Abstract
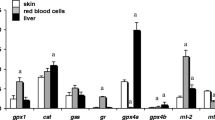
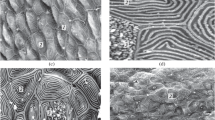
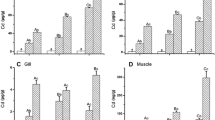
The skin of carp, Cyprinus carpio, was studied at the ultrastructural level after exposure of the fish to low and high concentrations of cadmium in the water (22 and 560 μg/L, respectively) for different periods. The effects of the low concentration of cadmium were similar to those of the high concentration, although they appeared later. The basal lamina and the skin surface became highly undulating. Chloride cells appeared between the pavement cells. Necrotic pavement cells were seen from the first day on, while apoptotic pavement cells appeared after several days. Filament cells contained many electron-transparent and electron-dense secretory vesicles. Mitotic cells were commonly seen, mainly in cells adjacent to club cells or close to the epidermal surface. Mucous cells differentiated close to the skin surface. They became elongated and synthesized highly electron-dense mucosomes. The epidermis became infiltrated by many leucocytes. As the experiment progressed, many leucocytes degenerated, and their remnants were found within macrophages and club cells. Fibroblasts displayed intense synthesis and, in fish from the low cadmium concentration, deposited a dense network of collagen fibers in the dermis. Melanosomes were located in the extensions of melanocytes. In these cells aggregation of melanosomes and apoptotic processes were common. Several of these changes were observed earlier under the impact of stressors other than cadmium. Some changes, such as the appearance of tumorlike bodies at the skin surface, the appearance of Merkel cells throughout the epidermis, and the coupling of leucocytes, may be specific for cadmium.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benedetti I, Albano AG, Mola L (1989) Histomorphological changes in some organs of the brown bullhead, Ictalurus nebulosus LeSueur, following short- and long-term exposure to copper. J Fish Biol 34:273–280
Bengtsson A, Bengtsson BE, Lithner G (1988) Vertebral defects in fourhorn sculpin, Myoxocephalus guadricornis L., exposed to heavy metal pollution in the Gulf of Bothnia. J Fish Biol 33:517–529
Blackstock N, Pickering AD (1980) Acidophilic granular cells in the epidermis of the brown trout, Salmo trutta L. Cell Tissue Res 210:359–369
Bryan GW (1979) Bioaccumulation of marine pollutants. Phil Trans R Soc Lond B 286:483–503
Bucke D, Feist SW, Norton MG, Rolfe MS (1983) A histopathological report of some epidermal anomalies of Dover sole, Solea solea L., and other flatfish species in coastal waters off south east England. J Fish Biol 23:565–578
Cataldi E, Crosetti D, Conte G, D'Ovidio D, Cataudella S (1988) Morphological changes in the oesophageal epithelium during adaptation to salinities to Oreochromis mossambicus, O. niloticus and their hybrid. J Fish Biol 32:191–196
Couch JA (1985) Prospective study of infectious and non-infectious diseases in oysters and fishes in three Gulf of Mexico estuaries. Dis Aquat Org 1:59–82
Dethlefsen V, Tiews K (1985) Review on the effects of pollution on marine fish life and fisheries in the North Sea. J Appl Ichthyol 3:97–118
Eaton JG (1974) Chronic cadmium toxicity to the bluegill, Lepomis macrochirus, Rafinesque. Trans Am Fish Soc 103:729–735
Fu H, Steinebach OM, van der Hamer CJA, Balm PHM, Lock RAC (1990) Involvement of cortisol and metallothionein-like proteins in the physiological responses of tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus) to sublethal cadmium stress. Aquatic Toxicol 16:257–270
Iger Y (1992) Adaptive reactions in the skin of the common carp (Cyprinus carpio) under the impact of wounding and ecological factors, PhD thesis, Hebrew University of Jerusalem, Jerusalem, Israel
Iger Y, Abraham M (1990) The process of skin healing in experimentally wounded carp. J Fish Biol 36:421–437
Iger Y, Abraham M, Dotan A, Fattal B, Rahamim E (1988) Cellular responses in the skin of carp maintained in organically fertilized water. J Fish Biol 33:711–720
Iger Y, Hilge V, Abraham M (1992) The ultrastructure of fish-skin during stress in aquaculture. In: Moav B, Hilge V, Rosenthal H (eds) Progress in aquaculture research. EAS (Special Pub. No. 17), Oostende, The Netherlands, pp 205–214
Iger Y, Wendelaar Bonga SE (1993) Cellular responses of the skin of carp (Cyprinus carpio) exposed to acidified water. Cell Tissue Res (accepted)
Karlsson-Norrgren L, Rumm P, Haux C, Forlin L (1985) Cadmium induced changes in gill morphology of zebrafish, Brachydanio rerio (Hamilton Buchanan) and rainbow trout, Salmo gairdneri Richardson. J Fish Biol 27:81–95
Lamas J, Anadon R, Devesa S, Toranzo AE (1990) Visceral neoplasia and epidermal papillomas in cultured turbot Scophthalmus maximus. Dis Aquat Org 8:179–187
Mallatt J (1985) Fish gill structural changes induced by toxicants and other irritants: a statistical review. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 42:630–648
Murad A, Houston AH (1988) Leucocytes and leucopoietic capacity in goldfish, Carassius auratus, exposed to sublethal levels of cadmium. Aquat Toxicol 13:141–154
Oronsaye JAO, Brafield AE (1984) The effect of dissolved cadmium on the chloride cells of the gills of the stickleback, Gasterosteus aculeatus L. J Fish Biol 25:253–258
Pärt P, Lock RAC (1983) Diffusion of calcium, cadmium and mercury in a mucous solution from rainbow trout. Comp Biochem Physiol 76C:259–263
Pevzner RA, Hernadi L, Solanki J (1986) Effect of mercury on the fish (Alburnus alburnus) chemoreceptor taste buds. A scanning electron microscopic study. Acta Biol Hung 37:159–167
Pfeiffer W (1977) The distribution of fright reaction and alarm substance cells in fishes. Copeia 1977:653–665
Pickering AD, Pottinger TG (1987) Crowding causes prolonged leucopenia in salmonid fish, despite interrenal acclimation. J Fish Biol 30:701–712
Pratap HB, Wendelaar Bonga SE (1990) Effects of water-borne cadmium on plasma cortisol and glucose in the cichlid fish Oreochromis mossambicus. Comp Biochem Physiol 95C:313–317
—, — (1993) Effects of ambient and dietary cadmium on pavement cells, chloride cells, and Na+/K+-ATPase activity in the gills of the freshwater teleost Oreochromis mossambicus at normal and high calcium levels in the ambient water. Aquat Toxicol 26:133–150
Pratap HB, Fu H, Lock RAC, Wendelaar Bonga SE (1989) Effect of waterborne and dietary cadmium on plasma ions of the teleost Oreochromis mossambicus in relation to water calcium levels. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 18:568–575
Sarna S, Pilas B, Land EJ, Truscott TG (1986) Interaction of radicals from water radiolysis with melanin. Biochim Biophys Acta 883:162–167
Smith IR, Zaidlik BA (1987) Regression and development of epidermal papillomas effecting white suckers, Catostomus commersoni (Lacepede), from Lake Ontario, Canada. J Fish Dis 10:487–494
Tort L, Torres P (1988) The effects of sublethal concentrations of cadmium on haematological parameters in the dogfish, Scyliorhinus canicula. J Fish Biol 32:277–282
Verbost PM, van Rooij J, Flik G, Lock RAC, Wendelaar Bonga SE (1989) The movement of cadmium through freshwater trout branchial epithelium and its interference with calcium transport. J Exp Biol 145:185–197
Wendelaar Bonga SE, Lock RAC (1992) Toxicants and osmoregulation in fish. Neth J Zool 42:478–493
Wendelaar Bonga SE, Flik G, Balm PHM, van der Meij JCA (1990) The ultrastructure of chloride cells in the gills of the teleost Oreochromis mossambicus during exposure to acidified water. Cell Tissue Res 259:575–585
Whitear M (1986) The skin of fishes including cyclostomes-epidermis. In: Bereiter Hahn J, Matoltsy AG, Richards KS (eds) Biology of the integument, Vol 2—vertebrates. Springer-Verlag, Heidelberg, pp 8–38
Wyllie AH (1981) Cell death: A new classification separating apoptosis from necrosis. In: Bowen ID, Lockshin RA (eds) Cell death in biology and pathology. Chapman and Hall, London, pp 9–34
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Iger, Y., Lock, R.A.C., van der Meij, J.C.A. et al. Effects of water-borne cadmium on the skin of the common carp (Cyprinus carpio). Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 26, 342–350 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00203561
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00203561