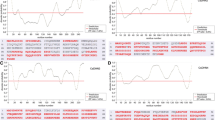
Abstract
The cDNA clone GAB-9 was selected from a cDNA gene library constructed from the mRNA of embryonic axes of chick-pea (Cicer arietinum L.) seeds imbibed for 12 h in the presence of abscisic acid. The sequence of this cDNA has an open reading frame of 546 nucleotides that code for 182 amino acids. The polypeptide encoded by the corresponding mRNA is of approx. 20.5 kDa, is basic, and has a broad hydrophobic central region flanked by two hydrophilic regions. The unusual characteristics of this protein, which is similar to late-embryogenesis-abundant proteins, and its possible function are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ABA:
-
abscisic acid
- HSP:
-
heat-shock proteins
- LEA:
-
late embryogenesis abundant
References
Baker J, Steele C, Dure L III (1988) Sequence and characterization of 6 Lea proteins and their genes from cotton. Plant Mol Biol 11:277–291
Bowler C, Chua N-H (1994) Emerging themes of plant signal transduction. Plant Cell 6: 1529–1541
Colorado P, Nicolas G, Rodríguez D (1991) Calcium dependence of the effects of abscisic acid on RNA synthesis during germination of Cicer arietinum seeds. Physiol Plant 83: 457–462
Colorado P, Rodríguez A, Nicolás G, Rodríguez D (1994) Abscisic acid and stress regulate gene expression during germination of chick-pea seeds. Possible role of calcium. Physiol Plant 91: 461–467
Colorado P, Nicolás C, Nicolás G, Rodríguez D (1995) Expression of three ABA-regulated clones and their relationship to maturation processes during the embryogenesis of chick-pea seeds. Physiol Plant 94: 1–6
Curry J, Walker-Simmons MK (1993) Unusual sequence of group 3 LEA mRNA inducible by dehydration stress in wheat. Plant Mol Biol 21: 907–912
Dure L III (1993) A repeating 11-mer amino acid motif and plant desiccation. Plant J 3: 363–369
Dure L III, Greenway SC, Galau G A (1981) Developmental biochemistry of cottonseed embryogenesis and germination. XVI. Changing ribosomic RNA populations as shown by in vitro and in vivo protein synthesis. Biochemistry 20: 4162–4168
Dure L, Crouch M, Harada J, Ho THD, Mundy J, Quatrano R, Thomas T, Sung ZR (1989) Common amino acid sequence domains among the LEA proteins of higher plants. Plant Mol Biol 12: 475–486
Finkelstein RR, Tenberge K, Shumway JE, Crouch ML (1985) Role of ABA in maturation of rape seed embryos. Plant Physiol 78: 630–636
Fujii-Kuriyama Y, Mizukami Y, Kawajiri K, Muramatsu M (1982) Primary structure of a cytochrome P450: Coding nucleotide sequence of phenobarbital-inducible cytochrome P-450 cDNA from rat liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 79: 2793–2797
Galau GA, Hughes DW, Dure L (1986) Abscisic acid induction of cloned cotton late embryogenesis-abundant (Lea) mRNAs. Plant Mol Biol 7: 155–170
Gilroy S, Fricker MD, Read ND Trewavas AJ (1991) Role of calcium in signal transduction of Commelina guard cells. Plant Cell 3: 333–344
Harada JJ, DeLisle AJ, Baden CS, Crouch ML (1989) Unusual sequence of an abscisic acid-inducible mRNA which accumulates late in Brassica napus seed development. Plant Mol Biol 12: 395–401
Ho THD, Sachs MM (1989) Stress-induced proteins: Characterization and the regulation of their synthesis. In: Marcus A (ed.) The biochemistry of plants, vol. 15. Academic Press, Inc., pp 347–378
Hui A, Ellinor FT, Krizanova O, Wang JJ, Diebold RJ, Schwartz A (1991) Molecular cloning of multiple subtypes of a novel rat brain isoform of the α1 subunit of the voltage dependent calcium channel. Neuron 7: 35–44
Kermode AR, Bewley JD (1987) Regulatory processes involved in the switch from seed development to germination: Possible roles for desiccation and ABA. In: Monti L, Porceddu E (eds) Drought resistance in plants physiological and genetic aspects. Brussels: EEC, pp 59–76
Koornneef M (1986) Genetic aspects of abscisic acid. In: Blonstein AD, King PJ (eds) Plant genetic research. A genetic approach to plant biochemistry. Springer-Verlag, Vienna, pp 35–54
Litts JC, Colwell GW, Chakerian RL, Quatrano RS (1987) The nucleotide sequence of a cDNA clone encoding the wheat Em protein. Nucleic Acids Res 15: 3607–3618
Mundy J, Chua N-H (1988) Abscisic acid and water-stress induce the expression of a novel rice gene. EMBO J 7: 2279–2286
Mundy J, Hejgaad J, Hansen A, Hallgren L, Jorgensen KG, Munck L (1986) Differential synthesis in vitro of barley aleurone and starchy endosperm proteins. Plant Physiol. 81: 630–636
Pearson WR, Lipman DJ (1988) Improved tools for biological sequence analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85: 2444–2448
Plant AL, Cohen A, Moses MS, Bray EA (1991) Nucleotide sequence and spatial expression pattern of a droughtand abscisic acid-induced gene of tomato. Plant Physiol 97: 900–906
Quatrano RS (1987) The role of hormones during seed development. In: Davies P (ed.) Plant hormones and their role in plant growth and development. Martinus Nijhoff Publishers, Dordrecht, pp 494–514
Rodríguez D, Nicolás G, Aldasoro JJ, Hernández-Nistal J, Babiano J, Matilla A (1985) Altered development of polysomal RNA activity in chick-pea (Cicer arietinum L.) embryonic axes. Effects of abscisic acid and temperature. Planta 164: 517–523
Sanger F, Nicklen S, Coulson AR (1977) DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 74: 5463–5467
Schroeder JI, Thuleau P (1991) Ca2+ channels in higher plant cells. Plant Cell 3: 555–559
Sidman KE, George DG, Baker WC, Hunt LT (1988) The protein identification resource (PIR). Nucleic Acids Res 16: 1869–1871
Skriver K, Mundy J (1990) Gene expression in response to abscisic acid and osmotic stress. Plant Cell 2: 503–512
Thomas TL (1993) Gene expression during plant embryogenesis and germination: An overview. Plant Cell 5: 1401–1410
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
The nucleotide sequence data reported appear in the EMBL under the accession number X79680.
We thank Dr J.L. Revuelta for helpful discussion. This work was supported by grants from Direction General de Investigation Científica y Técnica, Spain (PB90-0536) and Junta de Castilla y León (SA-33/11/92).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Colorado, P., Nicolas, G. & Rodríguez, D. Unusual sequence and characteristics of a chick-pea seed protein which is regulated by abscisic acid and is similar to late-embryogenesis-abundant proteins. Planta 196, 622–625 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00203664
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00203664